The expression of plasma Vaspin in patients with heart failure and its clinical significance
-
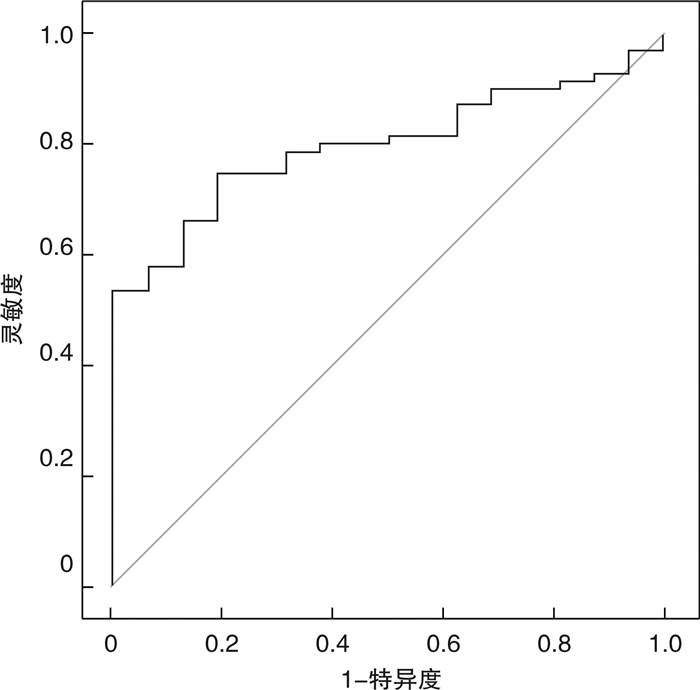
摘要: 目的 探讨心力衰竭(HF)患者血浆内脏脂肪特异性丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂(Vaspin)的表达及其临床意义。方法 选取2020年12月—2021年4月山西医科大学第二医院心内科住院患者87例,根据是否患有HF,分为非HF组(16例)和HF组(71例)。HF组根据左室射血分数(LVEF)分为射血分数保留型心力衰竭(HFpEF)组39例、射血分数中间值心力衰竭(HFmrEF)组10例和射血分数降低型心力衰竭(HFrEF)组22例。收集年龄、性别、合并冠心病、合并2型糖尿病情况、总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、肾小球滤过率(eGFR)、N末端B型利钠肽前体(NT-proBNP)等生化指标。酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)测定血浆Vaspin水平。超声心动图测量左房内径(LAD)、左室舒张末期内径(LVEDd)、LVEF。结果 四组间比较,HFpEF组、HFmrEF组、HFrEF组血浆Vaspin浓度均低于非HF组(P< 0.05),HFpEF组、HFmrEF组、HFrEF组组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。HF组血浆Vaspin浓度低于非HF组(P< 0.01)。Spearman相关分析显示血浆Vaspin与HF发生呈负相关(P< 0.05)。二元Logistic回归分析显示,低水平TC及低水平Vaspin为HF的影响因素(P< 0.05)。血浆Vaspin水平预测HF发生的绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.799(95%CI:0.706~0.893,P< 0.01),最佳临界值为22.79 ng/mL,灵敏度、特异度分别为74.6%和81.2%。结论 HF患者Vaspin水平显著降低,与HF呈负相关,可预测HF。Abstract: Objective To explore the expression of plasma Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor (Vaspin) in patients with Heart failure (HF) and its clinical significance.Methods A total of 87 inpatients in the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University from December 2020 to April 2021 were selected. They were divided into the non-HF group (16 cases) and the HF group(71 cases). According to the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), the HF group was divided into preserved ejection fraction heart failure (HFpEF) group(39 cases), median ejection fraction heart failure (HFmrEF) group(10 cases), and reduced ejection fraction heart failure(HFrEF) group(22 cases). We collected age, gender, patients with coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes, total cholesterol(TC), triglycerides(TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol(LDL-C), glomerular filtration rate(eGFR), N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide precursor (NT-proBNP), and other biochemical indicators. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)was used to determine the plasma Vaspin levels. Echocardiography measured left atrial inner diameter (LAD), left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDd), and LVEF.Results The plasma Vaspin concentration in the HFpEF, HFmrEF, and HFrEF groups was lower than the non-HF group (P< 0.05), and there was no statistical difference between the HFpEF, HFmrEF, and HFrEF groups (P>0.05). The plasma Vaspin concentration in the total HF group was lower than that in the non-HF group (P< 0.01). Spearman correlation analysis showed that plasma Vaspin was negatively correlated with the occurrence of HF(P< 0.05). Binary Logistic regression analysis showed the low-level TC and low-level Vaspin as influent factors of HF(P< 0.05). The AUC for the prediction of HF by plasma Vaspin levels was 0.799[95%CI: 0.706~0.893,P< 0.01], the best cut-off value was 22.79 ng/mL, and sensitivity and specificity were 74.6% and 81.2%.Conclusion Vaspin levels in patients with HF are significantly reduced, which is negatively correlated with HF and can predict HF.
-
Key words:
- heart failure /
- Vaspin /
- prediction /
- influent factors
-

-
表 1 4组受试者基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline data of 4 groups of subjects
例(%), M(Q1, Q3), X±S 变量 非HF组(16例) HFpEF组(39例) HFmrEF组(10例) HFrEF组(22例) t/χ2 P 男性 8(50.00) 24(61.50) 8(80.00) 15(68.20) 2.335 0.506 年龄/岁 69.24±6.92 73.84±12.63 67.00±15.11 62.05±15.262) 30.646 0.037 BMI/(kg·m-2) 23.98±2.29 23.53±5.38 24.37±4.03 22.05±3.27 31.531 0.204 合并冠心病 2(12.00) 18(46.00) 7(70.00)1) 10(45.00) 10.111 0.018 合并2型糖尿病 3(19.00) 9(23.00) 2(20.00) 4(18.00) 0.338 0.979 eGFR/[mL·min-1·(1.73m2)-1] 111.84±28.82 73.01±29.711) 76.06±33.691) 80.55±33.541) 6.429 0.001 TC/(mmol·L-1) 5.00±1.51 3.70±1.131) 3.50±0.611) 2.97±0.701)2) 10.903 < 0.001 TG/(mmol·L-1) 1.20(1.07,2.17) 0.97(0.73,1.60) 0.98(0.67,1.50) 0.87(0.70,0.98)1) 11.106 0.011 HDL-C/(mmol·L-1) 1.23±0.36 1.12±0.36 1.16±0.33 0.99±0.351) 1.535 0.212 LDL-C/(mmol·L-1) 2.32±0.49 1.97±0.85 1.88±0.47 1.69±0.501) 2.648 0.055 NT-proBNP/(ng·L-1) 71(65,125) 1956(1151,5000)1) 2014(1013,4224)1) 5217(1159,8334)1) 40.113 < 0.001 LAD/mm 32.47±2.94 39.45±10.601) 42.9±4.461) 45.15±6.271)2) 8.624 < 0.001 LVEDd/mm 48.00±3.50 49.36±7.62 58.90±6.571)2)3) 64.80±9.561)2) 23.700 < 0.001 LVEF/% 69.50(66.00,71.00) 62.00(56.00,67.00) 42.50(40.75,46.25)1)2) 29.50(23.00,34.00)1)2) 66.522 < 0.001 Vaspin/(ng·mL-1) 24.70±3.04 19.53±5.711) 19.25±4.851) 18.71±7.041) 4.450 0.006 注:与非HF组比较,1)P < 0.05;与HFpEF组比较,2)P < 0.05;与HFrEF比较,3)P < 0.05。 表 2 血浆Vaspin的相关性比较
Table 2. Correlation comparison of plasma Vaspin
变量 血浆Vaspin浓度 r P BMI 0.073 0.515 eGFR 0.287 0.007 TC 0.239 0.033 TG 0.270 0.014 NT-proBNP -0.413 0.000 LVEF 0.221 0.039 HF -0.402 0.000 表 3 非HF组与HF组之间的二元logistic回归
Table 3. Binary logistic regression between non-HF group and HF group
影响因素 B值 SE Wals值 P值 OR值 95%CI 下限 上限 TC -1.200 0.367 10.675 0.001 0.301 0.147 0.619 Vaspin -0.204 0.086 5.598 0.018 0.815 0.688 0.966 -
[1] Tomasoni D, Adamo M, Lombardi CM, et al. Highlights in heart failure[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2019, 6(6): 1105-1127. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12555
[2] Carbone S, Lavie CJ, Elagizi A, et al. The impact of obesity in heart failure[J]. Heart Fail Clin, 2020, 16(1): 71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2019.08.008
[3] Weiner J, Zieger K, Pippel J, et al. Molecular mechanisms of vaspin action-from adipose tissue to skin and bone, from blood vessels to the brain[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1111: 159-188.
[4] Recinella L, Orlando G, Ferrante C, et al. Adipokines: new potential therapeutic target for obesity and metabolic, rheumatic, and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11: 578966.
[5] Sato K, Shirai R, Yamaguchi M, et al. Anti-atherogenic effects of vaspin on human aortic smooth muscle cell/macrophage responses and hyperlipidemic mouse plaque phenotype[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(6).
[6] Hida K, Wada J, Eguchi J, et al. Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor: a unique insulin-sensitizing adipocytokine in obesity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2005, 102(30): 10610-10615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504703102
[7] 黄鈺婷, 张恺, 苏菁, 等. 射血分数保留型心力衰竭与微血管内皮炎症[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(6): 512-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB202106004.htm
[8] Kastl SP, Katsaros KM, Krychtiuk KA, et al. The adipokine vaspin is associated with decreased coronary in-stent restenosis in vivo and inhibits migration of human coronary smooth muscle cells in vitro[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(5): e0232483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232483
[9] Singh M, Benencia F. Inflammatory processes in obesity: focus on endothelial dysfunction and the role of adipokines as inflammatory mediators[J]. Int Rev Immunol, 2019, 38(4): 157-171. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2019.1638921
[10] 滕宗艳, 韩丽红, 张海金, 等. 血清vaspin与慢性心力衰竭相关性研究[J]. 哈尔滨医科大学学报, 2020, 54(3): 289-292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1905.2020.03.015
[11] Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Buhadilly AK. Rosuvastatin Improves Vaspin Serum Levels in Obese Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome[J]. Diseases, 2018, 6(1).
[12] Kadoglou N, Kassimis G, Patsourakos N, et al. Omentin-1 and vaspin serum levels in patients with pre-clinical carotid atherosclerosis and the effect of statin therapy on them[J]. Cytokine, 2021, 138: 155364.
[13] Niazi M, Galehdar N, Jamshidi M, et al. A Review of the Role of Statins in Heart Failure Treatment[J]. Curr Clin Pharmacol, 2020, 15(1): 30-37.
[14] Pazgan-Simon M, Kukla M, Zuwała-Jagiełło J, et al. Serum visfatin and vaspin levels in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(1): e0227459.
[15] Breitfeld J, Wiele N, Gutsmann B, et al. Circulating Adipokine VASPIN Is Associated with Serum Lipid Profiles in Humans[J]. Lipids, 2019, 54(4): 203-210.
[16] Liu Y, Gong M, Liu S, et al. Effects of blood glucose on vaspin secretion in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus[J]. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2021, 37(3): 221-224.
[17] Türkcan A, Scharinger B, Grabmann G, et al. Combination of cadmium and high cholesterol levels as a risk factor for heart fibrosis[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2015, 145(2): 360-371.
[18] Zhao Q, Li J, Yang J, et al. Association of total cholesterol and HDL-C levels and outcome in coronary heart disease patients with heart failure[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2017, 96(9): e6094.
[19] Gnanenthiran SR, Ng ACC, Cumming R, et al. Low total cholesterol is associated with increased major adverse cardiovascular events in men aged≥70 years not taking statins[J]. Heart. 2020, 106(9): 698-705.
[20] Zhao TJ, Yang QK, Bi LD, et al. Prognostic value of DCTA scoring system in heart failure[J]. Herz, 2021, 46(Suppl 2): 243-252.
-




 下载:
下载: