Comparison of efficacy and safety between excimer laser and conventional percutaneous coronary intervention in complex coronary lesions
-
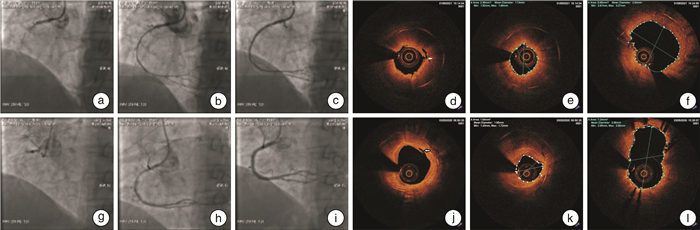
摘要: 目的 比较准分子激光冠状动脉(冠脉)消融术(ELCA)与常规经皮冠脉介入治疗(PCI)在复杂冠脉病变中的疗效和安全性。方法 纳入2018年12月—2021年1月江苏大学附属医院心内科拟行介入治疗的复杂冠脉病变病例12例,分为ELCA组和常规PCI组,分别先行ELCA预处理和经皮冠状动脉球囊成形术(PTCA)预处理,之后继续完成PCI治疗。预处理后及PCI完成后行光学相干断层扫描(OCT)观察内膜斑块撕裂情况(撕裂数)、最小管腔直径(MLD)和最小管腔面积(MLA)。观察PCI成功率和临床成功率、PCI并发症、术后住院日、术后住院期间和6个月随访期主要不良心脏事件(MACE)。结果 ELCA组靶病变6处,常规PCI组靶病变7处,病变特征相似。2组PCI成功率和临床成功率均为100%,PCI并发症为0。ELCA组和常规PCI组分别有3处和7处病变行OCT检查,MLD、MLA和内膜撕裂数2组差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。2组住院期间均无MACE发生,术后住院日差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。6个月内ELCA组发生3次MACE(60.0%),常规PCI组2次(28.6%),差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 ELCA辅助治疗复杂冠脉病变安全有效,且不劣于常规PCI治疗,但未显示出降低中期MACE的益处。
-
关键词:
- 准分子激光冠状动脉消融术 /
- 支架内再狭窄 /
- 慢性完全闭塞性病变 /
- 钙化病变
Abstract: Objective To compare the efficacy and safety of excimer laser coronary atherectomy(ELCA) and conventional percutaneous coronary intervention(PCI) in complex coronary lesions.Methods Twelve cases of complex coronary artery disease planned to undergo interventional treatment in the Department of Cardiology of the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University from December 2018 to January 2021 were included. They were randomly divided into the ELCA group and conventional PCI group. They were pretreated with ELCA and percutaneous coronary angioplasty(PTCA) respectively and then continued to complete PCI treatment. After pretreatment and PCI, optical coherence tomography(OCT) was performed to observe the tear of intimal plaque(tear number), minimum lumen diameter(MLD) and minimum lumen area(MLA). The PCI success rate, clinical success rate, PCI complications, postoperative hospitalization, major adverse cardiac events(MACE) during postoperative hospitalization days, and 6-month follow-up were observed.Results There were 6 target lesions in the ELCA group and 7 target lesions in conventional PCI group. The success rate of PCI and clinical success rate were 100% in both groups, and the complications of PCI were 0. Three and seven lesions were examined by OCT in ELCA group and conventional PCI group respectively. The number of MLD, MLA, and intimal tear were similar in the two groups(P>0.05). There was no MACE in both groups during hospitalization, and the postoperative hospitalization days were similar(P>0.05). MACE occurred 3 times in ELCA group(60.0%) and 2 times in conventional PCI group(28.6%) within 6 months(P>0.05).Conclusion ELCA adjuvant therapy for complex coronary artery lesions is safe and effective, and is not inferior to conventional PCI, but it does not show the benefit in reducing medium-term MACE. -

-
表 1 基线特征和病变特征
Table 1. baseline and lesion characteristics
例(%), X±S 项目 ELCA组(5例) 常规PCI组(7例) P值 男性 5(100.0) 5(71.4) 0.470 年龄/岁 65.20±12.64 62.57±5.06 0.678 高血压 2(40.0) 7(100.0) 0.045 糖尿病 1(20.0) 3(42.9) 0.558 吸烟 3(60.0) 2(28.6) 0.257 LDL/(mmol·L-1) 1.44±0.53 3.68±1.46 0.009 LVEF/% 58.40±13.50 65.57±7.68 0.266 eGFR/[mL·min-1·(1.73 m2)-1] 77.78± 18.06 100.06± 24.44 0.116 靶病变/处 6 7 三支病变 2(40.0) 4(57.1) 1.000 ISR 6(100.0) 4(57.1) 0.192 CTO 0(0) 3(42.9) 0.192 完全闭塞(ISR和CTO) 3(50.0) 7(100.0) 0.070 严重钙化病变 1(16.7) 2(28.6) 1.000 表 2 手术操作和术后随访情况
Table 2. operation and postoperative follow-up
例(%), X±S 项目 ELCA组(5例) 常规PCI组(7例) P值 完成OCT数 3(50.0) 7(100.0) OCT1 MLD/mm 1.47±0.371) 1.29±0.211) 0.360 MLA/mm2 2.14±0.621) 1.82±0.512) 0.428 内膜撕裂数/处 7.00±3.46 3.86±1.21 0.055 OCT2 MLD/mm 2.56±0.27 2.21±0.54 0.321 MLA/mm2 6.48±1.16 5.61±2.44 0.578 PCI成功 5(100.0) 7(100.0) 临床成功 5(100.0) 7(100.0) PCI并发症 0(0) 0(0) 住院期间MACE 0(0) 0(0) 术后住院日/d 4.20±1.79 5.00±2.00 0.493 6个月MACE 3(60.0) 2(28.6) 0.558 注:与OCT2比较,1)P < 0.01;2)P < 0.05。 -
[1] 戴心怡, 丁澍. 准分子激光冠脉斑块消融术在复杂冠脉病变中的临床应用[J]. 实用心电学杂志, 2021, 30(2): 135-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXD202102016.htm
[2] Tsutsui RS, Sammour Y, Kalra A, et al. Excimer Laser Atherectomy in Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Contemporary Review[J]. Cardiovasc Revasc Med, 2021, 25: 75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2020.10.016
[3] Dallan LAP, Pereira GTR, Alaiti MA, et al. Laser imaging: unraveling laser atherectomy mechanisms of action with optical coherence tomography[J]. Curr Cardiovasc Imaging Rep, 2019, 12(8): 1-8.
[4] Egred M, Brilakis ES. Excimer Laser Coronary Angioplasty(ELCA): Fundamentals, Mechanism of Action, and Clinical Applications[J]. J Invasive Cardiol, 2020, 32(2): E27-E35.
[5] 张婷婷, 礼兆悦, 涂应锋. 光学相干断层成像技术在冠状动脉支架失败中的研究进展[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(12): 1157-1161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB202112018.htm
[6] Ichimoto E, Kadohira T, Nakayama T, et al. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes after Treatment with Excimer Laser Coronary Atherectomy for In-Stent Restenosis of Drug-Eluting Stent[J]. Int Heart J, 2018, 59(1): 14-20. doi: 10.1536/ihj.16-638
[7] Badr S, Ben-Dor I, Dvir D, et al. The state of the excimer laser for coronary intervention in the drug-eluting stent era[J]. Cardiovasc Revasc Med, 2013, 14(2): 93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2012.12.008
[8] Ambrosini V, Sorropago G, Laurenzano E, et al. Early outcome of high energy Laser(Excimer)facilitated coronary angioplasty on hard and complex calcified and balloon-resistant coronary lesions: LEONARDO Study[J]. Cardiovasc Revasc Med, 2015, 16(3): 141-146. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2015.02.002
[9] Li H, Ai H, Li L, et al. The therapeutic effects of excimer laser coronary atherectomy therapy for in-stent restenosis chronic total occlusions[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2021, 21(1): 399. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02208-x
[10] 刘巍, 周玉杰, 赵迎新, 等. 新型准分子激光在复杂冠状动脉病变介入治疗中的应用[J]. 中国医药, 2018, 13(4): 504-507. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2018.04.007
[11] 李琪, 刘健, 卢明瑜, 等. 准分子激光冠状动脉斑块消融术治疗复杂冠状动脉病变的近期临床效果观察[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2019, 27(1): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8812.2019.01.009
-




 下载:
下载: