Comparison assessment of left ventricular wall thickness measured by contrast-enhanced and standard echocardiography
-
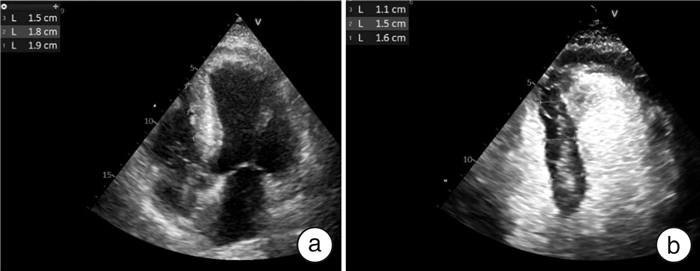
摘要: 目的 评价在生理和病理情况下超声造影技术测量左心室心肌厚度及左心室质量指数的价值。方法 选取进行过常规超声及超声造影检查的72例患者,包括31例入院检查后无明确心脏相关疾病者作为对照组、11例扩张型心肌病患者(扩张型心肌病组)、11例肥厚型心肌病患者(肥厚型心肌病组)及20例心肌梗死的患者(心肌梗死组),按心肌17节段分段法,分别在常规超声及超声造影下测量各节段心肌厚度及左心室质量指数并进行比较。结果 总体情况下,超声造影所测平均心肌厚度及左心室质量指数均显著低于常规超声的测量值(P < 0.05);按心肌节段分析,在大部分心肌节段中,造影测量的心肌节段厚度显著低于常规超声的测量值(P < 0.05)。按疾病分组情况下,造影情况下各组的平均心肌厚度均显著低于常规超声的测量值(P < 0.05),且对照组、扩张型心肌病组和心肌梗死组的左心室质量指数超声造影测量结果显著低于常规超声测量(P < 0.05)。结论 在多数情况下,超声造影测量所得心肌厚度及左心室质量指数的数值显著低于常规超声。Abstract: Objective The study was performed to evaluate the value of contrast-enhanced echocardiography in measuring left ventricular myocardial thickness and left ventricular mass index under physiological and pathological conditions.Methods 72 patients who underwent standard echocardiography and contrast-enhanced echocardiography were enrolled, including control group without definite heart-related diseases(n=31), dilated cardiomyopathy group(n=11), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy group(n=11), and myocardial infarction group(n=20). The 17-segment myocardial thickness and left ventricular mass index were measured by standard echocardiography and contrast-enhanced echocardiography.Results Under contrast-enhanced echocardiography, the mean myocardial thickness and left ventricular mass index were significantly lower than those determined by standard echocardiography(P < 0.05). In most myocardium segments, based on the analysis of independent myocardium segments, the myocardium thickness determined by contrast-enhanced echocardiography was significantly lower than that determined by standard echocardiography(P < 0.05). The average myocardial thickness of each group determined by contrast-enhanced echocardiography was also significantly lower than that of standard echocardiography(P < 0.05). In the normal group, the dilated cardiomyopathy group, and the myocardial infarction group, the left ventricular mass index determined by contrast-enhanced echocardiography was significantly lower than those determined by standard determination(P < 0.05).Conclusion In most cases, the values of myocardial thickness and left ventricular mass index determined by contrast-enhanced echocardiography are significantly lower than those obtained by standard echocardiography. This analysis indicates that contrast-enhanced echocardiography may be a valuable method to measure left ventricular myocardial thickness and left ventricular mass index in some situations.
-

-
表 1 患者一般临床资料及超声参数
Table 1. General clinical data and echocardiographic parameters of patient
例(%), X±S 指标 总体(72例) 对照组(30例) 扩张型心肌病组(11例) 肥厚型心肌组(11例) 心肌梗死组(20例) P值 年龄/岁 56.22±15.04 54.90±15.40 51.82±19.12 60.36±14.88 58.35±12.07 0.50 男性 51(70.83) 16(53.33) 10(90.9) 8(72.72) 17(85.0) 0.04 体表面积/m2 1.82±0.19 1.74±0.19 1.93±0.19 1.87±0.19 1.86±0.16 0.01 心率/(次·min-1) 80.40±14.65 80.30±13.45 90.27±16.37 67.73±10.00 82.10±13.39 0.01 高血压 14(19.44) 0(0) 1(9.09) 1(9.09) 12(60.00) 0.01 糖尿病 10(13.89) 0(0) 2(18.18) 0(0) 8(40.00) 0.01 高脂血症 6(8.33) 0(0) 0(0) 0(0) 6(30.00) 0.01 左心房前后径/cm 4.36±3.72 3.61±0.54 4.57±0.74 4.46±0.61 4.76±5.73 0.76 舒张末期容积/mL 109.43±57.68 89.90±23.37 210.64±80.13 85.82±32.01 96.05±25.27 0.01 EF(双平面法)/% 53.50±16.23 61.56±5.21 28.18±11.85 71.18±13.72 45.60±7.03 0.01 E/(m·s-1) 0.76±0.23 0.83±0.23 0.80±0.25 0.68±0.21 0.68±0.19 0.05 A/(m·s-1) 0.75±0.22 0.71±0.18 0.68±0.30 0.85±0.30 0.77±0.22 0.27 TR/(m·s-1) 2.51±0.41 2.33±0.33 2.70±0.37 2.58±0.43 2.54±0.53 0.17 表 2 心肌厚度均值比较
Table 2. Comparison of mean myocardial thickness
cm, X±S 组别 超声造影 常规超声 P值 总体(72例) 0.75±0.13 0.89±0.14 < 0.01 对照组(30例) 0.70±0.07 0.82±0.10 < 0.01 扩张型心肌病组(11例) 0.66±0.11 0.77±0.12 < 0.01 肥厚型心肌组(11例) 0.95±0.08 1.10±0.06 < 0.01 心肌梗死组(20例) 0.77±0.13 0.92±0.11 < 0.01 表 3 17节段心肌厚度比较
Table 3. Comparison of myocardial segments thickness
cm, X±S 节段 超声造影 常规造影 P值 前间隔基底段 1.02±0.35 1.13±0.34 < 0.05 前壁基底段 0.69±0.12 0.77±0.34 < 0.05 前侧壁基底段 0.71±0.12 0.81±0.12 < 0.05 下侧壁基底段 0.74±0.14 0.83±0.14 < 0.05 下壁基底段 0.74±0.16 0.89±0.15 < 0.05 下间隔基底段 0.94±0.34 1.13±0.38 < 0.05 前间隔中间段 0.85±0.27 0.88±0.27 0.20 前壁中间段 0.69±0.11 0.68±0.34 0.71 前侧壁中间段 0.69±0.11 0.73±0.27 0.29 下侧壁中间段 0.73±0.13 0.95±0.74 < 0.05 下壁中间段 0.76±0.18 0.93±0.20 < 0.05 下间隔中间段 0.82±0.23 0.99±0.29 < 0.05 室间隔心尖段 0.67±0.14 0.62±0.40 0.29 前壁心尖段 0.66±0.14 0.78±0.16 < 0.05 侧壁心尖段 0.69±0.13 0.83±0.16 < 0.05 下壁心尖段 0.72±0.17 0.83±0.27 < 0.05 心尖帽 0.64±0.15 0.76±0.18 < 0.05 均值 0.75±0.13 0.89±0.14 < 0.05 表 4 左心室质量指数比较
Table 4. Comparison of left ventricular mass index
g/m2, X±S 项目 总体(72例) 对照组(30例) 扩张型心肌病组(11例) 肥厚型心肌组(11例) 心肌梗死组(20例) 超声造影 93.44±24.37 80.52±19.89 110.90±18.49 113.7±20.46 90.51±23.20 常规超声 106.54±27.54 92.89±20.27 134.38±24.65 126.09±22.27 98.92±23.99 P值 < 0.05 < 0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 < 0.05 表 5 2种方法在诊断心肌肥厚(≥1.2 cm)的一致性分析
Table 5. Consistency analysis of two methods in diagnosing myocardial hypertrophy(≥1.2 cm)
个(%) 常规超声 超声造影 Kappa值 P值 是 否 是 62(62.62) 37(37.37) 0.74 0.00 否 3(0.29) 1029(99.71) 表 6 2种方法在诊断肥厚型心肌病(≥1.5 cm)的一致性分析
Table 6. Consistency analysis of two methods in diagnosing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(≥1.5 cm)
个(%) 常规超声 超声造影 Kappa值 P值 是 否 是 16(37.21) 27(62.79) 0.47 0.00 否 7(0.64) 1081(99.36) -
[1] Ciccone MM, Scicchitano P, Zito A, et al. Correlation between coronary artery disease severity, left ventricular mass index and carotid intima media thickness, assessed by radio-frequency[J]. Cardiovasc Ultrasound, 2011, 9: 32. doi: 10.1186/1476-7120-9-32
[2] Katikireddy CK, Acharya T. Myocardial segmental thickness variability on echocardiography is a highly sensitive and specific marker to distinguish ischemic and non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy in new onset heart failure[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2019, 35(5): 791-798. doi: 10.1007/s10554-018-01515-3
[3] Khalid A, Lim E, Chan BT, et al. Assessing regional left ventricular thickening dysfunction and dyssynchrony via personalized modeling and 3D wall thickness measurements for acute myocardial infarction[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 49(4): 1006-1019. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26302
[4] Budhwani N, Patel S, Dwyer EM Jr. Electrocardiographic diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy: the effect of left ventricular wall thickness, size, and mass on the specific criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy[J]. Am Heart J, 2005, 149(4): 709-714. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2004.07.040
[5] Webb J, Villa A, Bekri I, et al. Usefulness of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Measure Left Ventricular Wall Thickness for Determining Risk Scores for Sudden Cardiac Death in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2017, 119(9): 1450-1455. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.01.021
[6] Cho YH, Kang JW, Choi SH, et al. Reference parameters for left ventricular wall thickness, thickening, and motion in stress myocardial perfusion CT: Global and regional assessment[J]. Clin Imaging, 2019, 56: 81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2019.04.002
[7] Maanja M, Schlegel TT, Kozor R, et al. The electrical determinants of increased wall thickness and mass in left ventricular hypertrophy[J]. J Electrocardiol, 2020, 58: 80-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2019.09.024
[8] Takigawa M, Martin R, Cheniti G, et al. Detailed comparison between the wall thickness and voltages in chronic myocardial infarction[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2019, 30(2): 195-204. doi: 10.1111/jce.13767
[9] Rocha LA, Zielinsky P, Nicoloso L, et al. Development of the Z-score for the measurement of myocardial thickness by two-dimensional echocardiography in normal fetuses[J]. Echocardiography, 2021, 38(1): 97-102. doi: 10.1111/echo.14953
[10] Sepúlveda-Martínez A, García-Otero L, Soveral I, et al. Comparison of 2D versus M-mode echocardiography for assessing fetal myocardial wall thickness[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2019, 32(14): 2319-2327. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1432041
[11] Bois JP, Geske JB, Foley TA, et al. Comparison of Maximal Wall Thickness in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Differs Between Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Transthoracic Echocardiography[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2017, 119(4): 643-650. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.11.010
[12] Krupickova S, Risch J, Gati S, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance normal values in children for biventricular wall thickness and mass[J]. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 2021, 23(1): 1. doi: 10.1186/s12968-020-00692-2
[13] Porter TR, Mulvagh SL, Abdelmoneim SS, et al. Clinical Applications of Ultrasonic Enhancing Agents in Echocardiography: 2018 American Society of Echocardiography Guidelines Update[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2018, 31(3): 241-274. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2017.11.013
[14] Hindieh W, Weissler-Snir A, Hammer H, et al. Discrepant Measurements of Maximal Left Ventricular Wall Thickness Between Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Echocardiography in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2017, 10(8).
[15] Urbano-Moral JA, Gonzalez-Gonzalez AM, Maldonado G, et al. Contrast-Enhanced Echocardiographic Measurement of Left Ventricular Wall Thickness in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Comparison with Standard Echocardiography and Cardiac Magnetic Resonance[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2020, 33(9): 1106-1115. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2020.04.009
[16] Maron MS, Lesser JR, Maron BJ. Management implications of massive left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy significantly underestimated by echocardiography but identified by cardiovascular magnetic resonance[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2010, 105(12): 1842-1843. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.01.367
-




 下载:
下载: