Advances in the application of artificial intelligence in multimodality cardiac imaging
-
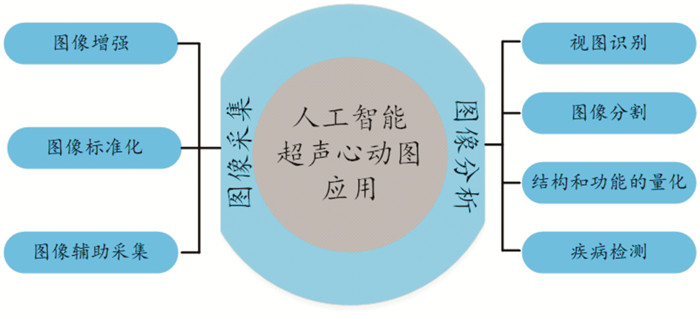
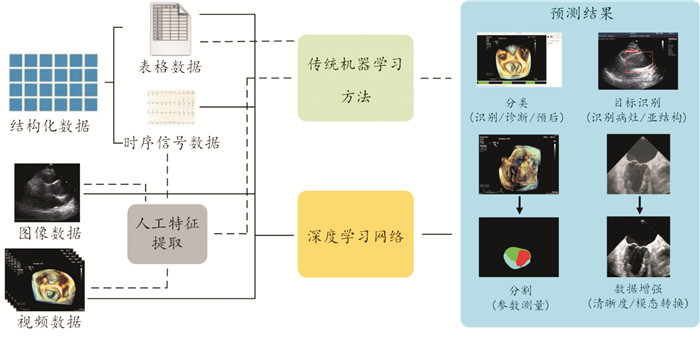
摘要: 人工智能(artificial intelligence,AI)在医疗领域的应用正在逐渐发展壮大。通过多种模态影像数据分析可以帮助医生提高诊断效率,减少劳动强度,以及打破医疗的时空限制等。机器学习是人工智能主要技术之一,它可以从大型数据库中自主提取信息,目前在心血管系统多模态影像中已有许多的研究和应用。本文综述AI在超声心动图、多层螺旋计算机体层摄影术、心脏磁共振、单光子发射计算机断层显像等多模态心脏影像中的研究现状、挑战及未来展望。Abstract: The application of Artificial Intelligence(AI) in the medical field is gradually developing. Multi-modal image data analysis can help doctors improve diagnostic efficiency, reduce labor intensity, and break the time and space limitations of medical treatment. Machine learning is one of the main technologies of AI, which can autonomously extract information from large databases. At present, there are many researches and applications in multimodal images of cardiovascular system. This paper summarizes the current research status, challenges, and future prospects of AI in multimodality cardiac imaging, including echocardiography, multislice spiral computed tomography, cardiac magnetic resonance, and single photon emission computed tomography(SPECT).
-

-
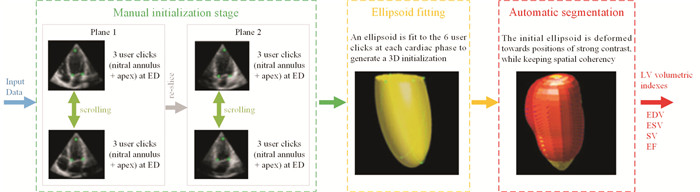
图 3 自动分割算法的数据流程[19]
Figure 3. Data flow of automatic segmentation algorithm
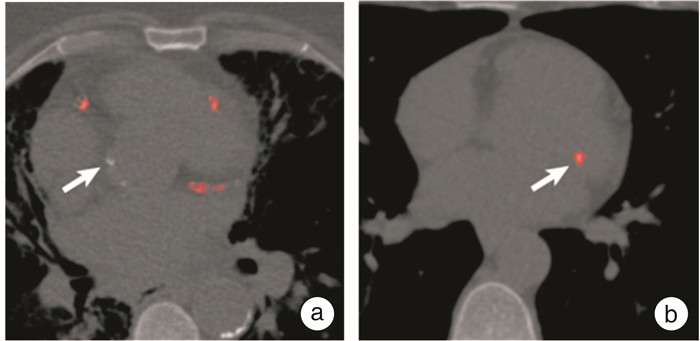
图 4 基于DL的自动冠状动脉钙化积分[39]
Figure 4. Automatic coronary artery calcification integration based on DL
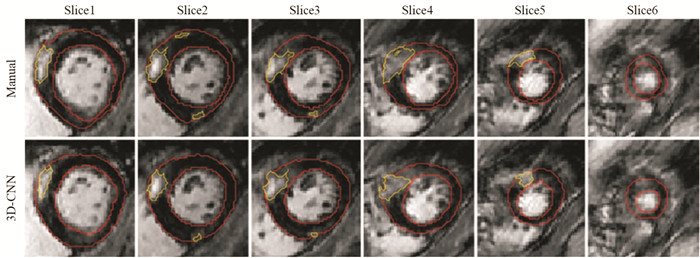
图 5 1例60岁男性被诊断肥厚性心肌病的MRI图像[48]
Figure 5. MRI images of a 60 year old male diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
表 1 文献汇总
Table 1. Literature Summary
成像方式 文献 超声心动图 图像采集 Abdi等[4],Diller等[5],Narang等[6],Schneider等[7] 图像分析 视图识别 Zhang等[8],Azarmehr等[9],Zhu等[10] 图像分割 Zhang等[8],Cervantes-Guzmán等[11],Hu等[12],Nedadur等[13],Leclerc等[14],Diller等[16],Xu等[17],Andreassen等[18] 结构和功能的量化 Zhang等[8],Barbosa等[19],Ouyang等[20],Reddy等[21] 疾病检测及管理 Zhang等[8],Upton等[22],Xu等[23],Yang等[24],Duffy等[25],Edwards等[26],Franke等[27],谢等[28],Namasivayam等[29],Zweck等[30],Biaggi等[31],Faletra等[32] 多层螺旋计算机体层摄影术 冠状动脉钙化评分 van等[36],Pieszko等[37],Mu等[38],Martin等[39] 冠脉狭窄和斑块分析 Lanzafame等[35],Al'Aref等[40],Kolossváry等[41] 冠状动脉CT血流储备分数 van等[42],Qiao等[43],Qiao等[44] 心脏磁共振 图像采集和后处理 Argentiero等[45],Sandino等[46],Fotaki等[47] 疾病诊断及危险分层 Fahmy等[48],Augusto等[50],刘等[51],Slomka等[49] 单光子发射计算机断层显像 图像自动识别及分割 Motwani等[52],Zhu等[53],Betancur等[54], 阻塞性冠状动脉疾病诊断 Motwani等[52],Arsanjani等[55],Miller等[56] 心血管事件的风险评估 Motwani等[52],Hu等[57],Mohebi等[58] -
[1] 王增武, 胡盛寿. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020》要点解读[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2021, (3): 209-218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2021.03.001
[2] 谢稳, 姚泽阳, 邱海龙, 等. 人工智能在先天性心脏病学中的应用[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2020, 27(03): 343-353.
[3] Barrios JP, Tison GH. Advancing cardiovascular medicine with machine learning: Progress, potential, and perspective[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2022, 3(12): 100869. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100869
[4] Abdi AH, Luong C, Tsang T, et al. Automatic quality assessment of echocardiograms using convolutional neural networks: feasibility on the apical four-chamber view[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2017, 36(6): 1221-1230. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2690836
[5] Diller GP, Lammers AE, Babu-Narayan S, et al. Denoising and artefact removal for transthoracic echocardiographic imaging in congenital heart disease: utility of diagnosis specific deep learning algorithms[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2019, 35(12): 2189-2196. doi: 10.1007/s10554-019-01671-0
[6] Narang A, Bae R, Hong H, et al. Utility of a deep-learning algorithm to guide novices to acquire echocardiograms for limited diagnostic use[J]. JAMA Cardiol, 2021, 6(6): 624-632. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0185
[7] Schneider M, Bartko P, Geller W, et al. A machine learning algorithm supports ultrasound-naïve novices in the acquisition of diagnostic echocardiography loops and provides accurate estimation of LVEF[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2021, 37(2): 577-586. doi: 10.1007/s10554-020-02046-6
[8] Zhang J, Gajjala S, Agrawal P, et al. Fully automated echocardiogram interpretation in clinical practice[J]. Circulation, 2018, 138(16): 1623-1635. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034338
[9] Azarmehr N, Ye X, Howard JP, et al. Neural architecture search of echocardiography view classifiers[J]. J Med Imaging(Bellingham), 2021, 8(3): 034002.
[10] Zhu Y, Ma J, Zhang Z, et al. Automatic view classification of contrast and non-contrast echocardiography[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 989091. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.989091
[11] Cervantes-Guzmán A, McPherson K, Olveres J, et al. Robust cardiac segmentation corrected with heuristics[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(10): e0293560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293560
[12] Hu J, Olaisen SH, Smistad E, et al. Automated 2-D and 3-D left atrial volume measurements using deep learning[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2023, 11: 110.
[13] Nedadur R, Wang B, Tsang W. Artificial intelligence for the echocardiographic assessment of valvular heart disease[J]. Heart, 2022, 108(20): 1592-1599. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2021-319725
[14] Leclerc S, Smistad E, Pedrosa J, et al. Deep learning for segmentation using an open large-scale dataset in 2D Echocardiography[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2019, 38(9): 2198-2210. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2900516
[15] Diller GP, Babu-Narayan S, Li W, et al. Utility of machine learning algorithms in assessing patients with a systemic right ventricle[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2019, 20(8): 925-931. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jey211
[16] Diller GP, Benesch Vidal ML, Kempny A, et al. A framework of deep learning networks provides expert-level accuracy for the detection and prognostication of pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2022, 23(11): 1447-1456. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeac147
[17] Xu L, Liu M, Shen Z, et al. DW-Net: A cascaded convolutional neural network for apical four-chamber view segmentation in fetal echocardiography[J]. Comput Med Imaging Graph, 2020, 80: 101690. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2019.101690
[18] Andreassen BS, Veronesi F, Gerard O, et al. Mitral annulus segmentation using deep learning in 3-D Transesophageal Echocardiography[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2020, 24(4): 994-1003. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2959430
[19] Barbosa D, Heyde B, Dietenbeck T, et al. Quantification of left ventricular volume and global function using a fast automated segmentation tool: validation in a clinical setting[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2013, 29(2): 309-316. doi: 10.1007/s10554-012-0103-8
[20] Ouyang D, He B, Ghorbani A, et al. Video-based AI for beat-to-beat assessment of cardiac function[J]. Nature, 2020, 580(7802): 252-256. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2145-8
[21] Reddy CD, Lopez L, Ouyang D, et al. Video-based deep learning for automated assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction in pediatric patients[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2023, 36(5): 482-489. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2023.01.015
[22] Upton R, Mumith A, Beqiri A, et al. Automated echocardiographic detection of severe coronary artery disease using artificial intelligence[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2022, 15(5): 715-727. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2021.10.013
[23] Xu Z, Yu F, Zhang B, et al. Intelligent diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy using transthoracic echocardiography videos[J]. Comput MethodsPrograms Biomed, 2022, 226: 107182.
[24] Yang F, Chen X, Lin X, et al. Automated analysis of doppler echocardiographic videos as a screening tool for valvular heart diseases[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2022, 15(4): 551-563. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2021.08.015
[25] Duffy G, Cheng PP, Yuan N, et al. High-throughput precision phenotyping of left ventricular hypertrophy with cardiovascular deep learning[J]. JAMA Cardiol, 2022, 7(4): 386-395. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.6059
[26] Edwards LA, Feng F, Iqbal M, et al. Machine learning for pediatric echocardiographic mitral regurgitation detection[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2023, 36(1): 96-104. e104. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2022.09.017
[27] Franke B, Schlief A, Walczak L, et al. Comparison of hemodynamics in biological surgical aortic valve replacement and transcatheter aortic valve implantation: An in-silico study[J]. Artif Organs, 2023, 47(2): 352-360. doi: 10.1111/aor.14405
[28] 谢明星. 医学影像人工智能在心脏瓣膜疾病介入诊疗中的应用[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(12): 929-933, 940. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.12.001
[29] Namasivayam M, Myers PD, Guttag JV, et al. Predicting outcomes in patients with aortic stenosis using machine learning: the Aortic Stenosis Risk(ASteRisk)score[J]. Open Heart, 2022, 9(1): 110.
[30] Zweck E, Spieker M, Horn P, et al. Machine learning identifies clinical parameters to predict mortality in patients undergoing transcatheter mitral valve repair[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2021, 14(18): 2027-2036. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2021.06.039
[31] Biaggi P, Sager DF, Külling J, et al. Potential value of fusion imaging and automated three-dimensional heart segmentation during transcatheter aortic valve replacement[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2020, 33(4): 516-517. e511. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2019.12.012
[32] Faletra FF, Pozzoli A, Agricola E, et al. Echocardiographic-fluoroscopic fusion imaging for transcatheter mitral valve repair guidance[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2018, 19(7): 715-726. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jey067
[33] Blaha MJ, Cainzos-Achirica M. Coronary CT angiography in new-onset stable chest pain: time for U.S. Guidelines to Be NICEr[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2019, 73(8): 903-905. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.2205
[34] Joshi M, Melo DP, Ouyang D, et al. Current and future applications of artificial intelligence in cardiac CT[J]. Curr Cardiol Rep, 2023, 25(3): 109-117. doi: 10.1007/s11886-022-01837-8
[35] Lanzafame LRM, Bucolo GM, Muscogiuri G, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiovascular CT and MR imaging[J]. Life(Basel), 2023, 13(2): 507.
[36] van Velzen SGM, Lessmann N, Velthuis BK, et al. Deep learning for automatic calcium scoring in CT: validation using multiple cardiac CT and chest CT protocols[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(1): 66-79. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020191621
[37] Pieszko K, Shanbhag A, Killekar A, et al. Deep learning of coronary calcium scores from PET/CT attenuation maps accurately predicts adverse cardiovascular events[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2023, 16(5): 675-687. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2022.06.006
[38] Mu D, Bai J, Chen W, et al. Calcium scoring at coronary CT angiography using deep learning[J]. Radiology, 2022, 302(2): 309-316. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021211483
[39] Martin SS, van Assen M, Rapaka S, et al. Evaluation of a Deep Learning-Based Automated CT Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring Algorithm[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020, 13(2 Pt 1): 524-526.
[40] Al'Aref SJ, Maliakal G, Singh G, et al. Machine learning of clinical variables and coronary artery calcium scoring for the prediction of obstructive coronary artery disease on coronary computed tomography angiography: analysis from the CONFIRM registry[J]. Eur Heart J, 2020, 41(3): 359-367. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz565
[41] Kolossváry M, Park J, Bang JI, et al. Identification of invasive and radionuclide imaging markers of coronary plaque vulnerability using radiomic analysis of coronary computed tomography angiography[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2019, 20(11): 1250-1258. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jez033
[42] van Assen M, Muscogiuri G, Caruso D, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiac radiology[J]. Radiol Med, 2020, 125(11): 1186-1199. doi: 10.1007/s11547-020-01277-w
[43] Qiao HY, Tang CX, Schoepf UJ, et al. One-year outcomes of CCTA alone versus machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: a single-center, prospective study[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(8): 5179-5188. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08604-x
[44] Qiao HY, Tang CX, Schoepf UJ, et al. Impact of machine learning-based coronary computed tomography angiography fractional flow reserve on treatment decisions and clinical outcomes in patients with suspected coronary artery disease[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(11): 5841-5851. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06964-w
[45] Argentiero A, Muscogiuri G, Rabbat MG, et al. The applications of artificial intelligence in cardiovascular magnetic resonance & mdash; a comprehensive review[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(10): 2866. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102866
[46] Sandino CM, Lai P, Vasanawala SS, et al. Accelerating cardiac cine MRI using a deep learning-based ESPIRiT reconstruction[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(1): 152-167. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28420
[47] Fotaki A, Fuin N, Nordio G, et al. Accelerating 3D Mtc-Boost in patients with congenital heart disease using a joint multi-scale variational neural network reconstruction[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2022, 92: 120-132. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2022.06.012
[48] Fahmy AS, Neisius U, Chan RH, et al. Three-dimensional deep convolutional neural networks for automated myocardial scar quantification in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a multicenter multivendor study[J]. Radiology, 2020, 294(1): 52-60. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019190737
[49] Slomka PJ, Dey D, Sitek A, et al. Cardiac imaging: working towards fully-automated machine analysis & interpretation[J]. Expert Rev Med Devices, 2017, 14(3): 197-212. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2017.1300057
[50] Augusto JB, Davies RH, Bhuva AN, et al. Diagnosis and risk stratification in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using machine learning wall thickness measurement: a comparison with human test-retest performance[J]. Lancet Digit Health, 2021, 3(1): e20-e28. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30267-3
[51] 刘亚男, 赵瑞峰. 人工智能在心血管影像中的应用进展[J]. 磁共振成像, 2021, 12(7): 114-116+124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC202107027.htm
[52] Motwani M. 2022 Artificial intelligence primer for the nuclear cardiologist[J]. J Nucl Cardiol, 2022: 12: 120.
[53] Zhu F, Li L, Zhao J, et al. A new method incorporating deep learning with shape priors for left ventricular segmentation in myocardial perfusion SPECT images[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2023, 160: 106954. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106954
[54] Betancur J, Rubeaux M, Fuchs TA, et al. Automatic valve plane localization in myocardial perfusion SPECT/CT by machine learning: anatomic and clinical validation[J]. J Nucl Med, 2017, 58(6): 961-967. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.116.179911
[55] Arsanjani R, Xu Y, Dey D, et al. Improved accuracy of myocardial perfusion SPECT for detection of coronary artery disease by machine learning in a large population[J]. J Nucl Cardiol, 2013, 20(4): 553-562. doi: 10.1007/s12350-013-9706-2
[56] Miller RJH, Kuronuma K, Singh A, et al. Explainable deep learning improves physician interpretation of myocardial perfusion imaging[J]. J Nucl Med, 2022, 63(11): 1768-1774.
[57] Hu LH, Betancur J, Sharir T, et al. Machine learning predicts per-vessel early coronary revascularization after fast myocardial perfusion SPECT: results from multicentre REFINE SPECT registry[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020, 21(5): 549-559. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jez177
[58] Mohebi M, Amini M, Alemzadeh-Ansari MJ, et al. Post-revascularization ejection fraction prediction for patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention based on myocardial perfusion SPECT imaging radiomics: a preliminary machine learning study[J]. J Digital Imaging, 2023, 36(4): 1348-1363.
[59] Gu B, Sidhu S, Weinreb RN, et al. Review of visualization approaches in deep learning models of glaucoma[J]. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol(Phila), 2023, 12(4): 392-401.
-




 下载:
下载: