Predictors of long-term≥3 years recurrence of atrial arrhythmias after the index catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the role of left atrial substrate remodeling
-
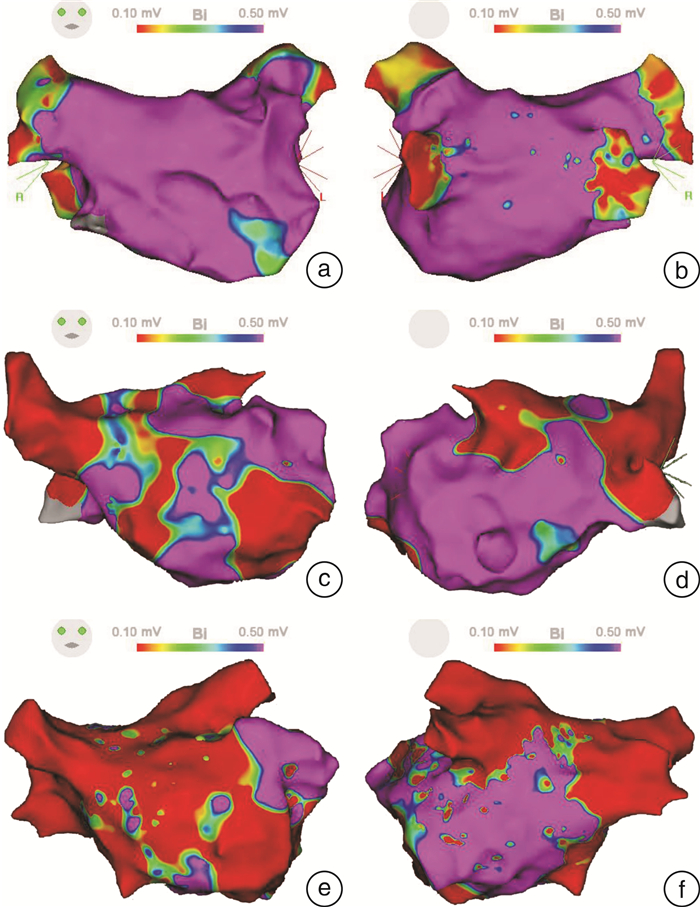
摘要: 目的 探讨阵发性心房颤动(房颤)经导管射频消融后超远期复发的预测因素,并评估阵发性房颤患者超远期复发过程中左心房基质重构的作用。方法 选择连续39例消融术后3年以上复发并接受再次消融手术的阵发性房颤患者,即超远期复发组。对照组为78例通过倾向性评分确定的首次消融术后随访超过3年仍无复发的阵发性房颤患者,即无复发组。结果 与无复发组相比,超远期复发组左心房基质的特征为:①左心房内径更大[(36.1±4.1) mm vs (38.5±4.3) mm,P=0.005];②传导时间更长[(184.8±66.9) ms vs (152.0±64.2) ms,P=0.012];③双极电压更低[(1.14±0.69) mV vs (1.55±0.57) mV,P=0.001];④低压区比例更高[(18.7±15.3)% vs (8.9±9.0)%,P < 0.001]。在超远期复发组中,与首次消融手术相比,再次消融术中发现:①左心房扩张[(38.5±4.3) mm vs (40.03± 4.4) mm,P=0.024];②左心房低电压区增加[(18.7±15.4) mV vs (28.3±16.9) mV,P < 0.001];③左心房瘢痕面积增加[(5.1±5.4)% vs (2.8±6.5)%,P=0.008]。结论 阵发性房颤射频消融术后超远期复发的患者发生了显著的电重构和结构重构,这些左心房基质重构可能参与超远期复发的机制。Abstract: Objective To investigate the predictors of long-term recurrence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation(AF) after transcatheter radiofrequency ablation, and to evaluate the role of left atrial matrix remodeling in the course of long-term recurrence of paroxysmal AF.Methods The 39 patients with paroxysmal AF who relapsed more than 3 years after ablation and underwent re-ablation were selected, as the long-term recurrence group. The control group consisted of 78 patients with paroxysmal AF who had no recurrence for more than 3 years after the first ablation according to the propensity score.Results Compared with the control group, the left atrial substrate in the long-term recurrence group demonstrated the following characteristics: (1) marked LA dilation[(36.1±4.1) mm vs(38.5±4.3) mm, P=0.005]. (2) longer conduction time[(184.8+66.9) ms vs(152.0+64.2) ms, P=0.012]. (3) lower bipolar voltage[(1.14±0.69) mV vs(1.55±0.57) mV, P=0.001]; (4) increasing proportion of low-voltage areas[(18.7±15.3)% vs(8.9±9.0)%, P < 0.001]. In the long-term recurrence group, compared with the first ablation, re-ablation patients showed: (1) left atrium expansion[(38.5 + 4.3) mm vs(40.03+4.4) mm, P=0.024]; (2) low voltage left atrium area increased[(18.7+15.4)mV vs(28.3+16.9) mV, P < 0.001]; (3) Left atrial scar area increased[(5.1±5.4)% vs(2.8±6.5)%, P=0.008].Conclusion Patients with paroxysmal AF who experienced significant electrical remodeling and structural remodeling after radiofrency ablation, and these left atrial matrix remodeling may be involved in the mechanism of long-term recurrence.
-

-
表 1 无复发组和超远期复发组一般临床资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general Clinical
X±S, 例(%) 项目 无复发组(78例) 超远期复发组(39例) P值 首次消融 再次消融 vs无复发组 vs首次消融 年龄/岁 61.1±10.8 60.8±10.4 65.3±10.1 0.888 < 0.001 女性 42(53.8) 21(53.8) - 1.000 - 房颤病史/月 49.5±54.0 62.2±53.7 - 0.234 - 体重指数/(kg/m2) 25.5±2.9 26.7±4.0 26.4±4.0 0.070 0.228 冠状动脉疾病 10(12.8) 2(5.1) 6(15.4) 0.332 0.219 高血压 54(69.2) 24(61.5) 26(66.7) 0.414 0.500 2型糖尿病 16(20.5) 7(17.9) 12(30.8) 0.810 0.063 卒中史 2(2.6) 2(5.1) 4(10.3) 0.600 0.500 CHA2DS2-VASc评分/分 2.01±1.43 1.79±1.26 2.51±1.36 0.421 0.001 左心房内径/mm 36.1±4.1 38.5±4.3 40.03±4.4 0.005 0.024 左室舒张末期内径/mm 46.6±3.8 47.7±4.7 46.3±6.3 0.197 0.195 左室收缩末期内径/mm 28.8±4.1 28.8±4.3 29.2±3.8 0.978 0.535 左室射血分数/% 67.8±6.9 68.3±6.6 66.6±5.4 0.736 0.189 Ⅰ类抗心律失常药 9(11.5) 7(17.9) 3(7.7) 0.396 0.310 Ⅲ类抗心律失常药 58(74.4) 27(69.2) 20(51.3) 0.661 0.165 β受体阻滞剂 23(29.5) 16(41.0) 15(38.5) 0.220 1.000 表 2 无复发组和超远期复发组心房标测结果比较
Table 2. Comparison of atrial mapping results
X±S, 例(%) 项目 无复发组
(78例)超远期复发组
(39例)P值 左心房容积/mL 87.8±19.6 97.5±21.9 0.011 左心房激动时间/ms 152.0±64.2 184.8±66.9 0.012 左心房电压/mV 1.55±0.57 1.14±0.69 0.001 左心房低电压比例/% 8.9±9.0 18.7±15.3 < 0.001 左心房瘢痕比例/% 1.0±3.6 2.8±6.5 0.104 表 3 超远期复发组首次和再次消融术中心房标测结果比较
Table 3. Comparison of atrial mapping results
X±S 指标 超远期程复发组(39例) P值 首次消融 再次消融 左心房容积/mL 97.5±21.9 119.9±44.7 < 0.001 左心房表面积/cm2 116.9±20.7 146.0±57.2 0.001 左心房激动时间/ms 184.8±66.9 207.9±73.5 0.172 左心房低电压区比例/% 18.7±15.4 28.3±16.9 < 0.001 左心房瘢痕比例/% 5.1±5.4 2.8±6.5 0.008 表 4 阵发性房颤肺静脉隔离后超远期复发的预测指标
Table 4. Prognostic index of long-term recurrence of paroxysmal AF after PVI
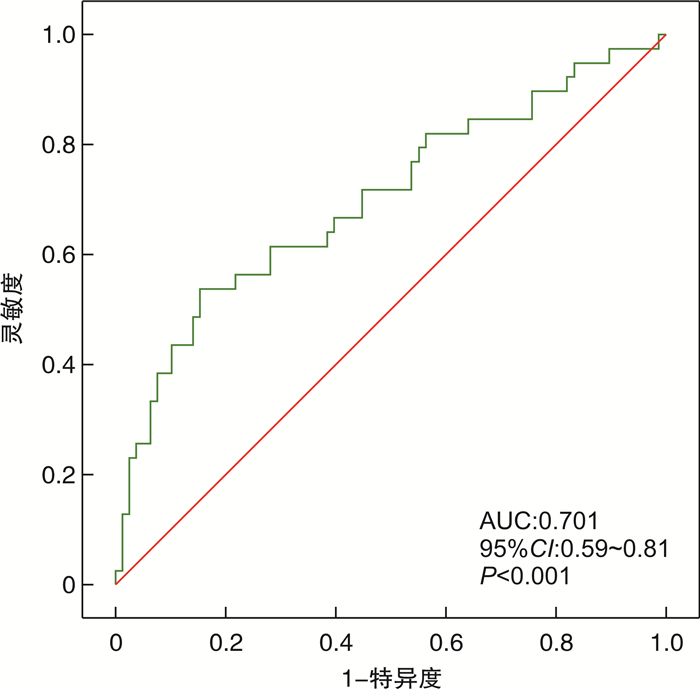
变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 OR 95%CI P 校正OR 95%CI P 体重指数 1.12 0.99~1.26 0.067 左心房内径 1.15 1.05~1.27 0.004 1.13 1.02~1.27 0.024 左心房容积 1.02 1.00~1.04 0.021 左心房激动时间 1.01 1.00~1.01 0.016 双极电压 0.33 0.17~0.66 0.002 左心房低电压区比例 1.07 1.03~1.11 < 0.001 1.07 1.03~1.11 0.001 左心房瘢痕比例 1.09 0.99~1.20 0.095 -
[1] Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery(EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology(ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association(EHRA)of the ESC[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42: 373-498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612
[2] Kis Z, Muka T, Franco OH, et al. The short and long-term efficacy of pulmonary vein isolation as a sole treatment strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Curr Cardiol Rev, 2017, 13: 199-208.
[3] Usui E, Miyazaki S, Taniguchi H, et al. Recurrence after "long-term success" in catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2015, 12: 893-898. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.01.043
[4] Shah S, Barakat AF, Saliba WI, et al. Recurrent atrial fibrillation after initial long-term ablation success: electrophysiological findings and outcomes of repeat ablation procedures[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2018, 11: e005785. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.117.005785
[5] Park JW, Yu HT, Kim TH, et al. Mechanisms of long-term recurrence 3 years after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2020, 6(8): 999-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2020.04.035
[6] Yamaguchi T, Marrouche NF. Recurrence post-atrial fibrillation ablation: think outside the pulmonary veins[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2018, 11(4): e006379. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.118.006379
[7] Rolf S, Kircher S, Arya A, et al. Tailored atrial substrate modification based on low-voltage areas in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2014, 7(5): 825-833. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.113.001251
[8] Choi SH, Yu HT, Kim D, et al. Late recurrence of atrial fibrillation 5 years after catheter ablation: predictors and outcome[J]. Europace, 2023, 25(5): 110. doi: 10.1093/europace/euad110
[9] Nery PB, Belliveau D, Nair GM, et al. Relationship between pulmonary vein reconnection and atrial fibrillation recurrence: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2016, 2(4): 474-483. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2016.02.003
[10] Kim TH, Park J, Uhm JS, et al. Pulmonary vein reconnection predicts good clinical outcome after second catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation[J]. Europace, 2017, 19(6): 961-967.
[11] Nattel S, Burstein B, Dobrev D. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and implications[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2008, 1(1): 62-73. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.107.754564
[12] Verma A, Wazni OM, Marrouche NF, et al. Pre-existent left atrial scarring in patients undergoing pulmonary vein antrum isolation: an independent predictor of procedural failure[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2005, 45(2): 285-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.10.035
[13] Wijffels MC, Kirchhof CJ, Dorland R, et al. Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation. A study in awake chronically instrumented goats[J]. Circulation, 1995, 92(7): 1954-1968. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.92.7.1954
[14] Pellman J, Sheikh F. Atrial fibrillation: mechanisms, therapeutics, and future directions[J]. Compr Physiol, 2015, 5(2): 649-665.
[15] Lee A, See VA, Lim TW, et al. Atrial fibrillation ablation by single ring isolation versus wide antral isolation: Effects on left atrial size and function[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2016, 206: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.12.012
[16] Tsao HM, Wu MH, Huang BH, et al. Morphologic remodeling of pulmonary veins and left atrium after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: insight from long-term follow-up of three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2005, 16(1): 7-12. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2005.04407.x
[17] Reant P, Lafitte S, Jan P, et al. Reverse remodeling of the left cardiac chambers after catheter ablation after 1 year in a series of patients with isolated atrial fibrillation[J]. Circulation, 2005, 112(19): 2896-2903. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.523928
[18] Rettmann ME, Holmes DR 3rd, Monahan KH, et al. Treatment-related changes in left atrial structure in atrial fibrillation: findings from the CABANA Imaging Substudy[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2021, 14(5): e008540. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.120.008540
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 233
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: