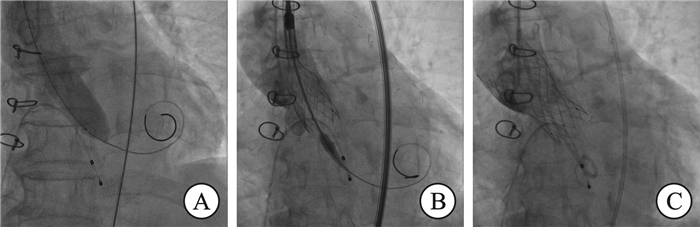
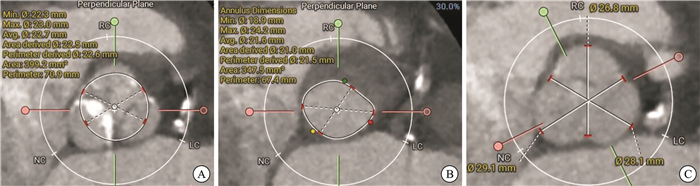
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement with percutaneous renal artery stenting via single artery approach: one case report
-
摘要: 82岁女性因头晕、晕厥就诊,诊断为重度主动脉瓣狭窄合并冠心病、高血压、糖尿病及右肾动脉狭窄,行“一站式”经导管主动脉瓣置换术(TAVR)联合经皮肾动脉支架置入术(PRAS)。术后主动脉瓣压差降至13 mmHg,左心室射血分数提升至68%,但并发急性肾损伤(肌酐峰值219 μmol/L),经治疗后缓解。半年随访,患者症状消失,心肾功能改善。
-
关键词:
- 单动脉入路技术 /
- 经导管主动脉瓣置换术 /
- 肾动脉狭窄 /
- 肾动脉支架置入术
Abstract: An 82-year-old woman presented with dizziness and syncope and was diagnosed with severe aortic stenosis, coronary heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, and right renal artery stenosis. She underwent a 'one-stop' transcatheter aortic valve replacement(TAVR) combined with percutaneous renal artery stenting(PRAS). Postoperatively, the aortic valve gradient decreased to 13 mmHg, left ventricular ejection fraction improved to 68%, but acute kidney injury occurred(peak creatinine 219 μmol/L), which resolved with treatment. At the six-month follow-up, the patient's symptoms disappeared, and cardiac and renal function were improved. -

-
[1] 中华医学会临床药学分会, 中国药学会医院药学专业委员会, 中华医学会肾脏病学分会. 碘对比剂诱导的急性肾损伤防治的专家共识[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2022, 38(3): 265-288.
[2] 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会结构性心脏病专业委员会. 中国经导管主动脉瓣置换术临床路径专家共识(2021版)[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2022, 37(1): 12-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2022.01.003
[3] Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 363(17): 1597-1607. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1008232
[4] Braghiroli J, Kapoor K, Thielhelm TP, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement in low risk patients: a review of PARTNER 3 and Evolut low risk trials[J]. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, 2020, 10(1): 59-71. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2019.09.12
[5] 卢麒麟, 卫志轩, 冯策, 等. 主动脉瓣狭窄合并冠心病患者行单纯介入治疗与单纯外科治疗的疗效对比分析[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2023, 39(6): 428-431. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2023.06.005
[6] 蒋雄京, 高润霖. 肾动脉支架术的临床地位和争论[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2010, 38(1): 3-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2010.01.002
[7] 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会血管疾病高血压分会专家共识起草组. 肾动脉狭窄的诊断和处理中国专家共识[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2017, 32(9): 835-844. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2017.09.002
[8] Cooper CJ, Murphy TP, Cutlip DE, et al. Stenting and medical therapy for atherosclerotic renal-artery stenosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 370(1): 13-22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1310753
[9] Watson P, Hadjipetrou P, Cox SV, et al. Effect of renal artery stenting on renal function and size in patients with atherosclerotic renovascular disease[J]. Circulation, 2000, 102(14): 1671-1677. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.14.1671
[10] Ritchie J, Kalra P. ASTRAL and beyond: who is appropriate to consider for renal artery revascularization?[J]. Vasc Dis Manage, 2011, 8(2): E12-E20.
[11] Yamamoto M, Hayashida K, Mouillet G, et al. Renal function-based contrast dosing predicts acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2013, 6(5): 479-486. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.02.007
[12] Van Linden A, Kempfert J, Rastan AJ, et al. Risk of acute kidney injury after minimally invasive transapical aortic valve implantation in 270 patients[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2011, 39(6): 835-842. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2010.11.034
[13] Madershahian N, Scherner M, Liakopoulos O, et al. Renal impairment and transapical aortic valve implantation: impact of contrast medium dose on kidney function and survival[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2012, 41(6): 1225-1232. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezr199
[14] Elhmidi Y, Bleiziffer S, Piazza N, et al. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation[J]. Am Heart J, 2011, 161(4): 735-739. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.01.009
[15] Bagur R, Webb JG, Nietlispach F, et al. Acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: predictive factors, prognostic value, and comparison with surgical aortic valve replacement[J]. Eur Heart J, 2010, 31(7): 865-874. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp552
[16] Najjar M, Salna M, George I. Acute kidney injury after aortic valve replacement: Incidence, risk factors and outcomes[J]. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther, 2015, 13(3): 301-316. doi: 10.1586/14779072.2015.1002467
[17] Crimi G, De Marzo V, De Marco F, et al. Acute Kidney Injury After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Mediates the Effect of Chronic Kidney Disease[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2022, 11(19): e024589. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024589
[18] Elhmidi Y, Bleiziffer S, Piazza N, et al. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation[J]. Am Heart J, 2011, 161(4): 735-739. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.01.009
[19] Barbash IM, Ben-Dor I, Dvir D, et al. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement[J]. Am Heart J, 2012, 163(6): 1031-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2012.01.009
[20] Ladia V, Panchal HB, O neil TJ, et al. Incidence of renal failure requiring hemodialysis following transcatheter aortic valve replacement[J]. Am J Med Sci, 2016, 352(3): 306-313. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2016.05.018
[21] Elbadawi A, Naqvi SY, Saad M, et al. In-hospital outcomes with transfemoral versus transapical access for transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients with peripheral arterial disease[J]. Cardiovasc Revasc Med, 2020, 21(5): 604-609. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2019.09.009
[22] Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Kashani K. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement; a kidney's perspective[J]. J Renal Inj Prev, 2016, 5(1): 1-7. doi: 10.15171/jrip.2016.01
[23] Katsaros O, Apostolos A, Ktenopoulos N, et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Access Sites: Same Goals, Distinct Aspects, Various Merits and Demerits[J]. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis, 2023, 11(1): 4.
[24] 姚晶, 刘新民, 苑飞, 等. 使用"All in One"单动脉/血管技术行经导管主动脉瓣置换术[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2023, 51(9): 990-994.
[25] 刘新民, 姚晶, 董哲, 等. 使用单动脉入路技术行经导管主动脉瓣置换术三例[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2022, 37(4): 421-424.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 26
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: