Risk factors of atrial fibrillation complicated with functional mitral regurgitation and the effect of catheter ablation
-
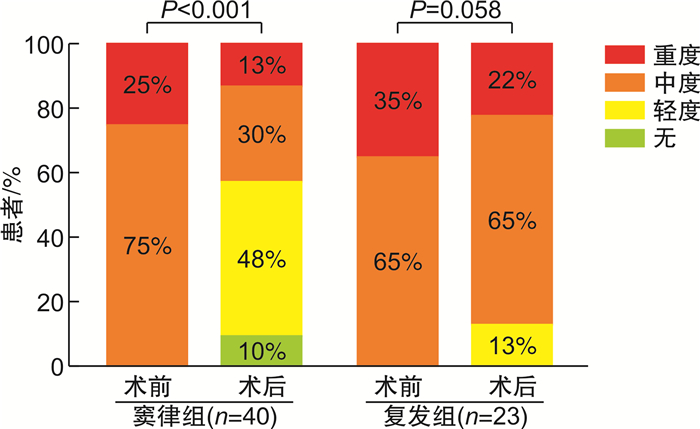
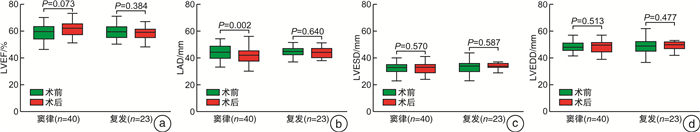
摘要: 目的 探讨心房颤动(AF)患者合并中、重度功能性二尖瓣反流(FMR)的危险因素以及AF导管消融对FMR的影响。方法 从2018年1月—2019年12月到我院心律失常科就诊的首次行AF导管消融的患者中,连续入选合并中、重度FMR的患者88例,无或轻度FMR患者277例。比较两组基线资料,应用logistic回归分析评价AF合并中、重度FMR的危险因素。依据AF合并中、重度FMR患者术后是否发生AF复发分为维持窦律组与AF复发组,比较两组术前、术后随访心脏彩超结果。结果 多因素logistic回归分析显示:年龄(OR=1.07;95%CI:1.03~1.10;P<0.001)、持续性AF(OR=4.92,95%CI:2.72~8.93,P<0.001)、左室射血分数(LVEF)(OR=0.95,95%CI:0.92~0.99,P=0.009)和左房直径(LAD)(OR=1.15,95%CI:1.09~1.22,P<0.001)是AF合并中、重度FMR的独立危险因素。对AF合并中、重度FMR组患者进行随访(23.3±6.7)个月,与术前相比,维持窦律患者LAD明显减小[(44.1±5.1) mm∶(41.6±5.6) mm,P=0.002],FMR程度明显改善(P=0.001)。而AF复发患者FMR较术前无明显改善(P=0.058),LAD亦未见明显降低(P>0.05)。结论 年龄、持续性AF、LVEF及LAD是AF合并中、重度FMR的独立危险因素,AF合并中、重度FMR患者经导管消融维持窦性心律能显著改善FMR程度。
-
关键词:
- 心房颤动 /
- 中、重度功能性二尖瓣反流 /
- 导管消融
Abstract: Objective To investigate the risk factors of atrial fibrillation(AF) patients with moderate and severe functional mitral regurgitation(FMR) and the effect of AF catheter ablation on FMR.Methods Among the patients who received AF catheter ablation for the first time, 88 patients with moderate and severe FMR and 277 patients with no or mild FMR were continuously selected in our hospital from January 2018 to December 2019. The baseline data of the two groups were compared, and the risk factors of moderate and severe FMR in AF were evaluated by logistics regression analysis. The patients with AF combined with moderate and severe FMR were divided into the maintenance of sinus rhythm group and the recurrence of AF group according to whether AF recurrence occurred after operation, and the results of cardiac color doppler ultrasound before and after operation were compared between the two groups.Results Multifactor Logistics regression analysis showed that: Age(OR=1.07, 95%CI: 1.03-1.10,P< 0.001), persistent AF(OR=4.92, 95%CI: 2.72-8.93,P< 0.001), left ventricular ejection fraction(LVEF)(OR=0.95, 95%CI: 0.92-0.99,P=0.009) and left atrial diameter(LAD)(OR=1.15, 95%CI: 1.09-1.22,P< 0.001) were independent risk factors for AF with moderate and severe FMR. The patients with AF combined with moderate and severe FMR were followed up for(23.3±6.7) months. Compared with the pre-operation, the LAD of patients with maintenance of sinus rhythm was significantly decreased[(44.1±5.1) mm vs. (41.6±5.6) mm,P=0.002], and the degree of FMR was significantly improved(P=0.001). In patients with AF recurrence, FMR was not significantly improved(P=0.058) and LAD was not significantly decreased(P> 0.05).Conclusion Age, persistent AF, LVEF and LAD were independent risk factors for AF with moderate and severe FMR, and catheter ablation to maintain sinus rhythm could significantly improve the degree of FMR in AF with moderate and severe FMR. -

-
表 1 两组患者基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline data between the two groups
例(%), X±S, M(P25, P75) 项目 SFMR组(88例) 对照组(277例) P值 年龄/岁 64.8±8.8 59.2±10.4 <0.001 男性 48(54.5) 173(62.5) 0.186 持续性AF 60(68.2) 58(20.9) <0.001 AF时间/d 12(2,36) 12(2,48) <0.001 BMI/(kg·m-2) 25.3±3.6 25.6±3.3 0.475 CHA2DS2-VASc评分/分 2.3±1.6 1.6±1.3 <0.001 糖尿病 13(14.8) 40(14.4) 0.939 高血压 47(53.4) 123(44.4) 0.140 卒中/TIA 10(11.4) 17(6.1) 0.103 心衰 6(6.8) 5(1.8) 0.042 冠心病 19(21.6) 31(11.2) 0.013 肾功能不全 1(1.1) 4(1.4) 1.000 超声心动图 LVEF/% 57.1±9.6 61.7±6.1 <0.001 LAD/mm 43.9±4.7 38.7±5.6 <0.001 LVESD/mm 34.0±5.6 31.7±3.9 0.001 LVEDD/mm 49.2±5.3 47.6±4.2 0.003 注:TIA:短暂性脑缺血发作;LVESD:左室收缩末期直径;LVEDD:左室舒张末期直径。 表 2 中、重度FMR的单因素与多因素logistic分析
Table 2. Univariate and multivariate analysis of risk factors for moderate and severe FMR
项目 单因素分析 多因素分析 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 年龄 1.06(1.03~1.09) <0.001 1.07(1.03~1.10) <0.001 性别 1.39(0.85~2.25) 1.187 持续性AF 8.09(4.74~13.80) <0.001 4.92(2.72~8.93) <0.001 BMI 0.97(0.91~1.05) 0.474 CHA2DS2-VASc评分 1.43(1.20~1.69) <0.001 糖尿病 0.97(0.50~1.92) 0.939 高血压 1.44(0.89~2.32) 1.141 卒中/TIA 1.96(0.86~4.46) 0.108 心衰 3.98(1.18~13.38) 0.026 冠心病 2.19(1.16~4.10) 0.015 肾功能不全 0.78(0.09~7.11) 0.829 LVEF 0.92(0.84~0.96) <0.001 0.95(0.92~0.99) 0.009 LAD 1.19(1.13~1.25) <0.001 1.15(1.09~1.22) <0.001 LVESD 1.11(1.05~1.17) <0.001 LVEDD 1.08(1.03~1.14) 0.004 -
[1] Goliasch G, Bartko PE, Pavo N, et al. Refining the prognostic impact of functional mitral regurgitation in chronic heart failure[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39(1): 3946.
[2] Li B, Luo FL, Luo XK, et al. Effects of atrial fibrosis induced by mitral regurgitation on atrial electrophysiology and susceptibility to atrial fibrillation in pigs[J]. Cardiovasc Pathol, 2019(40): 32-40.
[3] Nozomi W, Simon M, Shun N, et al. Functional mitral regurgitation: imaging insights, clinical outcomes and surgical principles[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2017, 60(3): 351-360. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2017.11.006
[4] 刘美, 范琰, 刘梅林. 老年心房颤动伴二尖瓣反流患者的临床特点和预后[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(5): 447-452. http://lcxb.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=9117efa0-a05e-41a1-8fa2-d1817476c1ce
[5] Nair Girish M, Nery Pablo B, Diwakaramenon S, et al. A systematic review of randomized trials comparing radiofrequency ablation with antiarrhythmic medications in patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2009, 20(2): 138-144. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2008.01285.x
[6] 赵丹清, 张付涛, 刘晓洁, 等. 心房颤动合并中重度功能性二尖瓣反流: 导管消融或药物治疗临床疗效的对比研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(10): 925-930. http://lcxb.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c0ca363e-53ca-40cc-b1fc-3b094f1c8e27
[7] Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2017, 14: e275-e444. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.05.012
[8] Liang JJ, Silvestry FE. Mechanistic insights into mitral regurgitation due to atrial fibrillation: "Atrial functional mitral regurgitation"[J]. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2016, 26(8): 681-689. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2016.04.012
[9] Anita WA, Michael JM, Gregg WS. Secondary mitral regurgitation in heart failure: pathophysiology, prognosis, and therapeutic considerations[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2015, 65(12): 1231-1248. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.02.009
[10] Gertz ZM, Raina A, Saghy L, et al. Evidence of atrial functional mitral regurgitation due to atrial fibrillation: reversal with arrhythmia control[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2011, 58: 1474-1481. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.06.032
[11] Goliasch G, Bartko PE, Pavo N, et al. Refining the prognostic impact of functional mitral regurgitation in chronic heart failure[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39: 39-46. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx402
[12] Al Qahtani SY, Ouf SG, Ghazal SN, et al. Reverse atrial remodeling and resolution of mitral regurgitation after rhythm control in atrial fibrillation: a case report[J]. Saudi Journal of Medicine & Medical Sciences, 2019, 7(2): 118-120.
[13] Deferm S, Bertrand PB, Verhaert D, et al. Mitral annular dynamics in AF versus sinus rhythm: novel insights in to the mechanism of AFMR[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2021, S1936-878X(21): 00440-X.
[14] Wu JT, Zaman JAB, Yakupoglu HY, et al. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with functional mitral regurgitation and left ventricular systolic dysfunction[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2020, 7: 596491. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.596491
[15] Markman TM, Markman TM, De Feria Alsina A, et al. Improvement in tricuspid regurgitation following catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2020, 31(11): 2883-2888. doi: 10.1111/jce.14707
[16] 宁曼, 董建增, 康俊萍, 等. 心房颤动合并功能性三尖瓣反流的危险因素分析及射频导管消融术对其影响[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2015, 95(33): 2660-2663. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2015.33.002
-




 下载:
下载: