The correlation between H-type hypertension-related cerebral infarction and serum MCP-1 and MCPIP1
-
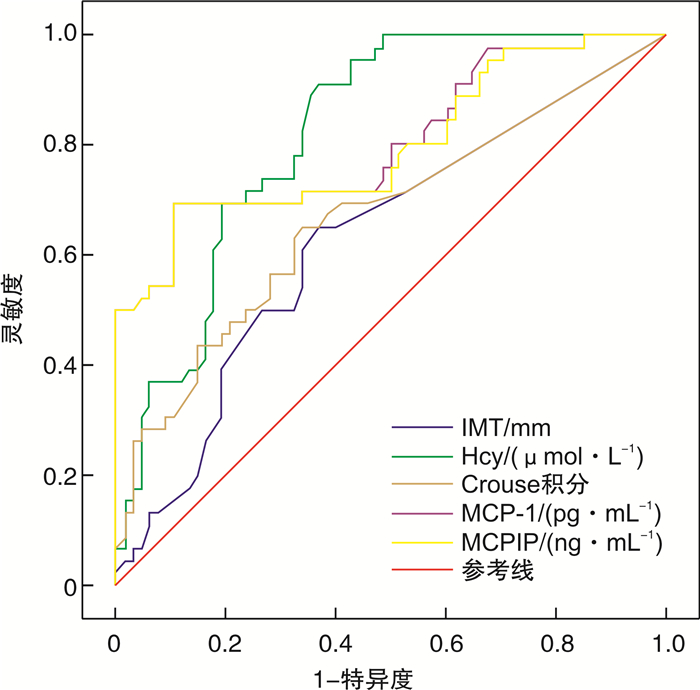
摘要: 目的 探究血清中单核细胞趋化蛋白-1(MCP-1)、单核细胞趋化蛋白-1诱导蛋白1(MCPIP1)浓度与H型高血压患者并发脑梗死的相关性。方法 随机选取2021年8月—2021年12月就诊于遵义医科大学第三附属医院(遵义市第一人民医院)住院完善颈动脉超声检查且符合纳入与排除标准的114例患者为研究对象。其中确诊为H型高血压合并脑梗死患者46例,H型高血压患者39例,单纯原发性高血压患者11例,以及同期体检中心的正常健康者18例。收集并分析4组患者一般临床资料、生化指标、颈动脉超声相关信息,采用ELISA法检测4组患者血清中MCP-1、MCPIP1的水平,以受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)分析MCP-1、MCPIP1在H型高血压并发脑梗死中的诊断价值。结果 H型高血压并发脑梗死组血清同型半胱氨酸(Hcy)、MCP-1、MCPIP1水平较其余3组明显升高,均差异具有统计学意义(均P< 0.05);与H型高血压组相比,血清MCP-1水平(OR=1.011,95%CI:1.003~1.018,P< 0.05)升高增加H型高血压并发脑梗死患病风险。Spearman相关性分析显示,H型高血压并发脑梗死患者颈动脉斑块Crouse积分与其血清Hcy水平呈正相关(r=0.486,P< 0.05)。H型高血压并发脑梗死组诊断价值的ROC曲线显示Hcy、MCP-1、MCPIP1对H型高血压并发脑梗死有一定诊断价值(P< 0.05)。结论 H型高血压并发脑梗死患者Hcy水平与颈动脉斑块Crouse积分相关;血清MCP-1、MCPIP1对H型高血压并发脑梗死具有早期预警价值。Abstract: Objective To explore the correlation between serum concentrations of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1(MCP-1), MCP-1-induced protein(MCPIP1) and cerebral infarction in patients with H-type hypertension.Methods A total of 114 patients who underwent carotid ultrasound examination and met the inclusion and exclusion criteria in the Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University from August 2021 to December 2021 were randomly selected as the research objects. Among them, 46 patients with H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction, 39 patients with H-type hypertension, and 11 patients with simple essential hypertension were selected as experimental groups, and 18 healthy people from the physical examination center were selected as the control group. ELISA was used to detect serum MCP-1 and MCPIP1 levels, and ROC Curve was used to analyze the correlation between MCP-1, MCPIP1 and H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction.Results The serum levels of homocysteinemia(Hcy), MCP-1, and MCPIP1 in the H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction group were significantly higher than those in the other three groups, and the differences were statistically significant(allP< 0.05). Compared with the H-type hypertension group, the increased serum MCP-1 level(OR=1.011, 95%CI: 1.003-1.018,P< 0.05) increased the risk of H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction. Spearman correlation analysis showed that the Crouse score of carotid plaque in patients with H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction was positively correlated with serum Hcy level(r=0.486,P< 0.05). The ROC curve showed that Hcy, MCP-1, and MCPIP1 had certain diagnostic values for type H hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction(P< 0.05).Conclusion Hcy levels in cerebral infarction patients with H-type hypertension is correlated with carotid IMT and plaque Crouse score. Serum MCP-1 and MCPIP1 may have early diagnosis value for H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction.
-

-
表 1 一般临床资料的比较
Table 1. General clinical data
例(%), M(P25, P75), X±S 项目 对照组(18例) HBP组(11例) HHBP组(39例) HHBP+脑梗死组(46例) F/χ2/Z P 年龄/岁 54.72±9.40 58.82±11.281) 63.89±10.271)2) 65.24±8.551)2) 6.05 < 0.001 男性 5(27.8) 6(54.5)1) 21(53.8)1) 32(69.6)1)2)3) 10.85 0.013 吸烟 3(16.7) 2(18.2) 17(43.6)1)2) 26(56.5)1)2)3) 11.32 0.009 饮酒 1(5.6) 1(9.1)1) 7(17.9)1)2) 11(23.9)1)2)3) 3.63 0.321 BMI 22.38±2.60 25.74±4.241) 24.00±2.48 24.05±2.74 3.38 0.021 IMT/mm — 0(0,1.80)1) 1.60(0,2.40)1)2) 1.90(0,2.40)1)2)3) 16.3 < 0.001 Crouse积分 — 0(0,1.80)1) 2.30(0,3.90)1)2) 2.90(0,4.90)1)2)3) 18.9 < 0.001 Hcy/(μmol·L-1) 9.2(8.8,9.6) 8.7(8.3,9.1) 14.4(12.1,17.9)1)2) 16.6(14.2,24.5)1)2)3) 44.75 0.000 MCP-1/(pg·mL-1) 379.58(301.9,473.2) 244.8(184.9,362.2) 271.7(187.2,368.9) 698.6(403.4,1199.2)1)2)3) 8.69 0.013 MCPIP1/(ng·mL-1) 1.81(1.34,2.43) 1.03(0.74,1.70) 1.18(0.75,1.74) 4.12(1.30,13.48)1)2)3) 8.76 0.011 TC/(mmol·L-1) 4.60±0.66 4.62±0.91 4.72±1.201) 4.76±1.701)2) 1.10 0.041 TG/(mmol·L-1) 1.26(1.04,1.75) 1.46(0.98,2.18) 1.68(1.14,2.09) 1.45(1.21,2.89) 2.90 0.229 HDL-C/(mmol·L-1) 1.28±0.19 1.27±0.21 1.16±0.211)2) 1.10±0.291)2) 2.29 0.042 LDL-C/(mmol·L-1) 2.64±0.48 2.69±0.67 2.80±0.76 2.81±0.68 0.33 0.801 FPG/(mmol·L-1) 5.07±1.01 5.16±0.94 5.60±1.65 5.42±1.26 0.77 0.530 PT/s 10.86±0.72 11.35±0.65 11.16±0.81 11.39±0.611) 2.68 0.048 APTT/s 21.30±5.70 25.60±3.631) 25.00±2.801) 25.49±2.701) 6.96 0.000 INR 0.93(0.89,1.01) 0.97(0.93,1.03) 0.96(0.90,1.03) 0.97(0.94,1.01) 1.19 0.550 Fbg/(g·L-1) 2.7(1.9,3.0) 2.8(2.4,3.3) 3.0(2.7,3.4)1)2) 2.9(2.6,3.7) 6.38 0.041 TT/s 16.14±1.54 17.05±0.84 16.45±0.74 16.37±1.71 0.58 0.630 与对照组比较,1) P < 0.05;与HBP组比较,2) P < 0.05;与HHBP组比较,3) P < 0.05。 表 2 H型高血压并发脑梗死的多因素logistic回归分析
Table 2. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction
因素 B SE Wald P OR 95% CI 性别 1.465 0.799 3.364 0.067 0.452 0.094~2.729 年龄 0.038 0.032 1.349 0.146 0.774 0.240~1.106 吸烟史 1.601 0.870 3.391 0.066 0.287 0.202~1.243 饮酒史 0.375 0.787 0.227 0.634 0.634 0.037~1.109 IMT 0.191 0.119 2.578 0.108 0.826 0.654~1.043 Crouse积分 0.188 0.060 9.819 0.002 1.207 1.073~1.358 MCP-1 0.011 0.004 8.129 0.004 1.011 1.003~1.018 MCPIP1 0.515 0.374 1.898 0.168 0.598 0.287~1.243 Hcy 0.023 0.040 0.338 0.651 1.023 0.947~1.106 表 3 各指标对H型高血压合并脑梗死诊断价值的ROC分析
Table 3. The diagnostic value of various indexes for H-type hypertension complicated with cerebral infarction analyzed by ROC analysis
项目 AUC(95% CI) 约登指数 灵敏度 特异度 P Hcy 0.823(0.749~0.898) 0.545 0.913 0.632 < 0.001 IMT 0.631(0.526~0.736) 0.284 0.652 0.603 0.018 Crouse积分 0.671(0.567~0.775) 0.413 0.653 0.662 0.002 MCP-1 0.806(0.721~0.892) 0.593 0.696 0.897 < 0.001 MCPIP1 0.800(0.713~0.888) 0.591 0.695 0.885 < 0.001 -
[1] 中华人民共和国2020年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R]. 中国统计, 2021(3): 8-22.
[2] Liberale L, Badimon L, Montecucco F, et al. Inflammation, Aging, and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2022, 79(8): 837-847. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.12.017
[3] 《中国高血压防治指南》修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南2018年修订版[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2019, 19(1): 1-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXFZ201901001.htm
[4] 李建平, 卢新政, 霍勇, 等. H型高血压诊断与治疗专家共识[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2016, 24(2): 123-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201602013.htm
[5] Ma LY, Chen WW, Gao RL, et al. China cardiovascular diseases report 2018: an updated summary[J]. J Geriatr Cardiol, 2020, 17(1): 1-8.
[6] 孔祥辉, 李明, 伍丽, 等. H型高血压患者颈动脉结构变化及其与血浆硫化氢水平相关性的研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2018, 34(9): 887-891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB201809011.htm
[7] Zhu S, Liu M, Bennett S, et al. The molecular structure and role of CCL2 (MCP-1) and C-C chemokine receptor CCR2 in skeletal biology and diseases[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(10): 7211-7222. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30375
[8] Zhao D, Liu J, Wang W, et al. Epidemiological transition of stroke in China: twenty-one-year observational study from the Sino-MONICA-Beijing Project[J]. Stroke, 2008, 39(6): 1668-1674. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.502807
[9] Qin X, Huo Y. H-Type hypertension, stroke and diabetes in China: Opportunities for primary prevention[J]. J Diabetes, 2016, 8(1): 38-40. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12333
[10] 李世英, 李峥, 张晋霞, 等. 氧化型低密度脂蛋白、单核细胞趋化蛋白1与脑梗死颈动脉粥样硬化的关系[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2016, 24(5): 495-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KDYZ201605013.htm
[11] Zhang H, Yao J, Huang Z, et al. Prognostic Value of Baseline d-Dimer Level in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis[J]. Angiology, 2022, 73(1): 18-25.
[12] 郭福佳, 周香, 袁正强. 单核细胞趋化蛋白-1与早发冠心病及其传统危险因素关系的研究进展[J]. 岭南心血管病杂志, 2020, 26(3): 352-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXGB202003023.htm
[13] Zhu S, Liu M, Bennett S, et al. The molecular structure and role of CCL2 (MCP-1) and C-C chemokine receptor CCR2 in skeletal biology and diseases[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(10): 7211-7222.
[14] He X, Li DR, Cui C, et al. Clinical significance of serum MCP-1 and VE-cadherin levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 21(4): 804-808.
[15] Li M, Chen Y, Zhang Y, et al. Correlation between monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 and coronary plaque characteristics[J]. Exp Biol Med, 2020, 245: 1335-1343.
[16] Bianconi V, Sahebkar A, Atkin SL, et al. The regulation and importance of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1[J]. Curr Opin Hematol, 2018, 25(1): 44-51.
[17] 葛冰磊, 俞善春, 金纪伟. 急性缺血性脑卒中患者血清Hcy、GAL3、MCP-1表达及其临床意义[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2019, 21(6): 893-897.
-




 下载:
下载: