Research progress of the relationship between left atrial morphology, function and thrombosis in patients with atrial fibrillation
-
摘要: 心房颤动(房颤)是最常见的心律失常之一,而血栓事件是房颤患者最严重的并发症。目前临床上主要通过CHA2DS2-VASc评分指导抗凝治疗,但有较多不足。有研究发现左心房的结构与功能与血栓形成有相关性,或有望成为房颤患者抗凝治疗的补充方法。现对左心房结构及功能预测非瓣膜性房颤患者血栓形成的价值进行综述。Abstract: Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common arrhythmias, and thrombotic events are the most serious complications in patients with atrial fibrillation. At present, anticoagulation therapy is mainly guided by CHA2DS2-VASC score in clinical practice, but there are many deficiencies. Some studies have found that the structure and function of the left atrium are related to thrombosis, which may be a complementary method for anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. This article reviews the value of left atrial structure and function in predicting thrombosis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.
-
Key words:
- atrial fibrillation /
- thrombosis /
- left atrial structure /
- left atrial function
-

-
[1] Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery(EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology(ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association(EHRA)of the ESC[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(5): 373-498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612
[2] Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study[J]. Circulation, 2014, 129(8): 837-847. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119
[3] Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(10): e56-e528.
[4] 任燕, 王显, 郭炜华, 等. 基于Marshall策略的联合消融治疗持续性心房颤动的新进展[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(5): 352-355. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.05.003
[5] Lau DH, Linz D, Schotten U, et al. Pathophysiology of Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Rotors, Foci and Fibrosis[J]. Heart Lung Circ, 2017, 26(9): 887-893. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2017.05.119
[6] Wijesurendra RS, Casadei B. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation[J]. Heart, 2019, 105(24): 1860-1867. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2018-314267
[7] Jordan K, Yaghi S, Poppas A, et al. Left Atrial Volume Index Is Associated With Cardioembolic Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation Detection After Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source[J]. Stroke, 2019, 50(8): 1997-2001. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025384
[8] 韩蕊, 梅迎晨, 郑梅, 等. 阵发性心房颤动患者经导管射频消融术后左心房变化及复发的危险因素分析[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2021, 33(9): 62-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2021.09.013
[9] 贺鹏康, 杨颖, 范芳芳, 等. 左心房顺应性参数与阵发性心房颤动射频消融术后复发率相关性分析[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2020, 28(2): 94-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8812.2020.02.006
[10] 张琦, 赖杰, 毛雯, 等. CHA2DS2-VASc评分结合左心房内径在预测非瓣膜性心房颤动患者脑卒中风险评估中的应用[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2020, 12(7): 835-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2020.07.15
[11] Radwan HI. Relation between left atrial measurements and thromboembolic risk markers assessed by echocardiography in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: A cross-sectional study[J]. Egypt Heart J, 2017, 69(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ehj.2016.05.004
[12] 程慧, 李国庆, 姚娟, 等. 心房颤动患者左心房内径与左心房血栓发生的关系[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2009, 24(6): 451-453. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXH200906023.htm
[13] 余倩, 毕亚艳. 炎症在心房颤动高凝状态中的作用机制[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2018, 10(6): 748-749. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZXX201806031.htm
[14] Veinot JP, Harrity PJ, Gentile F, et al. Anatomy of the normal left atrial appendage: a quantitative study of age-related changes in 500 autopsy hearts: implications for echocardiographic examination[J]. Circulation, 1997, 96(9): 3112-3115. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.96.9.3112
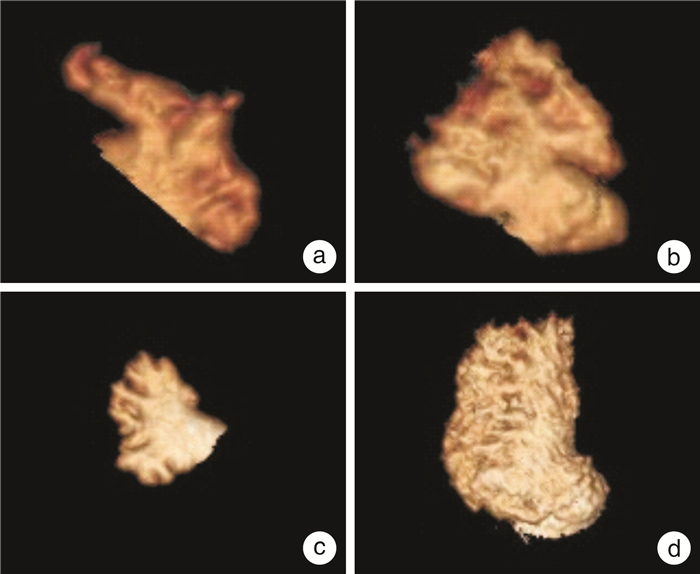
[15] Wang F, Zhu M, Wang X, et al. Predictive value of left atrial appendage lobes on left atrial thrombus or spontaneous echo contrast in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2018, 18(1): 153. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0889-y
[16] 庞乃栋, 张楠, 郭敏, 等. 左心耳电隔离在持续性心房颤动治疗中的研究进展[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(1): 6-10. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.01.002
[17] Sharma SP, Cheng J, Turagam MK, et al. Feasibility of Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion in Left Atrial Appendage Thrombus: A Systematic Review[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2020, 6(4): 414-424. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2019.11.017
[18] Lee Y, Park H C, Lee Y, et al. Comparison of Morphologic Features and Flow Velocity of the Left Atrial Appendage Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Alone, Transient Ischemic Attack, and Cardioembolic Stroke[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2017, 119(10): 1596-1604. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.02.016
[19] Anselmino M, Frea S, Gili S, et al. Left atrial appendage morphology at transesophageal echocardiography: how to improve reproducibility?[J]. Minerva Cardiol Angiol, 2021, 69(2): 178-184.
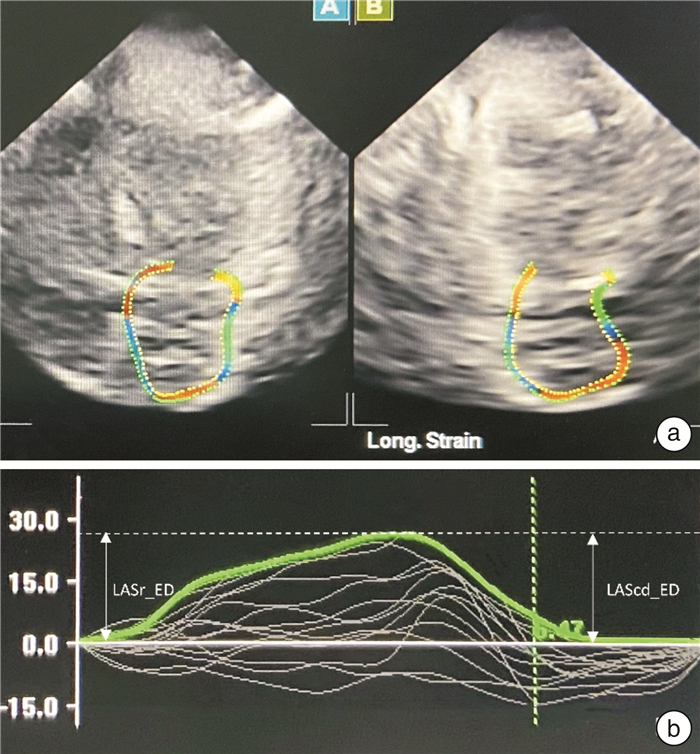
[20] Khurram IM, Dewire J, Mager M, et al. Relationship between left atrial appendage morphology and stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2013, 10(12): 1843-1849.
[21] Yaghi S, Chang AD, Akiki R, et al. The left atrial appendage morphology is associated with embolic stroke subtypes using a simple classification system: A proof of concept study[J]. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr, 2020, 14(1): 27-33.
[22] Lee JM, Shim J, Uhm JS, et al. Impact of increased orifice size and decreased flow velocity of left atrial appendage on stroke in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2014, 113(6): 963-969.
[23] García-Isla G, Olivares AL, Silva E, et al. Sensitivity analysis of geometrical parameters to study haemodynamics and thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage[J]. Int J Numer MethodsBiomed Eng, 2018: e3100.
[24] Nedios S, Kornej J, Koutalas E, et al. Left atrial appendage morphology and thromboembolic risk after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2014, 11(12): 2239-2246.
[25] Zhao Y, Zhang PP, Xu QF, et al. Relationship between left atrial appendage morphology and thrombus formation in patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2015, 188: 86-88.
[26] Goldman ME, Pearce LA, Hart RG, et al. Pathophysiologic correlates of thromboembolism in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: I. Reduced flow velocity in the left atrial appendage(The Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation[SPAF-Ⅲ]study)[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 1999, 12(12): 1080-1087.
[27] Ito T, Suwa M. Left atrial spontaneous echo contrast: relationship with clinical and echocardiographic parameters[J]. Echo Res Pract, 2019, 6(2): R65-R73.
[28] Matsumoto Y, Morino Y, Kumagai A, et al. Characteristics of Anatomy and Function of the Left Atrial Appendage and Their Relationships in Patients with Cardioembolic Stroke: A 3-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography Study[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2017, 26(3): 470-479.
[29] Doukky R, Garcia-Sayan E, Gage H, et al. The value of diastolic function parameters in the prediction of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation[J]. Cardiovasc Ultrasound, 2014, 12: 10.
[30] Badano LP, Kolias TJ, Muraru D, et al. Standardization of left atrial, right ventricular, and right atrial deformation imaging using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: a consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/Industry Task Force to standardize deformation imaging[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2018, 19(6): 591-600.
[31] Sardana M, Konda P, Hashmath Z, et al. Usefulness of Left Ventricular Strain by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Feature-Tracking to Predict Cardiovascular Events in Patients With and Without Heart Failure[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2019, 123(8): 1301-1308.
[32] Donal E, Lip GY, Galderisi M, et al. EACVI/EHRA Expert Consensus Document on the role of multi-modality imaging for the evaluation of patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2016, 17(4): 355-383.
[33] Zhu MR, Wang M, Ma XX, et al. The value of left atrial strain and strain rate in predicting left atrial appendage stasis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation[J]. Cardiol J, 2018, 25(1): 87-96.
[34] 魏泽人, 张天磊, 杨宁, 等. 斑点追踪超声心动图预测非瓣膜性心房颤动患者左心耳血栓形成的研究进展[J]. 心血管病学进展, 2020, 41(3): 219-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXGB202003001.htm
[35] Borre ED, Goode A, Raitz G, et al. Predicting Thromboembolic and Bleeding Event Risk in Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2018, 118(12): 2171-2187.
[36] 郭宥廷, 庄心宇, 刘荣宸, 等. 左房内径对非瓣膜性心房颤动患者缺血性卒中风险的预测价值研究[J]. 老年医学与保健, 2020, 26(2): 195-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYBJ202002008.htm
-




 下载:
下载: