Study on the relationship between PIN1 gene polymorphism and essential hypertension among ethnic groups in Guizhou
-
摘要: 目的 探讨肽基脯氨酰顺反异构酶(PIN1)基因单核苷酸多态性(SNP)与贵州苗族、布依族、汉族人群原发性高血压的关联性。方法 通过病例-对照研究方法,选取贵州雷山苗族、荔波布依族及贵阳汉族的原发性高血压和健康对照人群,采用Sequenom MassARRAY基因分型技术对以上人群PIN1基因多态性位点rs2233678、rs2233679进行基因分型,分析SNP与贵州人群原发性高血压的遗传关系。结果 在贵州苗族、布依族、汉族人群中,高血压组和对照组性别和BMI间的差异均无统计学意义;高血压组的平均年龄均大于对照组,且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。rs2233678、rs2233679在不同人群的分布均符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡。在苗族、布依族及汉族高血压组和对照组人群中,rs2233678、rs2233679等位基因及基因型差异均无统计学意义;rs2233678和rs2233679存在强连锁不平衡,以rs2233678-rs2233679构建的单倍型GC和单倍型GT与原发性高血压不存在显著关联性;多因子降维分析显示,rs2233678、rs2233679与BMI对于贵州总人群高血压的发生具有强协同作用(χ2=9.328,P=0.002);rs2233679和BMI对于贵州苗族人群高血压的发生具有强协同作用(χ2=5.624,P=0.018);rs2233678和rs2233679对于贵州布依族人群高血压的发生具有强协同作用(χ2=5.323,P=0.021)。结论 PIN1基因rs2233678、rs2233679可能共同影响贵州人群原发性高血压的发生。
-
关键词:
- 原发性高血压 /
- 肽基脯氨酰顺反异构酶 /
- 基因多态性 /
- 贵州民族
Abstract: Objective To investigate the association of peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase(PIN1) gene single nucleotide polymorphism(SNP) with essential hypertension in Guizhou Han, Miao and Buyi populations.Methods A case-control study was used to select patients with essential hypertension and healthy controls from Leishan Miao, Libo Buyi and Guiyang Han populations in Guizhou. Sequenom MassARRAY genotyping technique was used to genotype the PIN1 gene polymorphisms rs2233678 and rs2233679 in these populations. We analyzed the genetic relationship between SNP and essential hypertension in Guizhou populations.Results There were no significant differences in gender and BMI between the hypertension group and the control group among the Miao, Buyi and Han populations in Guizhou(P>0.05). The mean age of the hypertension group was greater than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P=0.001, P < 0.001 and P=0.004). The distributions of rs2233678 and rs2233679 in different populations were in line with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium(P>0.05). There was no significant difference in allele and genotype of rs2233678 and rs2233679 among Miao, Buyi and Han hypertension group and control group(P>0.05). There was strong linkage disequilibrium between rs2233678 and rs2233679, and the haplotype GC and haplotype GT constructed with rs2233678-rs2233679 were not significantly associated with essential hypertension(P>0.05). The results of multi-factor dimensionality reduction analysis showed that rs2233678, rs2233679 and BMI had strong synergistic effect on the occurrence of hypertension in the general population of Guizhou(χ2=9.328, P=0.002). rs2233679 and BMI had strong synergistic effect on the occurrence of hypertension in Guizhou Miao population(χ2=5.624, P=0.018). rs2233678 and rs2233679 had strong synergistic effect on the occurrence of hypertension in the Guizhou Buyi population(χ2=5.323, P=0.021).Conclusion PIN1 gene rs2233678 and rs2233679 may jointly affect the occurrence of essential hypertension in Guizhou populations. -

-
表 1 贵州苗族、布依族、汉族研究对象基本特征
Table 1. Basic characteristics of research objects of Miao, Buyi and Han populations in Guizhou
X±S, 例(%) 民族 男性 年龄/岁 BMI正常 BMI过低 BMI超重 BMI肥胖 总人群 对照组(335例) 151(45.1) 51.93±13.91 176(52.5) 17(5.1) 105(31.3) 37(11.0) 高血压组(343例) 164(47.8) 58.87±12.85 156(45.5) 14(4.1) 123(35.9) 50(14.6) t/χ2 0.511 -6.744 0.038 2.619 3.031 P 0.475 < 0.001 0.845 0.106 0.082 苗族 对照组(111例) 44(39.6) 51.15±15.92 55(49.5) 5(4.5) 39(35.1) 12(10.8) 高血压组(110例) 58(52.7) 57.91±13.69 48(43.6) 3(2.7) 42(38.2) 17(15.5) t/χ2 3.808 -3.381 0.248 0.500 1.308 P 0.051 0.001 0.724 0.479 0.253 布依族 对照组(117例) 52(44.4) 51.63±13.99 65(55.6) 8(6.8) 33(28.2) 11(9.4) 高血压组(119例) 61(51.3) 60.93±12.91 58(48.7) 8(6.7) 41(34.5) 12(10.1) t/χ2 1.098 -5.308 0.046 1.258 0.196 P 0.295 < 0.001 0.830 0.262 0.658 汉族 对照组(107例) 55(51.4) 53.07±11.40 56(52.3) 4(3.7) 33(30.8) 14(13.1) 高血压组(114例) 45(39.5) 57.63±11.74 50(43.9) 3(2.6) 40(35.1) 21(18.4) t/χ2 3.17 -2.925 0.049 1.005 1.733 P 0.075 0.004 1.000 0.316 0.188 表 2 PIN1等位基因及基因型分布
Table 2. Distribution of PIN1 alleles and genotypes
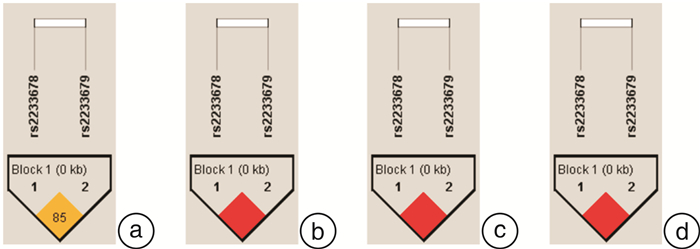
频次(%) 位点 等位基因/基因型 3民族汇总(678例) Pa Pb 苗族(221例) Pa Pb 对照组 高血压组 对照组 高血压组 rs2233678 G 658(98) 672(98) 0.737 0.735 219(99) 216(98) 0.990 0.990 C 12(2) 14(2) 3(1) 4(2) GG 323(96) 329(96) 108(97) 106(96) GC 12(4) 14(4) 3(3) 4(4) Phwe 0.739 0.699 0.885 0.846 rs2233679 C 377(56) 404(59) 0.328 0.287 131(59) 132(60) 0.832 0.976 T 293(44) 282(41) 91(41) 88(40) CC 110(33) 115(34) 37(33) 38(35) CT 157(47) 174(51) 57(51) 56(51) TT 68(20) 54(16) 17(15) 16(15) Phwe 0.383 0.377 0.517 0.525 位点 等位基因/基因型 布依族(236例) Pa Pb 汉族(221例) Pa Pb 对照组 高血压组 对照组 高血压组 rs2233678 G 228(97) 233(98) 0.739 0.736 211(99) 223(98) 0.790 0.788 C 6(3) 5(2) 3(1) 5(2) GG 111(95) 114(96) 104(97) 109(96) GC 6(5) 5(4) 3(3) 5(4) Phwe 0.776 0.815 0.883 0.811 rs2233679 C 120(51) 137(58) 0.171 0.269 126(59) 135(59) 0.943 0.566 T 114(49) 101(42) 88(41) 93(41) CC 35(30) 40(34) 38(36) 37(32) CT 50(43) 57(48) 50(47) 61(54) TT 32(27) 22(18) 19(18) 16(14) Phwe 0.117 0.831 0.717 0.250 注:Phwe:Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验P值;a:等位基因P值;b:基因型P值。 表 3 rs2233679遗传模式分析
Table 3. Genetic pattern analysis of rs2233679
频次(%) SNP 遗传模式 基因型 对照组
(335例)高血压组
(343例)OR(95%CI) P 调整OR(95%CI)a P rs2233679 共显性 CC 110(33) 115(33) 1 1 CT 157(47) 174(51) 1.06(0.755~1.488) 0.736 0.985(0.690~1.406) 0.932 TT 68(20) 54(16) 0.760(0.488~1.183) 0.223 0.703(0.442~1.119) 0.137 显性 CC 110(33) 115(33) 1 1 CT-TT 225(67) 228(67) 0.969(0.704~1.334) 0.848 0.898(0.642~1.257) 0.532 隐性 CC-CT 267(80) 289(84) 1 1 TT 68(20) 54(16) 0.734(0.495~1.088) 0.123 0.710(0.469~1.074) 0.105 超显性 CC-TT 178(53) 169(49) 1 1 CT 157(47) 174(51) 1.167(0.864~1.578) 0.314 1.113(0.811~1.528) 0.508 加性 — — — 0.898(0.724~1.114) 0.329 0.860(0.686~1.078) 0.190 a:调整年龄、性别、BMI。 表 4 贵州人群高血压组与对照组的单倍型关联分析
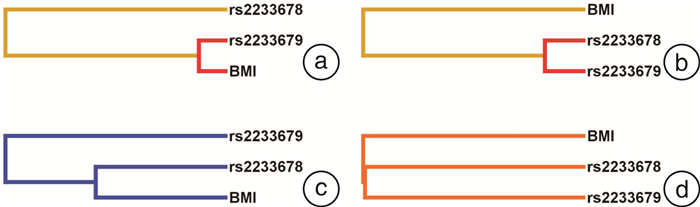
Table 4. Haplotype association analysis between hypertension group and control group in Guizhou populations
频次(%) 民族 单倍型a 对照组 高血压组 χ2 OR(95%CI) P 总人群(678例) GC 365(54) 390(57) 1 GT 293(44) 282(41) 0.891 1.110(0.894~1.379) 0.345 苗族(221例) GC 129(58) 128(58) 1 GT 90(41) 88(40) 0.006 1.015(0.692~1.487) 0.940 布依族(236例) GC 114(49) 132(55) 1 GT 114(49) 101(42) 2.049 1.307(0.906~1.886) 0.152 汉族(221例) GC 123(57) 130(57) 1 GT 88(41) 93(41) 0.000 1.000(0.683~1.465) 1.000 a:单倍型SNP组合:rs2233678-rs2233679,频率 < 0.03的单倍型不纳入分析。 表 5 SNP与BMI对于高血压影响的交互分析
Table 5. Interaction analysis of SNP and BMI on hypertension
民族 Locus No. Model 训练平衡准确度 测试平衡准确度 交叉验证一致性 χ2 Pa 总人群 1 BMI 0.540 0.534 10/10 4.414 0.036 2 rs2233679,BMI 0.553 0.514 10/10 7.938 0.005 3 rs2233678,rs2233679,BMI 0.558 0.527 10/10 9.328 0.002 苗族 1 BMI 0.539 0.529 10/10 1.307 0.253 2 rs2233679,BMI 0.584 0.502 10/10 5.624 0.018 3 rs2233678,rs2233679,BMI 0.585 0.484 10/10 5.624 0.018 布依族 1 rs2233679 0.546 0.499 7/10 2.626 0.105 2 rs2233678,rs2233679 0.572 0.495 5/10 5.323 0.021 3 rs2233678,rs2233679,BMI 0.602 0.560 10/10 9.441 0.002 汉族 1 BMI 0.551 0.446 6/10 2.029 0.154 2 rs2233679,BMI 0.561 0.418 9/10 2.794 0.095 3 rs2233678,rs2233679,BMI 0.565 0.412 10/10 3.377 0.066 注:训练/测试平衡准确度表示训练集和测试集的准确率,用于评估交互模型的预测误差,范围为0~1,数值越大,准确率越高;交叉验证一致性表示十重交叉验证,比较同一个因子组合被确定的次数,并得到相应的训练/测试平衡准确度;a:置换检验P值,P < 0.05表示模型具有统计学意义;N/10表示10次交叉验证中有N次该结果都显著。 表 6 贵州人群与南方汉族等位基因频率的比较
Table 6. Comparison of allele frequencies between Guizhou populations and southern Han population
频次(%) 位点 等位基因 南方汉族a 苗族对照 布依族对照 汉族对照 Pb Pb Pb Pc Pd Pe rs2233678 G 203(97) 219(99) 228(97) 211(99) 0.294 0.631 0.322 0.553 1.000 0.590 C 7(3) 3(1) 6(3) 3(1) rs2233679 C 125(60) 131(59) 120(51) 126(59) 0.913 0.081 0.892 0.097 0.978 0.107 T 85(40) 91(41) 114(49) 88(41) a:数据来自Ensemble数据库;b:苗族、布依族、汉族分别与南方汉族比较;c:苗族与布依族比较;d:苗族与贵州汉族比较;e:布依族与贵州汉族比较。 -
[1] 白梦坡, 穆耶赛尔·麦麦提明, 刘惠娟, 等. 原发性高血压患者亚临床甲状腺功能减退与中心动脉压相关指标及脉搏波速度之间的关系[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(4): 318-322. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.04.013
[2] 张梅, 吴静, 张笑, 等. 2018年中国成年居民高血压患病与控制状况研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(10): 1780-1789.
[3] Wang Z, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al. Status of hypertension in china: results from the china hypertension survey, 2012-2015[J]. Circulation, 2018, 137(22): 2344-2356. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032380
[4] Padmanabhan S, Dominiczak AF. Genomics of hypertension: the road to precision medicine[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2021, 18(4): 235-250. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00466-4
[5] Tanira MO, Al Balushi KA. Genetic variations related to hypertension: a review[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2005, 19(1): 7-19. doi: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1001780
[6] 张雪, 吕磊, 王鹏, 等. 肽基脯氨酰异构酶Pin1在动脉粥样硬化的血管平滑肌细胞衰老中的作用[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2018, 34(21): 3585-3588. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2018.21.023
[7] Chiasson VL, Munshi N, Chatterjee P, et al. Pin1 deficiency causes endothelial dysfunction and hypertension[J]. Hypertension, 2011, 58(3): 431-438. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.172338
[8] Wang JZ, Zhang YH, Bai J, et al. A preliminary identification of PIN1 SNP linkage in patients with coronary heart disease from Handan, China[J]. Rev Port Cardiol(Engl Ed), 2021, 40(2): 133-139. doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2020.05.015
[9] Wang JZ, Du WT, Bai J, et al. The association of rs2233679 in the PIN1 gene promoter with the risk of coronary artery disease in Chinese female individuals[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2020, 29(8): 104935. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104935
[10] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2021概要[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2022, 22(4): 20-36, 40.
[11] 王继光. 高血压数字平台和数字疗法[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(8): 606-609. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.08.002
[12] Faconti L, McNally RJ, Farukh B, et al. Differences in hypertension phenotypes between Africans and Europeans: role of environment[J]. J Hypertens, 2020, 38(7): 1278-1285. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002403
[13] 许桂香. 浅谈贵州苗族传统饮食文化[J]. 凯里学院学报, 2009, 27(5): 8-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDNS200905004.htm
[14] Coppel RL. Repeat structures in a Plasmodium falciparum protein(MESA)that binds human erythrocyte protein 4.1[J]. Mol Bio Parasitol, 1992, 50(2): 335-347. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90231-8
[15] Liou YC, Zhou XZ, Lu KP. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a molecular switch to determine the fate of phosphoproteins[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2011, 36(10): 501-514. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.07.001
[16] Lu KP, Zhou XZ. The prolyl isomerase PIN1: a pivotal new twist in phosphorylation signalling and disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 8(11): 904-916.
[17] Liu M, Yu P, Jiang H, et al. The essential role of pin1 via NF-κB signaling in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-)Mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(3): 100.
[18] Kurakula K, Hagdorn Q, van der Feen DE, et al. Inhibition of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 improves endothelial function and attenuates vascular remodelling in pulmonary hypertension by inhibiting TGF-β signalling[J]. Angiogenesis, 2022, 25(1): 99-112. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09812-7
[19] Paneni F, Costantino S, Castello L, et al. Targeting prolyl-isomerase Pin1 prevents mitochondrial oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction: insights in patients with diabetes[J]. Eur Heart J, 2015, 36(13): 817-828.
[20] 高帅, 杜占慧, 刘盼盼, 等. 脯氨酰顺反异构酶1及其抑制剂对大鼠肺动脉高压的影响及其机制[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2022, 39(3): 480-483.
[21] Albert PR. What is a functional genetic polymorphism? Defining classes of functionality[J]. J Psychiatry Neurosci, 2011, 36(6): 363-365.
[22] Qiu JJ, Yang RZ, Tang YJ, et al. BRD4 and PIN1 gene polymorphisms are associated with high pulse pressure risk in a southeastern Chinese population[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2020, 20(1): 475.
[23] Stanfill AG, Starlard-Davenport A. Primer in genetics and genomics, article 7-multifactorial concepts: gene-gene interactions[J]. Biol Res Nurs, 2018, 20(3): 359-364.
[24] Lee NY, Choi HK, Shim JH, et al. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 interacts with a ribosomal protein S6 kinase to enhance insulin-induced AP-1 activity and cellular transformation[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2009, 30(4): 671-681. https://academic.oup.com/carcin/article/30/4/671/2476794
[25] Rosen ED, Macdougald OA. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio, 2006, 7(12): 885-896. https://www.nature.com/articles/nrm2066
[26] Bhan V, Yan RT, Leiter LA, et al. Relation between obesity and the attainment of optimal blood pressure and lipid targets in high vascular risk outpatients[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2010, 106(9): 1270-1276. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002914910013755
[27] Zhang LN, Ji LD, Fei LJ, et al. Association between polymorphisms of alpha-adducin gene and essential hypertension in Chinese population[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013: 451094.
[28] 喻艳琴, 谢姣姣, 刁晓艳, 等. MTHFR基因rs1801133位点多态性与贵州苗族和布依族及汉族人群原发性高血压的关系[J]. 贵州医科大学学报, 2020, 45(3): 270-276, 280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYYB202003005.htm
-




 下载:
下载: