Efficacy of drug-coated balloon in the treatment of coronary small vessel disease: a meta-analysis
-
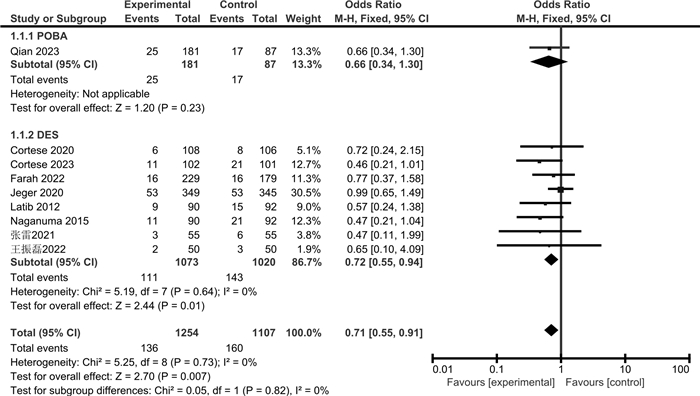
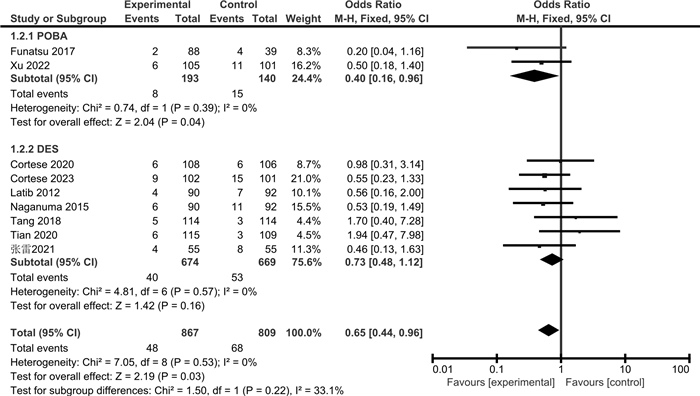
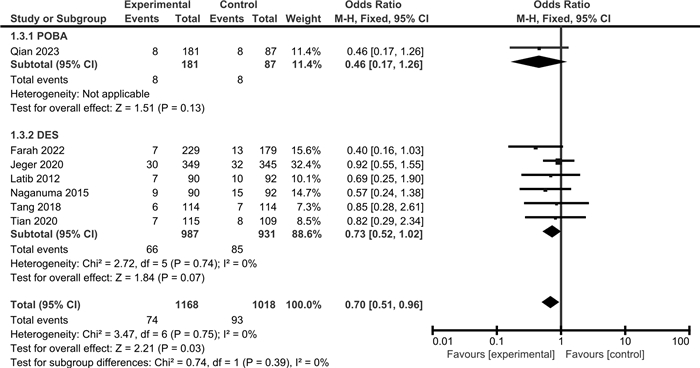
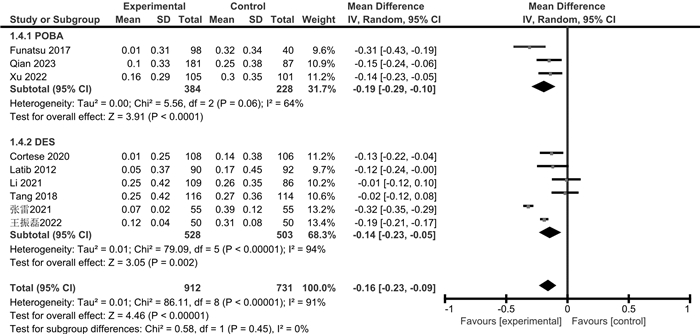
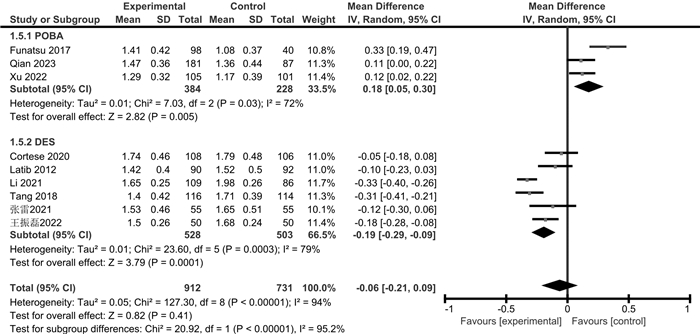
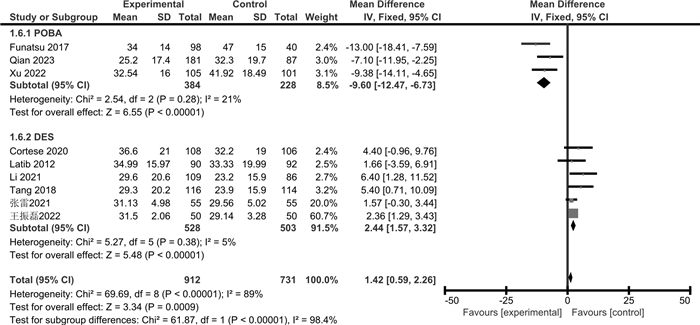
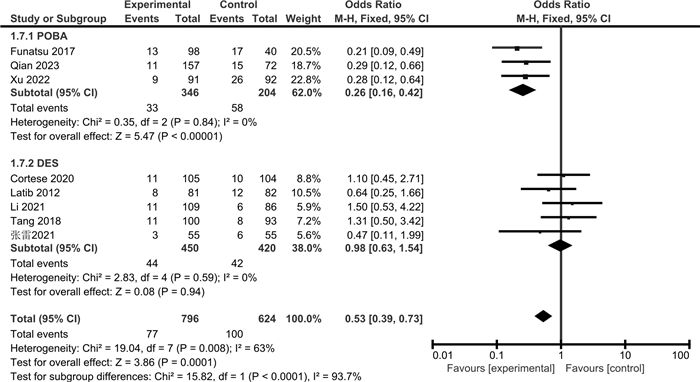
摘要: 目的 通过meta分析评价药物涂层球囊(DCB)与普通球囊血管成形术(POBA)或药物洗脱支架(DES)对冠状动脉小血管原发病变(SVD)的治疗效果。方法 检索Cochrane Library、PubMed、Web of Science、Embase、CBM、中国知网、万方、维普数据库,检索时限为建库至2023年4月。采用RevMan 5.3和Stata 15.1软件进行meta分析和发表偏倚检验,根据不同的对照措施分亚组进行分析。结果 共纳入14篇RCT,包括3 354例患者。Meta分析显示,与POBA相比,DCB可降低SVD患者的靶病变血运重建(TLR)和再狭窄(BR)发生率,减少晚期管腔丢失(LLL)和管腔直径狭窄度(DS),增加最小管腔直径(MLD);但对主要不良心血管事件(MACE)和靶血管血运重建(TVR)发生率的影响,差异无统计学意义。与DES相比,DCB可降低SVD患者的MACE发生率,减少LLL和MLD,增加DS;但对TLR、TVR和BR发生率的影响,差异无统计学意义。结论 与POBA和DES相比,DCB可在一定程度上改善SVD患者的预后,减少LLL,但仍需纳入更多大样本、高质量的RCT来验证其对其他结局指标的影响。
-
关键词:
- 药物涂层球囊 /
- 冠状动脉小血管原发病变 /
- 疗效 /
- meta分析
Abstract: Objective To evaluate the therapeutic effects of the drug-coated balloon(DCB), plain balloon angioplasty(POBA) and drug-eluting stent(DES) on coronary small vessel disease(SVD) by meta-analysis.Methods The Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, CBM, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP databases were searched from inception to April 2023. Meta-analysis and publication bias test were performed by RevMan 5.3 and Stata 15.1 software, and subgroup analysis was performed according to different control measures.Results A total of 14 RCTs involving 3 354 patients were included. Meta-analysis showed that compared with POBA, DCB reduced the incidence of target lesion revascularization(TLR) and restenosis(BR) in SVD patients, simultaneously reduced late lumen loss(LLL) and diameter stenosis(DS), and increased minimum lumen diameter(MLD), but there was no significant difference in the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events(MACE) and target vessel revascularization(TVR). Compared with DES, DCB reduced MACE, LLL, MLD, and increased DS in patients with SVD, but there was no significant difference in TLR, TVR, and BR.Conclusion Compared with POBA and DES, DCB can improve the prognosis of SVD patients to a certain extent and reduce the LLL, but more large-sample and high-quality RCTs are still needed to verify the clinical efficacy of other outcome indicators.-
Key words:
- drug-coated balloon /
- coronary small vessel disease /
- efficacy /
- meta-analysis
-

-
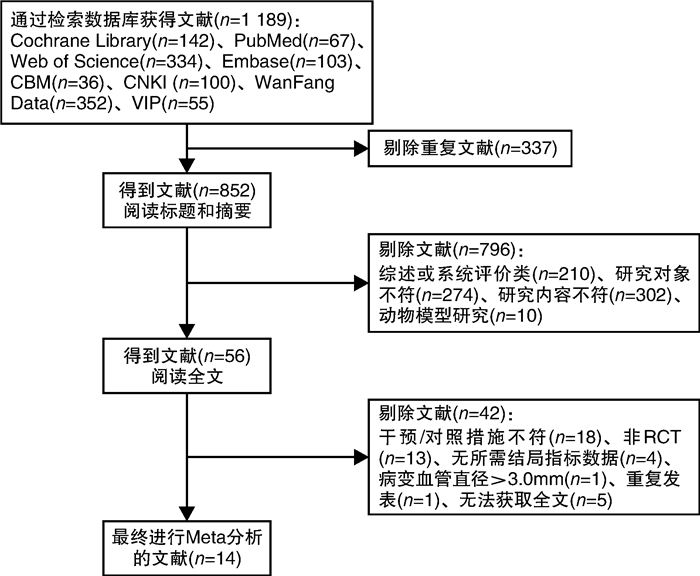
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 1. Basic characteristics of included studies
纳入研究 国家 研究类型 平均年龄
(T/C)/岁平均RVD
(T/C)/mm样本量
(T/C)/例干预措施
(T/C)造影/临床
随访/月结局指标 Qian 2023[10] 中国 多中心RCT 63.8/63.3 2.03/2.09 181/87 PCB/POBA 9/12 ①③④⑤⑥⑦ Cortese 2023[11] 意大利 多中心RCT 64/66 2.0~2.75/
2.0~2.75102/101 PCB/DES -/36 ①② Xu 2022[12] 中国 多中心RCT 61.3/61.6 1.99/2.05 105/101 PCB/POBA 9/12 ②④⑤⑥⑦ Farah 2022[13] 瑞士、德国
和奥地利多中心RCT 67.5/67.5 2.0~2.75/
2.0~2.75229/179 PCB/DES 12/12 ①③ 王振磊2022[14] 中国 RCT 65.6/65.5 - 50/50 PCB/DES 6/6 ①④⑤⑥ 张雷2021[15] 中国 RCT 68.9/69.1 - 55/55 PCB/DES 6/9 ①②④⑤⑥⑦ Li 2021[16] 中国 多中心RCT 59.9/59.9 2.11/2.17 109/86 PCB/DES 9/9 ④⑤⑥⑦ Cortese 2020[17] 意大利 多中心RCT 64/66 2.23/2.18 108/106 PCB/DES 6/12 ①②④⑤⑥⑦ Tian 2020[18] 中国 多中心RCT 60.1/60.5 2.42/2.42 115/109 PCB/DES -/24 ②③ Jeger 2020[19] 德国、瑞士
和奥地利多中心RCT 67.2/68.4 2~3/2~3 349/345 PCB/DES -/36 ①③ Tang 2018[20] 中国 多中心RCT 60.1/60.5 2.11/2.21 116/114 PCB/DES 9/12 ②③④⑤⑥⑦ Funatsu 2017[21] 日本 多中心RCT 68/69 2.0~2.75/
2.0~2.7598/40 PCB/POBA 6/6 ②④⑤⑥⑦ Naganuma 2015[22] 意大利 多中心RCT 64.8/66.4 2.41/2.41 90/92 PEB/PES 12/12 ①②③ Latib 2012[23] 意大利 多中心RCT 64.8/66.4 2.41/2.41 90/92 PEB/PES 6/6 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦ 注:T为试验组,C为对照组;RVD为参考血管直径;PCB为紫杉醇涂层球囊,POBA为普通球囊血管成形术,PEB为紫杉醇洗脱球囊,PES为紫杉醇洗脱支架;结局指标中,①为MACE,②为TLR,③为TVR,④为LLL,⑤为MLD,⑥为DS,⑦为BR。 表 2 纳入研究的偏倚风险评价结果
Table 2. Bias risk assessment results for included studies
纳入研究 随机方法 盲法 分配隐藏 结果数据的完整性 选择性报告研究结果 其他偏倚来源 总体偏倚风险 Qian 2023[10] 计算机随机 单盲 采用IWRS进行随机化并根据其发送的分组信息对患者进行相应治疗 有失访,ITT分析 无 不清楚 低风险 Cortese 2023[11] 不清楚 单盲 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 不清楚 Xu 2022[12] 计算机随机 单盲 患者和治疗医生知道
分组分配,结果评估者
对分配方案不知情有失访 无 不清楚 低风险 Farah 2022[13] 计算机随机 双盲 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 低风险 王振磊2022[14] 不清楚 不清楚 不清楚 无失访 无 不清楚 不清楚 张雷2021[15] 不清楚 不清楚 不清楚 无失访 无 不清楚 不清楚 Li 2021[16] 不清楚 不清楚 不清楚 有失访,ITT分析 无 不清楚 不清楚 Cortese 2020[17] 计算机随机 不清楚 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 低风险 Tian 2020[18] 不清楚 单盲 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 不清楚 Jeger 2020[19] 计算机随机 单盲 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 低风险 Tang 2018[20] 计算机随机 单盲 不清楚 有失访,ITT分析 无 不清楚 低风险 Funatsu 2017[21] 计算机随机 不清楚 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 低风险 Naganuma 2015[22] 不清楚 单盲 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 不清楚 Latib 2012[23] 不清楚 单盲 不清楚 有失访 无 不清楚 不清楚 注:IWRS为交互式Web响应系统。 -
[1] Wybraniec MT, Banka P, Bochenek T, et al. Small vessel coronary artery disease: How small can we go with myocardial revascularization?[J]. Cardiol J, 2021, 28(5): 767-778. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0127
[2] 汪志新, 孟宪亮, 张林. 药物涂层球囊在冠状动脉小血管病变中的应用[J]. 国际心血管病杂志, 2023, 50(01): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWXX202301001.htm
[3] Unverdorben M, Vallbracht C, Cremers B, et al. Paclitaxel-coated balloon catheter versus paclitaxel-coated stent for the treatment of coronary in-stent restenosis: the three-year results of the PEPCAD Ⅱ ISR study[J]. EuroIntervention, 2015, 11(8): 926-934. doi: 10.4244/EIJY14M08_12
[4] 韩芳旗, 卫聪颖, 陈斌. 血管内超声指导药物涂层球囊治疗冠状动脉小血管原发开口病变的疗效观察[J]. 海南医学, 2022, 33(21): 2737-2740. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2022.21.005
[5] 王雪娜, 张佩生, 梁雪, 等. 药物涂层球囊治疗糖尿病患者冠状动脉大血管原位病变的疗效与安全性分析[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(03): 181-185. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.03.004
[6] 刘蓉, 乔树宾, 崔锦刚, 等. 药物涂层球囊治疗冠状动脉大血管原发病变的有效性和安全性分析[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2022, 37(08): 800-803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXH202208004.htm
[7] 陈韵岱, 王建安, 刘斌, 等. 药物涂层球囊临床应用中国专家共识[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2016, 24(02): 61-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJXB201602001.htm
[8] Ma WR, Chandrasekharan KH, Nai CS, et al. Clinical outcomes of percutaneous coronary intervention for de novo lesions in small coronary arteries: A systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 1017833. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1017833
[9] 汪洋. Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具简介[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(11): 1322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX201911019.htm
[10] Qian J, Wu Y, Li C, et al. Drug-coated balloon for the treatment of small vessel disease: 9 months of angiographic results and 12 months of clinical outcomes of the PEPCAD China SVD study[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2023, 101(1): 33-43. doi: 10.1002/ccd.30472
[11] Cortese B, Testa G, Rivero F, et al. Long-Term Outcome of Drug-Coated Balloon vs Drug-Eluting Stent for Small Coronary Vessels: PICCOLETO-Ⅱ 3-Year Follow-Up[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2023, 16(9): 1054-1061. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2023.02.011
[12] Xu K, Fu G, Tong Q, et al. Biolimus-Coated Balloon in Small-Vessel Coronary Artery Disease: The BIO-RISE CHINA Study[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2022, 15(12): 1219-1226. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2022.03.024
[13] Farah A, Elgarhy M, Ohlow MA, et al. Efficacy and safety of drug-coated balloons according to coronary vessel size. A report from the BASKET-SMALL 2 trial[J]. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej, 2022, 18(2): 122-130.
[14] 王振磊, 丁赫, 许群锋. 药物涂层球囊和药物洗脱支架治疗冠状动脉小血管原发病变的疗效观察[J]. 贵州医药, 2022, 46(6): 949-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZYI202206061.htm
[15] 张雷, 李娜, 许俊杰, 等. 药物涂层球囊和药物洗脱支架治疗冠状动脉小血管原发病变中远期疗效的对比研究[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(20): 3561-3564. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202120029.htm
[16] Li L, Guan C, Meng S, et al. Short-and long-term functional results following drug-coated balloons versus drug-eluting stents in small coronary vessels: The RESTORE quantitative flow ratio study[J]. Intern J Cardiol, 2021, 327: 45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.11.035
[17] Cortese B, Palma G, Guimaraes MG, et al. Drug-Coated Balloon Versus Drug-Eluting Stent for Small Coronary Vessel Disease: PICCOLETO Ⅱ Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2020, 13(24): 2840-2849. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2020.08.035
[18] Tian J, Tang YD, Qiao S, et al. Two-year follow-up of a randomized multicenter study comparing a drug-coated balloon with a drug-eluting stent in native small coronary vessels: The RESTORE Small Vessel Disease China trial[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2020, 95 Suppl 1: 587-597.
[19] Jeger RV, Farah A, Ohlow MA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of drug-coated balloons versus drug-eluting stents for small coronary artery disease(BASKET-SMALL 2): 3-year follow-up of a randomised, non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10261): 1504-1510.
[20] Tang Y, Qiao S, Tian J, et al. Drug-Coated Balloon Versus Drug-Eluting Stent for Small-Vessel Disease: The RESTORE SVD China Randomized Trial[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2018, 11(23): 2381-2392.
[21] Funatsu A, Nakamura S, Inoue N, et al. A multicenter randomized comparison of paclitaxel-coated balloon with plain balloon angioplasty in patients with small vessel disease[J]. Clin Res Cardiol, 2017, 106(10): 824-832.
[22] Naganuma T, Latib A, Sgueglia GA, et al. A 2-year follow-up of a randomized multicenter study comparing a paclitaxel drug-eluting balloon with a paclitaxel-eluting stent in small coronary vessels the BELLO study[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2015, 184: 17-21.
[23] Latib A, Colombo A, Castriota F, et al. A randomized multicenter study comparing a paclitaxel drug-eluting balloon with a paclitaxel-eluting stent in small coronary vessels: the BELLO(Balloon Elution and Late Loss Optimization)study[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2012, 60(24): 2473-2480.
[24] 齐苗苗, 王琼英, 孙润民, 等. 药物涂层球囊与药物洗脱支架治疗冠状动脉小血管病变的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2021, 13(05): 527-531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZXX202105005.htm
[25] Sanz SJ, Chiarito M, Cortese B, et al. Drug-Coated balloons vs drug-eluting stents for the treatment of small coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis of randomized trials[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2021, 98(1): 66-75.
[26] Neumann FJ, Sousauva M, Ahlsson A, et al. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(2): 87-165.
[27] Li QY, Chang MY, Wang XY, et al. Efficacy and safety of drug-coated balloon in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 6552.
[28] 宋婷婷, 陈韬, 荆晶, 等. 药物涂层球囊在经皮冠状动脉介入治疗中的应用趋势——单中心5年数据分析[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2021, 29(11): 612-616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJXB202111004.htm
[29] 李逸臻, 贾永平, 吴磊, 等. 药物涂层球囊治疗原发冠状动脉小血管病变的临床疗效观察[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(12): 2067-2070. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202112024.htm
[30] 王亚玲, 饶明月, 郭安君, 等. 药物球囊治疗冠状动脉小血管病变的效果和不良反应观察[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2022, 43(5): 517-520.
[31] Arslani K, Jeger R. Drug-coated Balloons for Small Coronary Disease-A Literature Review[J]. Curr Cardiol Rep, 2021, 23(11): 173.
[32] Yeh RW, Bachinsky W, Stoler R, et al. Rationale and design of a randomized study comparing the agent drug coated balloon to plain old balloon angioplasty in patients with In-stent restenosis[J]. Am Heart J, 2021, 241: 101-107.
-




 下载:
下载: