VA-ECMO support for respiratory failure and right ventricular failure after left ventricular assist device implantation: a case report
-
摘要: 左心室辅助装置(left ventricular assist device,LVAD)的植入是目前治疗终末期心力衰竭的重要方法之一。LVAD植入后常见的并发症包括右心室衰竭(right ventricular failure,RVF)、出血、感染和脑血管意外等。即使经过严格的术前评估,RVF也可能难以预测。而LVAD植入术后出现需要体外膜肺氧合(extracorporeal membrane oxygenation,ECMO)的严重呼吸衰竭则报道更少。静脉-动脉ECMO(VA-ECMO)可以让肺部和右心室都得到充分的休息,但需注意和LVAD血流的竞争。本文介绍1例LVAD植入后出现急性呼吸衰竭及右心室衰竭患者接受VA-ECMO治疗的经验。Abstract: Implantation of left ventricular assist device(LVAD) is currently one of the important methods in the treatment of end-stage heart failure. Common complications following LVAD implantation include right ventricular failure(RVF), hemorrhage, infection, and cerebrovascular accident. Although patients have undergone rigorous preoperative evaluation, RVF can be difficult to predict. Severe respiratory failure requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation(ECMO) after LVAD implantation was less reported. Veno-arterial ECMO(VA-ECMO) can allow both the lung and the right ventricle to get a rest, but attention should be paid to the competition of blood flow between ECMO and LVAD. We report the experience of VA-ECMO therapy in one patient with acute respiratory failure and RVF after LVAD implantation.
-

-
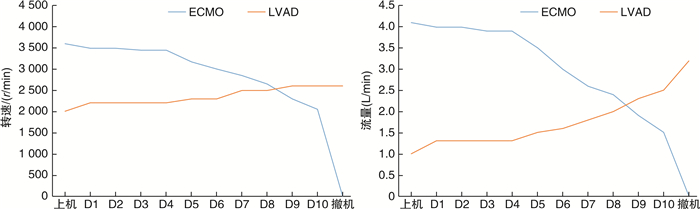
表 1 ECMO上机前和撤机后的临床参数
Table 1. Clinical parameters before and after ECMO
参数 上机前 撤机后 血压/mmHg 40/30 105/84 CVP/cmH2O 34 9 PAP/mmHg 53/20 48/24 PaO2/mmHg 45 80 Lac/(mmol/L) 14.6 1.1 LVEF/% 18 36 RVFAC/% 15 38 TAPSE/cm 0.4 1.0 ALT/(U/L) 61 9 AST/(U/L) 431 27 PaO2:动脉血氧分压;Lac:乳酸。 -
[1] Miller PE, Caraballo C, Ravindra NG, et al. Clinical Implications of Respiratory Failure in Patients Receiving Durable Left Ventricular Assist Devices for End-Stage Heart Failure[J]. Circ Heart Fail, 2019, 12(11): e006369. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.119.006369
[2] Piffard M, Coniat NL, Simon O, et al. Independent risk factors for ICU mortality after left ventricular assist device implantation[J]. Artificial Organs, 2020, 44(2): 153-161. doi: 10.1111/aor.13540
[3] Copeland H, Westfall S, Morton J, et al. Successful recovery with venovenous ECMO for ARDS after LVAD HeartMate 3 implantation: A case report[J]. J Card Surg, 2022, 37(8): 2450-2452. doi: 10.1111/jocs.16624
[4] Ali HR, Kiernan MS, Choudhary G, et al. Right Ventricular Failure Post-Implantation of Left Ventricular Assist Device: Prevalence, Pathophysiology, and Predictors[J]. ASAIO J, 2020, 66(6): 610-619. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001088
[5] Turner KR. Right Ventricular Failure After Left Ventricular Assist Device Placement-The Beginning of the End or Just Another Challenge?[J]. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth, 2019, 33(4): 1105-1121. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2018.07.047
[6] Frankfurter C, Molinero M, Vishram-Nielsen J, et al. Predicting the Risk of Right Ventricular Failure in Patients Undergoing Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation: A Systematic Review[J]. Circ Heart Fail, 2020, 13(10): e006994.
[7] Wang TS, Cevasco M, Birati EY, et al. Predicting, Recognizing, and Treating Right Heart Failure in Patients Undergoing Durable LVAD Therapy[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(11): 2984. doi: 10.3390/jcm11112984
[8] Kawabori M, Nordan T, Kapur NK, et al. Protect right: right ventricular failure prevention strategy for left ventricular assist device implantation[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2021, 59(5): 1128-1130. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezaa400
[9] Lo Coco V, De Piero ME, Massimi G, et al. Right ventricular failure after left ventricular assist device implantation: a review of the literature[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2021, 13(2): 1256-1269. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2228
[10] Lamba HK, Kim M, Santiago A, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation as a bridge to durable left ventricular assist device implantation in INTERMACS-1 patients[J]. J Artif Organs, 2022, 25(1): 16-23. doi: 10.1007/s10047-021-01275-3
-




 下载:
下载: