The predictive value of left atrial and pulmonary vein morphological characteristics for early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency ablation
-
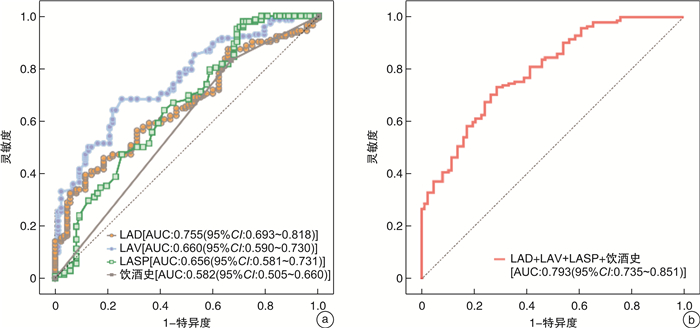
摘要: 目的 基于左心房和肺静脉CT血管成像(CT angiography,CTA)评估左心房和肺静脉形态学特征与射频消融术后心房颤动(房颤)早期复发的临床相关性。方法 回顾性分析我院2018年8月—2022年10月首次行射频消融术的患者,测量相关影像形态学参数,并于初始治疗后定期规律随访。收集患者临床资料,依据术后3个月内随访结果,将患者分为复发组和未复发组,对比分析两组患者临床及影像资料。采用logistic回归分析房颤复发的危险因素。采用受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线验证危险因素的预测价值。结果 共纳入229例患者,其中复发组87例,未复发组142例。未复发组与复发组患者左心房横径[LAD:(3.72±0.55)cm vs (4.37±0.82)cm,P<0.001]、左心房横径/同层面胸椎椎体横径(LAVD:2.36±0.43 vs 2.83±0.66,P<0.001)、左上肺静脉上下径[LSPV1:(1.97±0.46)cm vs (2.20±0.66)cm,P=0.002]、左心房容积[LAV:(56.07±24.40)cm3 vs (67.48±21.58)cm3,P<0.001]、左心房球度(LASP:0.63±0.05 vs 0.58±0.08,P<0.001),以及饮酒史比例(16.9% vs 33.3%,P=0.004)均差异有统计学意义。多因素logistic回归分析结果显示,LAD(OR=1.002,95%CI:1.000~1.097,P=0.001)、LAV(OR=3.056,95%CI:2.821~3.327,P=0.003)、LASP(OR=1.000,95%CI:1.000~1.001,P=0.010)以及饮酒史(OR=10.392,95%CI:3.068~132.555,P=0.024)为房颤术后早期复发的独立危险因素。ROC曲线分析结果显示,LAD、LAV、LASP、饮酒史联合预测房颤射频消融术后早期复发的曲线下面积为0.793(95%CI:0.735~0.851,P<0.001),灵敏度为70.42%,特异度为73.56%。结论 左心房相关CTA指标LAD、LAV、LASP及饮酒史可有效预测房颤患者射频消融术后早期复发。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the clinical correlation between left atrial and pulmonary vein morphological characteristics evaluate by CT angiography(CTA) and early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation(RFCA).Methods All patients who received the initial RFCA surgery in our hospital from August 2018 to October 2022 were retrospectively reviewed, and their image morphological parameters were measured, regular follow-up visits were conducted after the initial treatment. Clinical data were collected. Based on the 3 months' follow-up results after RFCA, patients were divided into the recurrence group and non-recurrence group. Clinical and imaging data of the two groups were compared. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk factors for recurrence of atrial fibrillation. The predictive value was validated by receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curves.Results A total of 229 patients were included, with 87 in the recurrence group and 142 in the non-recurrence group. The left atrial diameter[LAD: (3.72±0.55)cm vs (4.37±0.82)cm, P < 0.001], left atrio-vertebral diameter ratio(LAVD: 2.36±0.43 vs 2.83±0.66, P < 0.001), left superior pulmonary vein diameter[LSPV1: (1.97±0.46)cm vs (2.20±0.66)cm, P=0.002], left atrial volume[LAV: (56.07±24.40)cm3 vs (67.48±21.58)cm3, P < 0.001], left atrial sphericity(LASP: 0.63±0.05 vs 0.58±0.08, P < 0.001), and the proportion of alcohol history(16.9% vs 33.3%, P=0.004) were significantly different between the recurrence group and the non-recurrence group. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that LAD(OR=1.002, 95%CI: 1.000-1.097, P=0.001), LAV(OR=3.056, 95%CI: 2.821-3.327, P=0.003), LASP(OR=1.000, 95%CI: 1.000-1.001, P=0.010), and alcohol history(OR=10.392, 95%CI: 3.068-132.555, P=0.024) were independent risk factors for early postoperative recurrence. The ROC analysis results showed that the area under the curve for predicting early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after RFCA using the multi-factor combination of LAD, LAV, LASP, and alcohol history was 0.793(95%CI: 0.735-0.851, P < 0.001), with a sensitivity of 70.42% and a specificity of 73.56%.Conclusion Left atrium-related CTA indicators LAD, LAV and LASP, as well as alcohol history, may predict the early recurrence of atrial fibrillation patients after RFCA.
-
Key words:
- atrial fibrillation /
- CT angiography /
- radiofrequency catheter ablation
-

-
表 1 两组患者基线资料
Table 1. Baseline data
例(%), X±S 项目 未复发组(142例) 复发组(87例) χ2/t值 P值 男/女/例 99/43 61/26 0.004 0.949 年龄/岁 60.75±10.28 60.80±10.00 0.042 0.967 体重/kg 74.55±11.56 75.26±14.71 0.409 0.683 心率/(次/min) 85.35±24.41 86.24±19.11 0.292 0.771 阵发性房颤/持续性房颤 72/70 35/52 2.378 0.123 碎裂电位消融 20(14.08) 16(18.39) 0.755 0.385 高血压 60(42.3) 47(54.0) 3.002 0.083 糖尿病 20(14.1) 10(11.5) 0.318 0.573 吸烟史 37(26.1) 23(26.4) 0.004 0.949 饮酒史 24(16.9) 29(33.3) 8.189 0.004 血红蛋白/(g/L) 143.68±17.43 143.24±16.41 -0.187 0.852 尿素/(mmol/L) 5.67±1.38 5.96±2.13 1.223 0.223 肌酐/(μmmol/L) 68.13±13.24 69.56±18.42 0.681 0.496 尿酸/(μmmol/L) 328.48±81.53 343.49±101.48 1.231 0.220 谷氨酰转肽酶/(U/L) 39.24±33.95 40.69±28.87 0.332 0.740 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 1.12±0.30 1.16±0.23 1.003 0.317 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 2.50±0.79 2.62±0.85 1.128 0.260 NT-proBNP/(pg/mL) 613.77±725.96 615.97±572.54 0.024 0.981 CHA2DS2-VASc评分 1.78±1.61 2.21±1.64 1.930 0.055 HAS-BLED评分 1.42±1.24 1.60±1.14 1.071 0.285 NT-proBNP:氨基末端脑钠肽前体;CHA2DS2-VASc评分:非瓣膜性房颤脑卒中危险因素评分;HAS-BLED评分:出血风险评估评分。 表 2 两组患者影像学测量参数比较
Table 2. Imaging parameters
X±S 项目 未复发组(142例) 复发组(87例) t值 P值 LAD/cm 3.72±0.55 4.37±0.82 7.064 <0.001 VD/cm 1.60±0.19 1.57±0.18 -1.1676 0.244 LAVD 2.36±0.43 2.83±0.66 6.561 <0.001 LSPV1/cm 1.97±0.46 2.20±0.66 3.182 0.002 LSPV2/cm 1.49±0.45 1.37±0.44 -1.997 0.051 LSPV3/cm2 2.38±1.09 2.23±0.93 -1.023 0.307 LIPV1/cm 1.55±0.32 1.55±0.33 -0.099 0.921 LIPV2/cm 1.03±0.32 1.04±0.29 0.267 0.790 LIPV3/cm2 1.29±0.62 1.27±0.44 -0.248 0.805 RSPV1/cm 1.93±0.43 1.95±0.41 0.317 0.752 RSPV2/cm 1.64±0.38 1.60±0.35 -0.641 0.522 RSPV3/cm2 2.77±1.11 3.07±0.93 2.143 0.053 RIPV1/cm 1.44±0.43 1.40±0.42 -0.737 0.462 RIPV2/cm 1.29±0.39 1.22±0.35 -1.267 0.206 RIPV3/cm2 1.63±0.87 1.45±0.81 -1.551 0.122 LA1/cm 6.25±1.09 6.25±0.94 -0.007 0.995 LA2/cm 4.41±0.78 4.69±0.74 2.693 0.080 LAV/cm3 56.07±24.40 67.48±21.58 3.585 <0.001 LASP 0.63±0.05 0.58±0.08 -4.995 <0.001 LSPV1:左上肺静脉上下径;LSPV2:左上肺静脉前后径;LSPV3:左上肺静脉面积;LIPV1:左下肺静脉上下径;LIPV2:左下肺静脉前后径;LIPV3:左下肺静脉面积;RSPV1:右上肺静脉上下径;RSPV2:右上肺静脉前后径;RSPV3:右上肺静脉面积;RIPV1:右下肺静脉上下径;RIPV2:右下肺静脉前后径;RIPV3:右下肺静脉面积;LA1:左心房上下径;LA2:左心房前后径。 表 3 房颤患者术后早期复发的多因素logistic回归分析
Table 3. Risk factors of early postoperative recurrence analyzed by multivariate logistic regression analysis
变量 B值 S.E. Waldχ2值 P值 OR值 95%CI LAD -6.125 1.911 10.271 0.001 1.002 1.000~1.097 LAVD -0.762 0.477 2.549 0.110 1.595 1.201~3.284 LSPV1 -0.498 0.296 2.821 0.093 1.837 1.405~2.965 LAV 0.110 0.038 8.608 0.003 3.056 2.821~3.327 LASP -29.828 11.605 6.606 0.010 1.000 1.000~1.001 饮酒史 0.850 0.376 5.125 0.024 10.392 3.068~132.555 -
[1] Arbelo E, Dagres N. The 2020 ESC atrial fibrillation guidelines for atrial fibrillation catheter ablation, CABANA, and EAST[J]. Europace, 2022, 24(Suppl 2): ⅱ3-ⅱ7.
[2] 王庆亚, 林佳, 张宇祯, 等. 多指标联合评估模型对阵发性心房颤动导管射频消融术后复发的预测价值[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(1): 62-68. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2021.01.013
[3] Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: Executive summary[J]. Europace, 2018, 20(1): 157-208. doi: 10.1093/europace/eux275
[4] Stabile G, Iacopino S, Verlato R, et al. Predictive role of early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after cryoballoon ablation[J]. Europace, 2020, 22(12): 1798-1804. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaa239
[5] Choi JH, Kwon HJ, Kim HR, et al. Electrocardiographic predictors of early recurrence of atrial fibrillation[J]. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol, 2021, 26(6): e12884. doi: 10.1111/anec.12884
[6] 陈玲, 祁荣兴, 刘君. 左心房及肺静脉结构和功能成像预测房颤消融术后复发的研究进展[J]. 放射学实践, 2022, 37(5): 653-657. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202205025.htm
[7] Hopman L, Bhagirath P, Mulder MJ, et al. Left atrial sphericity in relation to atrial strain and strain rate in atrial fibrillation patients[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2023, 39(9): 1753-1763. doi: 10.1007/s10554-023-02866-2
[8] Sohrabi S, Hope M, Saloner D, et al. Left atrial transverse diameter on computed tomography angiography can accurately diagnose left atrial enlargement in patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. J Thorac Imaging, 2015, 30(3): 214-217. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0000000000000132
[9] Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. Corrigendum to: 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery(EACTS)[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(40): 4194. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab648
[10] Cherian TS, Callans DJ. Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation After Radiofrequency Ablation: What to Expect[J]. Card Electrophysiol Clin, 2020, 12(2): 187-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ccep.2020.02.003
[11] Fu K, Zhu X, Chu H, et al. Re-recognize early recurrence of persistent atrial fibrillation[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2023, 10: 1145695. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1145695
[12] Kim YG, Boo KY, Choi JI, et al. Early Recurrence Is Reliable Predictor of Late Recurrence After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2021, 7(3): 343-351. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2020.09.029
[13] Liu M, Li W, Wang H, et al. CTRP9 Ameliorates Atrial Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Vulnerability to Atrial Fibrillation in Post-Myocardial Infarction Rats[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2019, 8(21): e013133. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013133
[14] Montillet M, Baqué-Juston M, Tasu JP, et al. The Left Atrio-Vertebral Ratio: a new simple means for assessing left atrial enlargement on Computed Tomography[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(3): 1310-1317. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5041-3
[15] 王喆, 陈英伟, 董建增. 左心房结构相关指标对心房颤动导管消融术后复发的影响[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2020, 36(9): 786-789. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2020.09.002
[16] Njoku A, Kannabhiran M, Arora R, et al. Left atrial volume predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after radiofrequency ablation: a meta-analysis[J]. Europace, 2018, 20(1): 33-42. doi: 10.1093/europace/eux013
[17] Sanna GD, Moccia E, Canonico ME, et al. Left atrial remodeling in heart failure: the role of sphericity index(the SPHERICAT-HF study)[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2022, 38(8): 1723-1732. doi: 10.1007/s10554-022-02562-7
[18] Labarbera MA, Atta-Fosu T, Feeny AK, et al. New Radiomic Markers of Pulmonary Vein Morphology Associated With Post-Ablation Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation[J]. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med, 2022, 10: 1800209.
[19] Scott L Jr, Li N, Dobrev D. Role of inflammatory signaling in atrial fibrillation[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2019, 287: 195-200.
[20] Vitali F, Serenelli M, Airaksinen J, et al. CHA2DS2-VASc score predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after cardioversion: Systematic review and individual patient pooled meta-analysis[J]. Clin Cardiol, 2019, 42(3): 358-364. doi: 10.1002/clc.23147
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 222
- 施引文献: 0




 下载:
下载: