The prognostic value of left ventricular global function index in patients with acute myocardial infarction
-
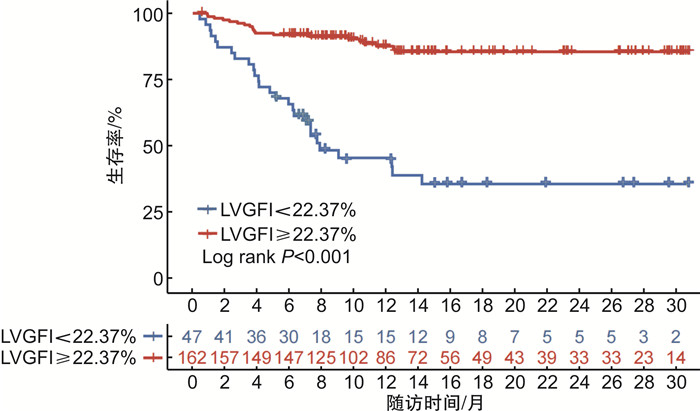
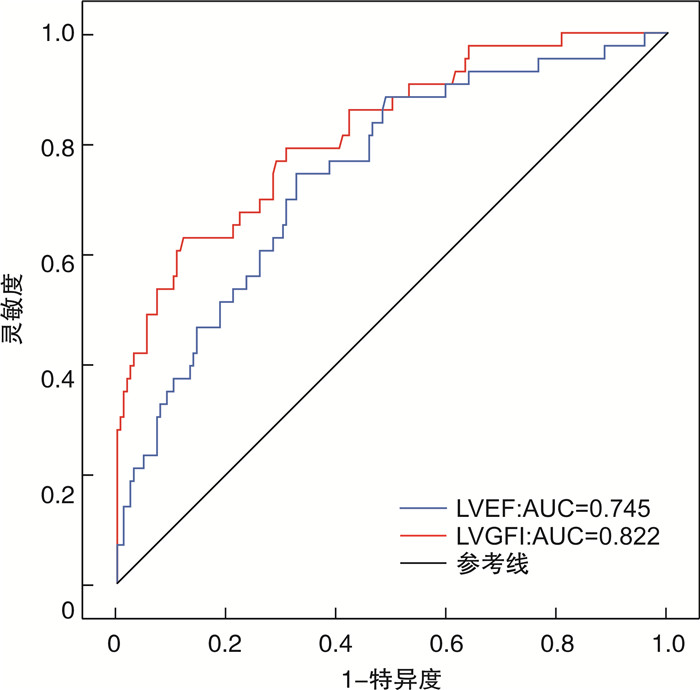
摘要: 目的 探讨左心室整体功能指数(LVGFI)对接受经皮冠状动脉介入(PCI)治疗的急性心肌梗死(AMI)患者发生主要不良心血管事件(MACE)的预测价值,并比较其与左心室射血分数(LVEF)的预测效能。方法 回顾性收集2020年12月—2022年6月于我院确诊并行PCI治疗的AMI患者209例,所有患者均在术后48 h内行常规心脏超声,并计算LVGFI。随访PCI术后1年MACE发生情况。采用多因素Cox回归分析评估LVGFI与临床结局的相关性,应用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线比较LVGFI及LVEF对MACE的预测价值。结果 随访期间共有43例(20.6%)患者发生MACE。MACE组LVGFI水平显著低于非MACE组(P < 0.001)。Cox回归分析结果显示,调整混杂因素后LVGFI仍是预测MACE的独立因子(HR=0.796,95%CI:0.642~0.989,P < 0.001)。ROC曲线结果显示,LVGFI和LVEF预测MACE的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.822、0.745,灵敏度分别为88.6%、67.5%,特异度分别为62.8%、74.4%。Kaplan-Meier生存分析表明,LVGFI < 22.37%组患者生存率低于LVGFI≥22.37%组(log rank P < 0.001)。结论 LVGFI是AMI患者PCI术后发生MACE的独立预测因子,且较LVEF表现出更好的预测性能。Abstract: Objective To investigate the predictive value of the left ventricular global function index(LVGFI) for major adverse cardiovascular events(MACE) in patients with acute myocardial infarction(AMI) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention(PCI), and to compare its predictive efficacy with left ventricular ejection fraction(LVEF).Methods Two hundred and nine AMI patients who underwent PCI in our hospital from December 2020 to June 2022 were included. All patients underwent routine cardiac ultrasound within 48 hours after the procedure, and LVGFI values were calculated. The occurrence of MACE within one year after PCI surgery was followed up. The Multiple factor Cox regression analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between LVGFI and clinical outcomes. The receiver working characteristic curve(ROC) was used to analyse the predictive value of LVGFI and LVEF on MACE.Results Forty-three patients(20.6%) occurred MACE during the follow-up period. The LVGFI level in the MACE group was significantly lower than that in the non-MACE group(P < 0.001). Cox regression analysis showed that LVGFI was still an independent factor for predicting MACE(HR=0.796, 95%CI: 0.642-0.989, P < 0.001). The ROC curve analysis showed that the AUC of LVGFI and LVEF in predicting MACE were 0.822 and 0.745, the sensitivities were 88.6% and 67.5%, and the specificities were 62.8% and 74.4%, respectively. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the survival rate of the LVGFI < 22.37% group was lower than that of the LVGFI≥22.37% group (log rank P < 0.001).Conclusion LVGFI is an independent predictor of MACE in AMI patients after PCI, and shows better predictive performance compare with LVEF.
-

-
表 1 非MACE组和MACE组临床资料及超声心动图参数比较
Table 1. Comparison of basic data and echocardiographic parameters between the non-MACE group MACE and MACE group
例(%), X ± S, M(Q1, Q3) 项目 非MACE组(166例) MACE组(43例) P 年龄/岁 62.7±10.9 61.7±13.1 0.588 男性 136(81.9) 40(93.0) 0.123 BMI/(kg/m2) 25.0±3.3 24.4±3.0 0.313 SBP/mmHg 122.7±17.5 118.6±17.1 0.383 DBP/mmHg 73.5±10.3 71.9±12.1 0.463 心率/(次/min) 72.9±11.2 76.2±15.1 0.119 STEMI 66(39.8) 32(74.4) < 0.001 Killip≥2级 17(10.2) 25(58.1) < 0.001 病变血管数≥2支 119(71.7) 35(81.4) 0.198 发病至PCI时间/h 4.8(3.0,10.2) 5.1(3.4,7.2) 0.490 罪犯血管 0.018 左前降支 68(41.0) 26(60.5) 左回旋支 41(24.7) 3(7.0) 右冠脉 57(34.3) 14(32.6) NT-proBNP/(pg/mL) 395.4(158.3,1 118.0) 968.5(382.5,2 325.0) 0.001 cTnI/(ng/mL) 0.6(0.1,2.6) 2.3(0.7,8.3) < 0.001 IVST/mm 1.0(0.9,1.1) 1.1(0.9,1.2) 0.051 LVPWT/mm 0.9±0.1 1.0±0.2 0.072 LVEDV/mL 116.0±27.9 116.4±31.4 0.927 LVESV/mL 44.4(35.3,58.1) 55.6(41.0,70.4) 0.010 LVSV/mL 63.9(56.1,75.4) 55.2(49.0,59.6) < 0.001 LVMI/(g/m2) 93.7±20.4 107.1±40.3 0.041 LVEF/% 57.8±7.6 50.0±9.7 < 0.001 LVGFI/% 26.9±3.7 21.3±4.5 < 0.001 表 2 PCI术后MACE发生影响因素的Cox回归分析
Table 2. Influencing factors of MACE after PCI analyzed by Cox regression analysis
参数 单因素 多因素 HR(95%CI) P HR(95%CI) P STEMI 3.76(1.89~7.46) < 0.001 1.153(0.510~2.608) 0.733 Killip≥2级 7.26(3.94~13.36) < 0.001 2.659(1.229~5.751) 0.013 罪犯血管 0.76(0.53~1.09) 0.132 NT-proBNP 2.44(1.46~4.06) 0.001 0.978(0.756~1.102) 0.225 cTnI 1.08(1.03~1.12) 0.001 1.034(0.983~1.087) 0.197 LVESV 1.02(1.01~1.03) 0.005 0.982(0.926~1.041) 0.534 LVSV 0.95(0.93~0.98) < 0.001 1.007(0.944~1.074) 0.841 LVMI 1.02(1.01~1.02) 0.001 0.999(0.977~1.023) 0.959 LVEF 0.93(0.90~0.95) < 0.001 0.971(0.828~1.140) 0.721 LVGFI 0.78(0.73~0.83) < 0.001 0.796(0.642~0.989) < 0.001 -
[1] Di Chiara A, Clagnan E, Valent F. Epidemiology and mortality in an Italian region after the adoption of the universal definition of myocardial infarction[J]. J Cardiovasc Med(Hagerstown), 2020, 21(1): 34-39. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000893
[2] 徐芳, 徐俊杰, 吴春苑, 等. 左室心肌做功对急性心肌梗死患者急诊PCI术后MACE发生的预测价值[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(12): 960-966. https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1c7u0vk01q3c0cr0263n0p70t7747387&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1
[3] Frantz S, Hundertmark MJ, Schulz-Menger J, et al. Left ventricular remodelling post-myocardial infarction: pathophysiology, imaging, and novel therapies[J]. Eur Heart J, 2022, 43(27): 2549-2561. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac223
[4] Karuzas A, Rumbinaite E, Verikas D, et al. Accuracy of three-dimensional systolic dyssynchrony and sphericity indexes for identifying early left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction[J]. Anatol J Cardiol, 2019, 22(1): 13-20.
[5] Mewton N, Opdahl A, Choi EY, et al. Left ventricular global function index by magnetic resonance imaging--a novel marker for assessment of cardiac performance for the prediction of cardiovascular events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis[J]. Hypertension, 2013, 61(4): 770-778. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.198028
[6] Nwabuo CC, Moreira HT, Vasconcellos HD, et al. Left ventricular global function index predicts incident heart failure and cardiovascular disease in young adults: the coronary artery risk development in young adults(CARDIA)study[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2019, 20(5): 533-540. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jey123
[7] Reinstadler SJ, Klug G, Feistritzer HJ, et al. Prognostic value of left ventricular global function index in patients after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2016, 17(2): 169-176. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev129
[8] Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction(2018)[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2018, 72(18): 2231-2264. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.1038
[9] Stiermaier T, Backhaus SJ, Lange T, et al. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Left Ventricular Mechanical Uniformity Alterations for Risk Assessment After Acute Myocardial Infarction[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2019, 8(16): e011576. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011576
[10] Kapustina AY, Minushkina LO, Alekhin MN, et al. Left ventricular global function index as a predictor of adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome[J]. Kardiologiia, 2021, 61(8): 23-31. doi: 10.18087/cardio.2021.8.n1508
[11] Doganay B, Celebi OO. Prognostic role of the left ventricular global function index in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome patients[J]. Biomark Med, 2023, 17(1): 5-16.
-




 下载:
下载: