A case of lenvatinib mesylate associated with acute myocardial infarction in postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma
-
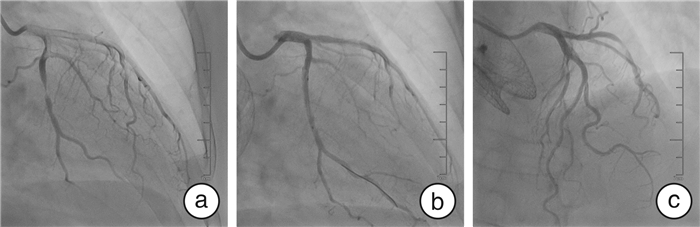
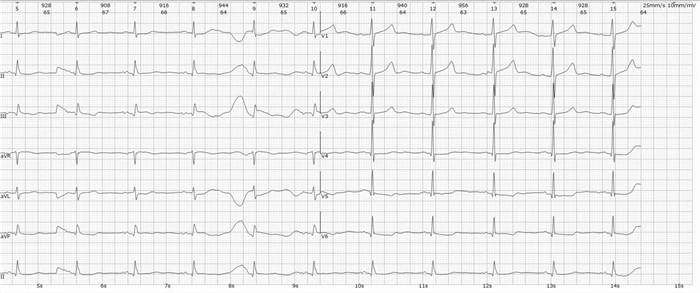
摘要: 本文报道1例63岁肝细胞癌术后的女性患者,采用甲磺酸仑伐替尼治疗21个月后出现药物相关的急性非ST段抬高型心肌梗死。提示在长期使用甲磺酸仑伐替尼等抗血管生成药物治疗时,需密切监测是否有急性冠状动脉血栓事件发生,以便及时发现和处理。Abstract: This article reports a 63-year-old female patient with hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery who developed drug-related acute non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction after 21 months of treatment with lenvatinib mesylate. It is important to closely monitor the occurrence of acute coronary thrombosis events during long-term use of antiangiogenic drugs such as lenvatinib mesylate, and timely detection and management of adverse reactions can effectively reduce the harm of lenvatinib mesylate related side effect.
-
Key words:
- acute myocardial infarction /
- lenvatinib mesylate /
- hepatoma
-

-
[1] Capozzi M, De Divitiis C, Ottaiano A, et al. Lenvatinib, a molecule with versatile application: from preclinical evidence to future development in anti-cancer treatment[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 3847-3860. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S188316
[2] Motzer RJ, Taylor MH, Evans T, et al. Lenvatinib dose, efficacy, and safety in the treatment of multiple malignancies[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2022, 22(4): 383-400. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2022.2039123
[3] Tella SH, Kommalapati A, Mahipal A. Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: targeted therapies[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2021, 10(1): 10. doi: 10.21037/cco-20-117
[4] Llovet JM, Kudo M, Merle P, et al. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus lenvatinib plus placebo for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(LEAP-002): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2023, 24(12): 1399-1410. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00469-2
[5] Goldman A, Bomze D, Dankner R, et al. Cardiovascular toxicities of antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a retrospective, pharmacovigilance study[J]. Target Oncol, 2021, 16(4): 471-483. doi: 10.1007/s11523-021-00817-2
[6] Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10126): 1163-1173. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1
[7] Pang Y, Eresen A, Zhang Z, et al. Adverse events of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2022, 12(6): 2770-2782.
[8] Kaae AC, Kreissl MC, Krüger M, et al. Kinase-inhibitors in iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer-focus on occurrence, mechanisms, and management of treatment-related hypertension[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(22): 1227.
[9] Mladěnka P, Applová L, Patočka J, et al. Comprehensive review of cardiovascular toxicity of drugs and related agents[J]. Med Res Rev, 2018, 38(4): 1332-1403. doi: 10.1002/med.21476
[10] Velusamy R, Nolan M, Murphy A, et al. Screening for coronary artery disease in cancer survivors[J]. JACC Cardio Oncol, 2023, 5(1): 22-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.12.007
[11] Doherty KR, Wappel RL, Talbert DR, et al. Multi-parameter in vitro toxicity testing of crizotinib, sunitinib, erlotinib, and nilotinib in human cardiomyocytes[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2013, 272(1): 245-55. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.04.027
[12] Paschke L, Lincke T, Mühlberg K, et al. Myocardial Infarction after Long-Term Treatment with a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor(TKI)with Anti-VEGF Receptor Activity[J]. Case Rep Endocrinol, 2019, 2019: 7927450.
[13] 时之秀, 杜训松, 曹洁. 老年冠心病患者PCI术后主要心脑血管不良事件发生情况及影响因素分析[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(2): 132-136. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.02.010
[14] Yusuf SW, Daraban N, Abbasi N, et al. Treatment and outcomes of acute coronary syndrome in the cancer population[J]. Clin Cardiol, 2012, 35(7): 443-450. doi: 10.1002/clc.22007
[15] Chen Y, Yang Y, Xu WJ, et al. Clinical application of interventional embolization in tumor-associated hemorrhage[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(6): 394. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.69
[16] Arora N, Gupta A, Singh PP. Biological agents in gastrointestinal cancers: adverse effects and their management[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2017, 8(3): 485-498. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2017.01.07
[17] Accordino MK, Neugut AI, Hershman DL. Cardiac effects of anticancer therapy in the elderly[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2014, 32(24): 2654-2661. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.55.0459
[18] 杨欣荣, 孙惠川, 谢青, 等. 仑伐替尼肝癌全病程应用中国专家指导意见[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22(2): 167-180.
-




 下载:
下载: