The efficacy of the quantitative cardiac motion quantification technique in assessing the degree of coronary artery stenosis and predicting prognosis in patients with coronary heart disease
-
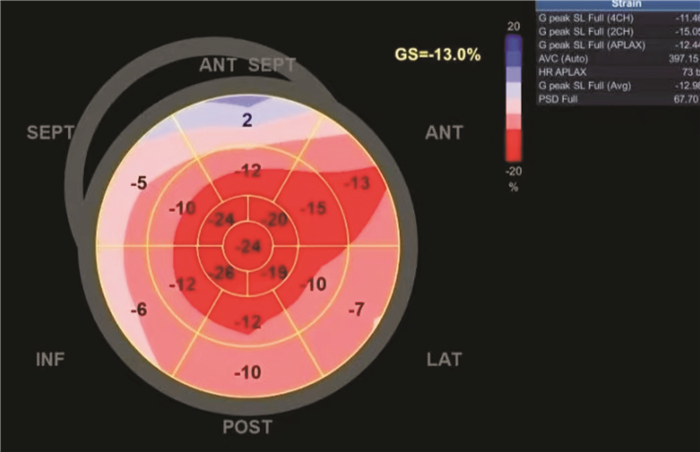
摘要: 目的 探讨心肌运动定量(CMQ)技术在冠心病冠状动脉(冠脉)狭窄程度中的评估价值及预测预后效能。方法 选取2018年12月——2020年12月本院收治的100例冠心病患者,所有患者均在入院后实施CMQ检查及传统冠脉造影(CAG)检查。并以CAG检查结果为金标准,分析CMQ技术对冠脉狭窄程度的诊断价值。随访1年,根据预后情况将患者分为预后良好组(70例)及预后不良组(30例)。比较两组CMQ相关参数。采用Spearman相关性检验分析CMQ相关参数与预后的相关性。绘制受试者工作曲线(ROC)检验CMQ参数评估患者预后的价值。结果 经CAG确诊,100例冠心病患者中Ⅲ级狭窄30例(30.00%),Ⅳ级狭窄70例(70.00%),CMQ技术评估冠脉狭窄程度的准确度为96.00%(96/100)。Kappa检验显示,CMQ评估的冠脉狭窄程度结果与CAG一致性较好(κ=0.903,P < 0.001)。预后不良组LVGLS、AP2LS、AP3LS及AP4LS绝对值均低于预后良好组(均P < 0.05)。Spearman检验显示,LVGLS、AP2LS、AP3LS、AP4LS与预后呈负相关(r=-0.412、-0.501、-0.375、-0.382,均P < 0.05)。ROC曲线显示,LVGLS、AP2LS、AP3LS、AP4LS单独及联合预测冠心病患者不良预后风险的AUC分别为0.773、0.787、0.783、0.766、0.910,其中联合预测的效能最高。结论 CMQ技术能准确评估冠心病患者冠脉狭窄程度,与CAG检查结果有较好的一致性,且CMQ相关参数LVGLS、AP2LS、AP3LS、AP4LS与冠心病患者预后关系密切,联合测定能很好地预测预后。Abstract: Objective To explore the evaluation value of cardiac motion quantification (CMQ) technique in the degree of coronary artery stenosis and the prognostic efficacy in patients with coronary heart disease.Methods One-hundred patients with coronary heart disease who were admitted to our hospital from December 2018 to December 2020 were included. All patients were underwent CMQ and angiography (CAG) examination. Taking the results of CAG examination as the gold standard, the diagnostic value of CMQ for coronary artery stenosis was analyzed. Follow-up for one year, patients were divided into the good prognosis group (n=70) and the poor prognosis group (n=30) based on their prognosis. The related parameters of CMQ were compared between the two groups. Spearman correlation test was used to analyse the relationship between the related parameters of CMQ and the prognosis. Receiver operating characteristic(ROC) analysis was used to test the value of CMQ parameters in evaluating the prognosis.Results CAG confirmed that there were 30 patients (30.00%) with grade Ⅲ stenosis, and 70 cases (70.00%) of grade Ⅳ stenosis. The accuracy of CMQ in evaluating the degree of coronary artery stenosis was 96.00% (96/100). The consistent Kappa measurement showed that the results of CMQ in evaluating the degree of coronary artery stenosis were consistent with CAG examination (κ=0.903, P < 0.001). The absolute values of left ventricular global systolic longitudinal peak strain (LVGLS), two-chamber longitudinal peak strain (AP2LS), three-chamber longitudinal peak strain (AP3LS), and four-chamber longitudinal peak strain (AP4LS) in the poor prognosis group were lower than those in the poor prognosis group (all P < 0.05). Spearman test showed that LVGLS, AP2LS, AP3LS, and AP4LS were negatively correlated with the prognosis, respectively (r=-0.412, -0.501, -0.375, -0.382, all P < 0.05). The ROC curve showed that the AUC of LVGLS, AP2LS, AP3LS, and AP4LS alone and in combination for predicting the risk of poor prognosis were 0.773, 0.787, 0.783, 0.766, and 0.910, respectively, with the highest efficacy observed in combination prediction.Conclusion CMQ technique can accurately evaluate the degree of coronary artery stenosis in patients with coronary heart disease, which is in good agreement with CAG examination. The related parameters of CMQ, such as LVGLS, AP2LS, AP3LS, and AP4LS, are closely related to the prognosis, and the combined determination can well predict the prognosis.
-

-
表 1 CMQ与CAG评估冠脉狭窄程度结果
Table 1. Coronary artery stenosis degree evaluated by CMQ and CAG
例 CMQ CAG 合计 Ⅳ级狭窄 Ⅲ级狭窄 Ⅳ级狭窄 27 1 28 Ⅲ级狭窄 3 69 72 合计 30 70 100 κ 0.903 P < 0.001 表 2 不同预后组患者CMQ参数比较
Table 2. Comparison of CMQ related parameters in patients with different prognoses
%, X±S 组别 LVGLS AP2LS AP3LS AP4LS 预后不良组(30例) 18.36±2.05 17.29±2.15 17.28±2.04 18.34±2.11 预后良好组(70例) 23.29±2.03 22.83±2.10 22.35±2.25 23.44±2.15 t 11.097 12.004 10.609 10.930 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 3 CMQ参数与预后的相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis between CMQ related parameters and prognosis
参数 LVGLS AP2LS AP3LS AP4LS r -0.412 -0.501 -0.375 -0.382 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 4 CMQ参数预测不良预后风险的效能
Table 4. Efficacy of CMQ related parameters in predicting the risk of poor prognosis
参数 AUC(95%CI) 截断值 SE P 灵敏度 特异度 约登指数 LVGLS 0.773(0.664~0.882) 20.350% 0.056 < 0.001 0.881 0.629 0.510 AP2LS 0.787(0.691~0.882) 20.190% 0.049 < 0.001 0.771 0.667 0.438 AP3LS 0.783(0.684~0.882) 19.700% 0.051 < 0.001 0.814 0.667 0.481 AP4LS 0.766(0.650~0.881) 20.300% 0.059 < 0.001 0.829 0.666 0.495 联合 0.910(0.843~0.978) 78.859 0.034 < 0.001 0.957 0.700 0.657 -
[1] Wool TH, Ashley SC, Gupta VA. Determination of Left Main Coronary Artery Stenosis Through Noninvasive Testing to Guide Revascularization in Ischemic Heart Disease[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2023, 204(1): 345-351.
[2] Cury RC, Leipsic J, Abbara S, et al. CAD-RADSTM 2.0-2022 Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System: An Expert Consensus Document of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography(SCCT), the American College of Cardiology(ACC), the American College of Radiology(ACR), and the North America Society of Cardiovascular Imaging(NASCI)[J]. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr, 2022, 16(6): 536-557. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2022.07.002
[3] Peerwani G, Aijaz S, Sheikh S, et al. Predictors of Non-Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease in Patients Undergoing Elective Coronary Angiography[J]. Glob Heart, 2023, 18(1): 26. doi: 10.5334/gh.1204
[4] Sirajuddin A, Mirmomen SM, Kligerman SJ, et al. Ischemic Heart Disease: Noninvasive Imaging Techniques and Findings[J]. Radiographics, 2021, 41(4): 990-1021. doi: 10.1148/rg.2021200125
[5] Yan JJ, Tian J, Yang H, et al. A clinical decision support system for predicting coronary artery stenosis in patients with suspected coronary heart disease[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2022, 151(Pt A): 106300.
[6] 程景华, 肖敏, 苟加梅. CMQ技术参数对急性心肌梗死再灌注术后心肌微循环障碍的评估价值[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2023, 18(7): 846-849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6966.2023.07.002
[7] 葛均波, 徐永健, 王辰, 等. 内科学(第9版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社. 2018: 227.
[8] 肖双, 李昭屏, 陈少敏, 等. 冠状动脉轻度狭窄对非阻塞性冠状动脉胸痛患者冠状动脉血流储备的影响[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2024, 40(7): 536-540. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2024.07.006
[9] Bertolone DT, Gallinoro E, Esposito G, et al. Contemporary Management of Stable Coronary Artery Disease[J]. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev, 2022, 29(3): 207-219. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00497-z
[10] Ghobrial M, Haley HA, Gosling R, et al. The new role of diagnostic angiography in coronary physiological assessment[J]. Heart, 2021, 107(10): 783-789. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-318289
[11] Vallée A, Zhang Y, Protogerou A, et al. Added value of aortic pulse wave velocity index for the detection of coronary heart disease by elective coronary angiography[J]. Blood Press, 2019, 28(6): 375-384. doi: 10.1080/08037051.2019.1641400
[12] Wang RR, Tian T, Li SQ, et al. Assessment of Left Ventricular Global Myocardial Work in Patients With Different Degrees of Coronary Artery Stenosis by Pressure-Strain Loops Analysis[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2021, 47(1): 33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.09.017
[13] 沈嘉祺, 王玉玖, 卞斐, 等. 二维超声斑点追踪成像技术评价冠心病患者冠脉旁路移植术后心肌功能的临床价值[J]. 滨州医学院学报, 2023, 46(3): 171-175.
[14] 刘云, 耿笑端, 栗河舟, 等. 超声心动图自动心肌运动定量技术评估川崎病患儿左心室收缩功能[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2022, 38(6): 842-847.
[15] 马盼弟. 3D-STI与2D-LS评估冠心病患者CABG术前心肌存活性[D]. 河南: 新乡医学院, 2021.
[16] 梁慧青, 刘昕, 薛娜. 实时三维斑点追踪成像评价前降支病变患者左室局部心肌功能[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2018, 27(1): 17-22. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2018.01.005
[17] 李一鸣, 吴存刚, 李玉宏. 自动心肌运动定量技术评估2型糖尿病患者左心室功能[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2023, 39(1): 34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2023.01.009
[18] 何鑫, 张淑伟, 葛丽丽. 自动心肌运动定量技术评价亚临床甲状腺功能减退左室功能[J]. 锦州医科大学学报, 2023, 44(4): 97-102.
[19] Le DE, Alkayed NJ, Cao Z, et al. Metabolomics of repetitive myocardial stunning in chronic multivessel coronary artery stenosis: Effect of non-selective and selective β1-receptor blockers[J]. J Physiol, 2024, 602(14): 3423-3448. doi: 10.1113/JP285720
[20] Wang YN, Chen WF, Wang Q. Segmental and transmural motion of the rat myocardium estimated using quantitative ultrasound with new strategies for infarct detection[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 11(7): 1236108.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 347
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: