Research progress on the role of interleukin-1 family and inflammasome-related members in cardiovascular diseases
-
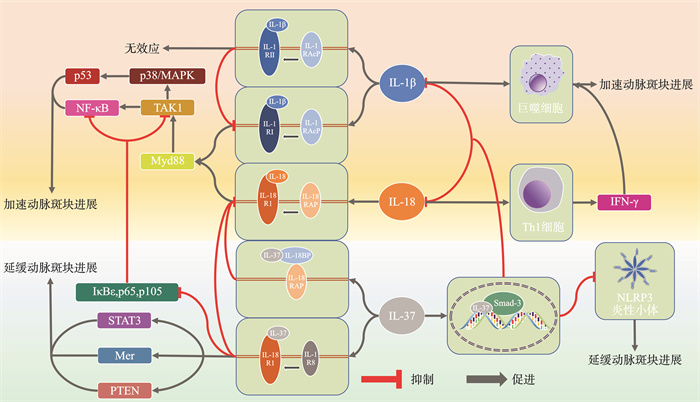
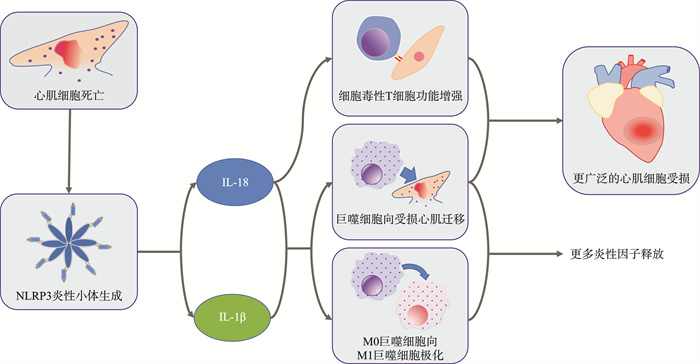
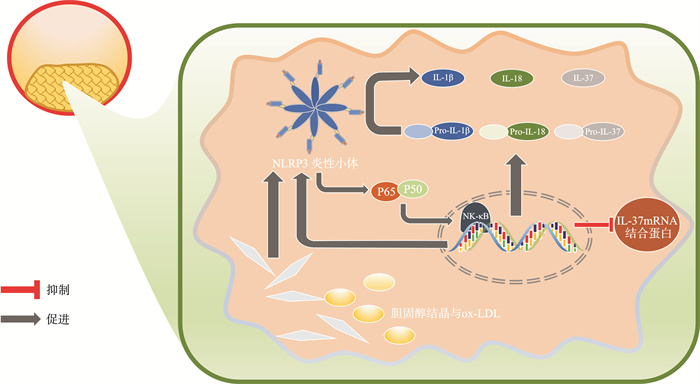
摘要: 近些年,心血管疾病(cardiovascular disease,CVD)与炎症的关系被逐步阐明。在炎症过程中,炎性小体扮演着重要作用。炎性小体通过激活半胱天冬酶1(caspase-1)产生白细胞介素-1(interleukin-1,IL-1)家族成员IL-1β(interleukin-1β)、IL-18(interleukin-18)、IL-37(interleukin-37)。IL-1β、IL-18作为促炎因子参与炎症级联反应,引起CVD中的不良炎症反应;IL-37作为白细胞介素-1家族的新成员,通过阻断IL-1β、IL-18通路发挥炎症抑制因子的作用,在一定程度上延缓CVD的进展。针对上述靶点的抗炎治疗为CVD患者提供了一种可能的治疗策略。Abstract: In recent years, the relationship between cardiovascular disease(CVD) and inflammation has been gradually elucidated. Inflammasome plays an important role in the inflammatory process. Inflammasome produces interleukin-1(IL-1) family members IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-37 by activating caspase-1. IL-1β and IL-18 participate in the inflammatory cascade as pro-inflammatory factors, causing adverse inflammatory responses in CVD; IL-37, as a new member of the interleukin-1 family, plays a role as an inflammation suppressor by blocking the IL-1β and IL-18 pathways, delaying the progression of CVD to a certain extent. CVD progression to a certain extent. Anti-inflammatory therapy targeting the above mentioned targets provides a possible diagnostic strategy for CVD patients.
-
Key words:
- interleukin-37 /
- interleukin-18 /
- interleukin-1β /
- cardiovascular disease
-

-
[1] Dinarello C, Arend W, Sims J, et al. IL-1 family nomenclature[J]. Nat Immunol, 2010, 11(11): 973. doi: 10.1038/ni1110-973
[2] Garlanda C, Dinarello CA, Mantovani A. The interleukin-1 family: back to the future[J]. Immunity, 2013, 39(6): 1003-1018. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.010
[3] Rathinam VA, Fitzgerald KA. Inflammasome Complexes: Emerging Mechanisms and Effector Functions[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(4): 792-800. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.046
[4] Latz E, Xiao TS, Stutz A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2013, 13(6): 397-411. doi: 10.1038/nri3452
[5] Horvath GL, Schrum JE, De Nardo CM, et al. Intracellular sensing of microbes and danger signals by the inflammasomes[J]. Immunol Rev, 2011, 243(1): 119-135. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01050.x
[6] Trindade BC, Chen GY. NOD1 and NOD2 in inflammatory and infectious diseases[J]. Immunol Rev, 2020, 297(1): 139-161. doi: 10.1111/imr.12902
[7] Zhan X, Li Q, Xu G, et al. The mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its pharmacological inhibitors[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 18(13): 1109938.
[8] Libby P, Lichtman SH, Hansson GK. Immune effector mechanisms implicated in atherosclerosis: from mice to humans[J]. Immunity, 2013, 38: 1092-1104. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.06.009
[9] Hoseini Z, Sepahvand F, Rashidi B, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome: Its regulation and involvement in atherosclerosis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(3): 2116-2132. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25930
[10] O'Rourke SA, Neto NGB, Devilly E, et al. Cholesterol crystals drive metabolic reprogramming and M1 macrophage polarisation in primary human macrophages[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2022, 352: 35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.05.015
[11] Khwaja B, Thankam FG, Agrawal DK. Mitochondrial DAMPs and altered mitochondrial dynamics in OxLDL burden in atherosclerosis[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2021, 476(4): 1915-1928. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04061-0
[12] Zhu Y, Xian X, Wang Z, et al. Research Progress on the Relationship between Atherosclerosis and Inflammation[J]. Biomolecules, 2018, 8(3): 80. doi: 10.3390/biom8030080
[13] Fidler TP, Xue C, Yalcinkaya M, et al. The AIM2 inflammasome exacerbates atherosclerosis in clonal haematopoiesis[J]. Nature, 2021, 592(7853): 296-301. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03341-5
[14] McCurdy S, Liu CA, Yap J, et al. Potential role of IL-37 in atherosclerosis[J]. Cytokine, 2019, 122: 154-169.
[15] Cavalli G, Dinarello CA. Suppression of inflammation and acquired immunity by IL-37[J]. Immunol Rev, 2018, 281(1): 179-190. doi: 10.1111/imr.12605
[16] Zhang C, Huang X, Xie B, et al. The multi-protective effect of IL-37-Smad3 against ox-LDL induced dysfunction of endothelial cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 172: 116268. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116268
[17] Yang Z, Kang L, Wang Y, et al. Role of IL-37 in Cardiovascular Disease Inflammation[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2019, 35(7): 923-930. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2019.04.007
[18] 中华医学会心血管病学分会, 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会, 中国医师协会心力衰竭专业委员会, 等. 中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2024[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2024, 52(3): 235-275.
[19] Kemp CD, Conte JV. The pathophysiology of heart failure[J]. Cardiovasc Pathol, 2021, 21: 365-371.
[20] 王敢, 钟江华. NLRP3炎性小体在慢性心力衰竭中的作用与机制[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2023, 39(8): 591-596. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2023.08.005
[21] Guo H, Callaway JB, Ting JP. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics[J]. Nat Med, 2015, 21(7): 677-687. doi: 10.1038/nm.3893
[22] Mangan MSJ, Olhava EJ, Roush WR, et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2018, 17(8): 588-606. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.97
[23] Bacmeister L, Schwarzl M, Warnke S, et al. Inflammation and fibrosis in murine models of heart failure[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2019, 114(3): 19. doi: 10.1007/s00395-019-0722-5
[24] Azhar G, Nagano K, Patyal P, et al. Deletion of Interleukin-1β Converting Enzyme Alters Mouse Cardiac Structure and Function[J]. Biology(Basel), 2024, 13(3): 172.
[25] Sun L, Yuan H, Zhao G. IL-37 alleviates Coxsackievirus B3-induced viral myocarditis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 20077. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22617-y
[26] Zhu R, Sun H, Yu K, et al. Interleukin-37 and Dendritic Cells Treated With Interleukin-37 Plus Troponin I Ameliorate Cardiac Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2016, 12(5): e004406.
[27] Yin D, Liu Y, Xue B, et al. IL-37 Modulates Myocardial Calcium Handling via the p-STAT3/SERCA2a Axis in HF-Related Engineered Human Heart Tissue[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2024, 13(13): e2303957. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303957
[28] Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction(2018)[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(3): 237-269. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy462
[29] Sreejit G, Abdel-Latif A, Athmanathan B, et al. Neutrophil-Derived S100A8/A9 Amplify Granulopoiesis After Myocardial Infarction[J]. Circulation, 2020, 141(13): 1080-1094. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.043833
[30] Chen Y, Hong J, Zhong H, et al. IL-37 Attenuates Platelet Activation and Thrombosis Through IL-1R8 Pathway[J]. Circ Res, 2023, 132(9): 134-150.
[31] Saadoun D, Vautier M, Cacoub P. Medium-and Large-Vessel Vasculitis[J]. Circulation, 2021, 143(3): 267-282. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046657
[32] Lee Y, Schulte DJ, Shimada K, et al. Interleukin-1β is crucial for the induction of coronary artery inflammation in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease[J]. Circulation, 2012, 125(12): 1542-1550. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.072769
[33] Shahi A, Afzali S, Firoozi Z, et al. Potential roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2023, 238(3): 513-532. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30948
[34] Arnold DD, Yalamanoglu A, Boyman O. Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy of IL-1-Targeted Biologics in Treating Immune-Mediated Disorders[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 888392. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.888392
[35] Cantarini L, Lopalco G, Caso F, et al. Effectiveness and tuberculosis-related safety profile of interleukin-1 blocking agents in the management of Behçet's disease[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2015, 14(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.008
[36] Lachmann HJ, Kone-Paut I, Kuemmerle-Deschner JB, et al. Use of canakinumab in the cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 360(23): 2416-2425. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810787
[37] Ortega-Paz L, Capodanno D, Angiolillo DJ. Canakinumab for secondary prevention of coronary artery disease[J]. Future Cardiol, 2021, 17(3): 427-442. doi: 10.2217/fca-2020-0211
[38] Mikkelsen RR, Hundahl MP, Torp CK, et al. Immunomodulatory and immunosuppressive therapies in cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A bedside-to-bench approach[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2022, 925: 174998. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174998
[39] Lutgens E, Atzler D, Döring Y, et al. Immunotherapy for cardiovascular disease[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(48): 3937-3946. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz283
[40] Dimosiari A, Patoulias D, Kitas GD, et al. Do Interleukin-1 and Interleukin-6 Antagonists Hold Any Place in the Treatment of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Related Co-Morbidities? An Overview of Available Clinical Evidence[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(4): 1302. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041302
[41] 谭建盛. 白术内酯Ⅲ对IL-1β介导大鼠关节软骨细胞损伤的作用研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2022.
[42] Kim SH, Eisenstein M, Reznikov L, et al. Structural requirements of six naturally occurring isoforms of the IL-18 binding protein to inhibit IL-18[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97(3): 1190-1195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.3.1190
[43] Kim S, Yu H, Azam T, et al. Interleukin-18 Binding Protein(IL-18BP): A Long Journey From Discovery to Clinical Application[J]. Immune Netw, 2024, 24(1): e1. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e1
[44] Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Zepp JA, et al. IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity[J]. Nat Immunol, 2010, 11(11): 1014-1022. doi: 10.1038/ni.1944
[45] Yang Y, Zhang ZX, Lian D, et al. IL-37 inhibits IL-18-induced tubular epithelial cell expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2015, 87(2): 396-408. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.295
[46] Ma W, Wu D, Long C, et al. Neutrophil-derived nanovesicles deliver IL-37 to mitigate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via endothelial cell targeting[J]. J Control Release, 2024, 370: 66-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.04.025
[47] Dinarello CA, Bufler P. Interleukin-37[J]. Semin Immunol, 2013, 25(6): 466-468. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.10.004
[48] Van Gorp H, Van Opdenbosch N, Lamkanfi M. Inflammasome-Dependent Cytokines at the Crossroads of Health and Autoinflammatory Disease[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2019, 11(1): a028563. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028563
[49] Li S, Amo-Aparicio J, Neff CP, et al. Role for nuclear interleukin-37 in the suppression of innate immunity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019, 116(10): 4456-4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821111116
[50] Li YF, Nanayakkara G, Sun Y, et al. Analyses of caspase-1-regulated transcriptomes in various tissues lead to identification of novel IL-1β-, IL-18-and sirtuin-1-independent pathways[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10(1): 40. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0406-2
[51] Nakahara T, Strauss HW. From inflammation to calcification in atherosclerosis[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2017, 44(5): 858-860. doi: 10.1007/s00259-016-3608-x
[52] Greener JG, Kandathil SM, Moffat L, et al. A guide to machine learning for biologists[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(1): 40-55. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00407-0
[53] Shah RV, Steffen LM, Nayor M, et al. Dietary metabolic signatures and cardiometabolic risk[J]. Eur Heart J, 2023, 44(7): 557-569. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac446
[54] Tayal U, Verdonschot JAJ, Hazebroek MR, et al. Precision Phenotyping of Dilated Cardiomyopathy Using Multidimensional Data[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2022, 79(22): 2219-2232. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.03.375
[55] Libby P. Interleukin-1 Beta as a Target for Atherosclerosis Therapy: Biological Basis of CANTOS and Beyond[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2017, 70(18): 2278-2289. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.09.028
[56] Ridker PM. From C-Reactive Protein to Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-1: Moving Upstream To Identify Novel Targets for Atheroprotection[J]. Circ Res, 2016, 118(1): 145-156. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306656
[57] Chen W, Schilperoort M, Cao Y, et al. Macrophage-targeted nanomedicine for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2022, 19(4): 228-249. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00629-x
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 371
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: