Preliminary study on the best cutoff value of plasma D-dimer in patients with trauma complicated with acute pulmonary embolism
-
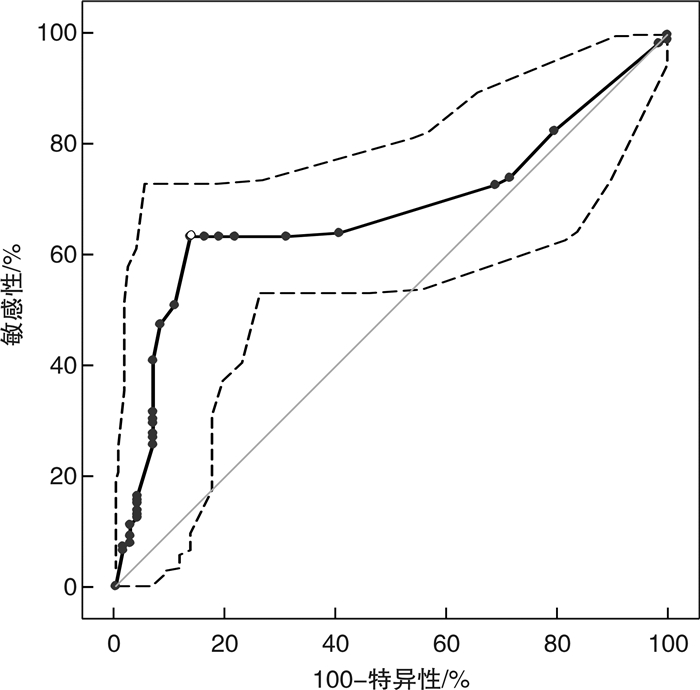
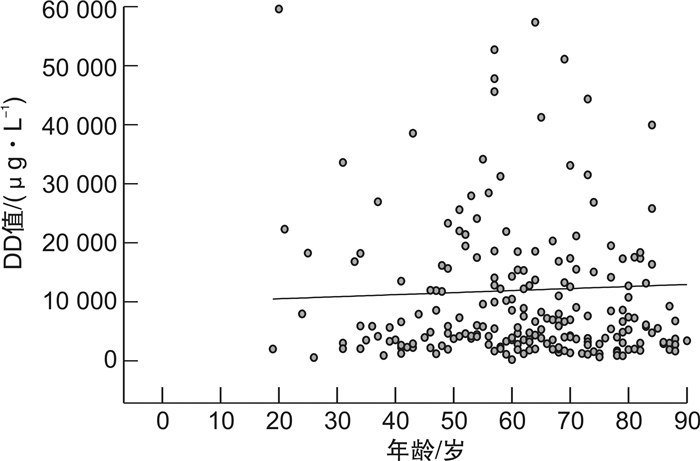
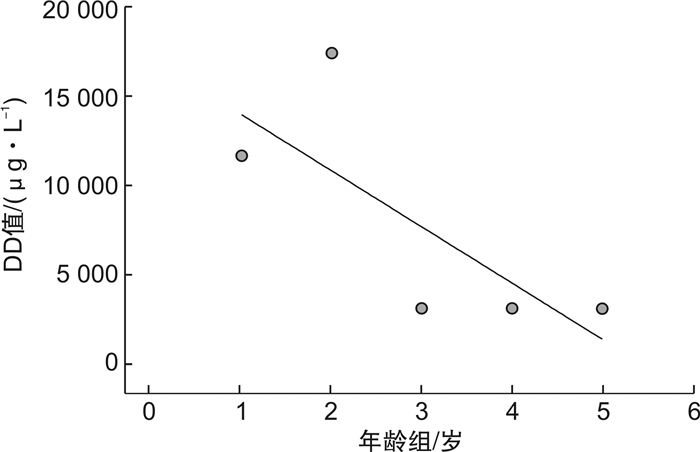
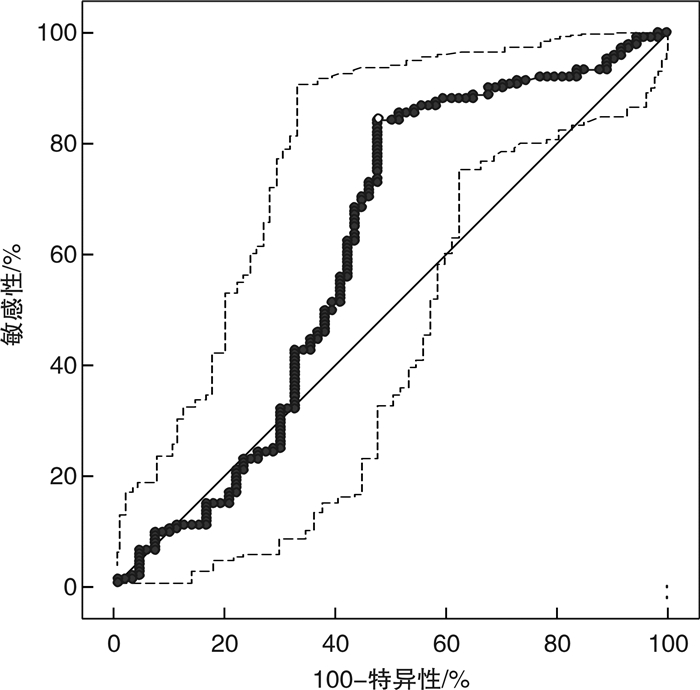
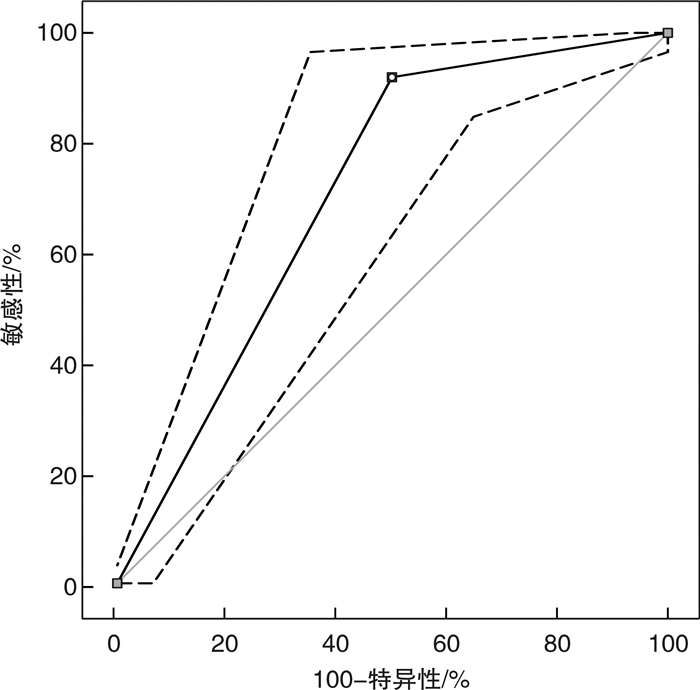
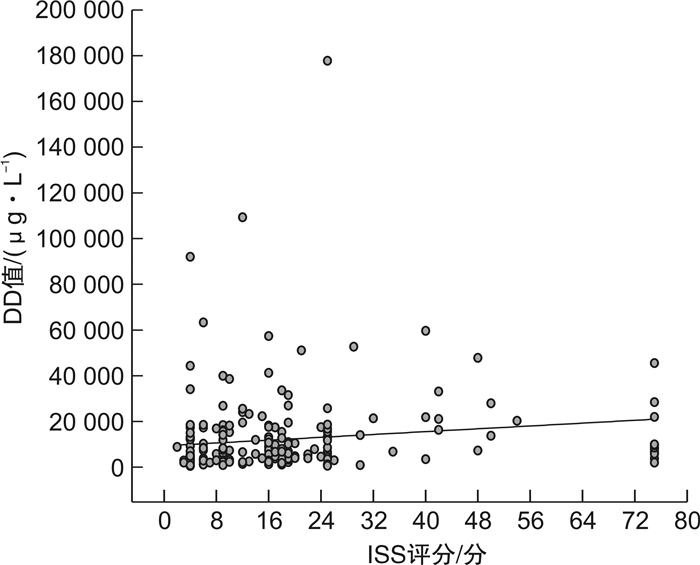
摘要: 目的 探索创伤合并急性肺动脉栓塞(APE)患者血浆D-二聚体(DD)的最佳截点值。方法 回顾性连续选取2014年1月—2020年1月我院收治的18~89岁225例创伤患者,其中合并APE组151例,非APE组74例。分析基础资料,应用血浆DD与CT肺动脉造影(CTPA)的ROC曲线得出新DD截点值,联合ISS评分及DD值ROC曲线,进一步改善诊断效能。结果 ① 在基础资料分析中,APE组DD及Wells评分均明显高于非APE组,APE组的ISS评分较高,其重伤及危重伤比例较高,而非APE组轻-中度伤的比例较高。②血浆DD值与ISS评分存在较弱的正相关性(r=0.0196)。ISS评分与CTPA结果的ROC分析得出最佳截点值15分。③血浆DD与年龄无明显相关性(r=0.00099)。④由于年龄与DD无明显相关性,血浆DD与CTPA结果进行ROC分析,得到新截点值3200 μg/L,灵敏度84.11%,特异度52.70%,阳性预测值78.4%,阴性预测值51.9%,曲线下面积0.609。为了改善诊断效能,我们应用ISS(15分)联合DD(3200 μg/L)与CTPA结果的ROC曲线分析,灵敏度92.05%(86.5%,95.8%),特异度50.00%(38.1%,61.9%),阳性预测值79%,阴性预测值75.5%,曲线下面积0.710。结论 创伤后合并APE应用传统截点值(550 μg/L)及年龄校正公式(年龄×10,年龄>50岁)诊断效能较低,应提高血浆DD截点值至3200 μg/L联合ISS评分(15分)用于该病的诊断,以提高诊断效能。Abstract: Objective To explore the optimal cutoff of plasma D-Dimer(DD) in patients who suffered from trauma complicated with acute pulmonary embolism(APE).Methods We enrolled in 225 patients between 18-89 years, who were treated in our hospital from January 2014 to January 2020. APE was suspected during the treatment. They were divided into APE group and non-APE group according to the results of CTPA. We analyzed the basic data of the two groups, and the ROC curve was used to evaluate APE.Results 1) In the basic data analysis, the DD and Wells scores were significantly higher in APE group than in non APE group. The ISS score of APE group was higher, and the proportion of serious and very serious trauma was higher, while the proportion of mild-moderate trauma in non APE group was higher. 2) There was positive correlation between plasma DD value and ISS score, r=0.0196.3) There is no significant correlation between DD and age, r=0.00099.4) Because there was no significant correlation between age and DD, ROC analysis of plasma DD and CTPA results showed that the new cutoff value was 3200 μg/L, SE 84.11%(77.3%, 89.5%), SP 52.70%(40.7%, 64.4%), PPV 78.4%, NPV 51.9%, AUC=0.609. In order to improve the diagnostic efficiency, we used the ROC curve analysis of ISS(15 points) combined with DD(3200 μg/L) and CTPA results, and SE was 92.05%(86.5%, 95.8%), SP was 50.00%(38.1%, 61.9%), PPV was 79%, NPV was 75.5%, AUC=0.710.Conclusion The diagnostic efficacy of traditional cutoff value(550ug/L) and age adjusted DD(age*10, age>50) for traumatic with APE is low. Increasing the plasma DD cutoff value to 3200 μg/L combined with ISS score is used for the diagnosis of APE to improve the diagnostic efficacy.
-
Key words:
- trauma /
- acute pulmonary embolism /
- D-dimer /
- age-adjusted D-dimer /
- ISS score
-

-
表 1 两组基础资料
Table 1. General data
例(%), X±S, M(P25, P75) 项目 APE组(151例) 非APE组(74例) P值 年龄/岁 62.66±15.65 64.15±18.27 0.528 男性 85(56.29) 44(59.45) 0.652 心率/(次·min-1) 81.74±13.87 83.13±16.92 0.514 咯血 3(1.99) 0(0) 0.222 活动性恶性肿瘤 8(5.29) 0(0) 0.044 既往VTE病史 2(1.32) 1(1.35) 0.987 DD/(μg·L-1) 6690(3810,14050) 3195(2010,15790) 0.008 简化Wells评分/分 3(1,3) 1(1,2) 0.000 致伤原因 交通事故伤 43(28.47) 23(31.08) 0.687 高处坠落伤 37(24.50) 15(20.27) 0.479 摔伤 71(47.01) 36(48.64) 0.818 ISS评分 < 16分(轻-中度伤) 50(33.11) 59(79.72) 0.000 16~25分(重伤) 62(41.05) 10(13.51) 0.000 >25分(危重伤) 39(25.82) 5(6.75) 0.001 -
[1] GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: a system aticanalysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J]. Lancet. 2017, 390(10100): 1151-210. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9
[2] Shuster R, Mathew J, Olaussen A, et al. Variables associated with pulmonary thromboembolism in injured patients: A systematic review[J]. Injury, 2018, 49(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2017.08.024
[3] Ho KM, Burrell M, Rao S, et al. Incidence and risk factors for fatal pulmonary embolism after major trauma: a nested cohort study[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2010, 105(5): 596-602. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeq254
[4] Guo YJ, Chang MH, Chen PL, et al. Predictive value of plasma(D)-dimer levels for cancer-related stroke: a 3-year retrospective study[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2014, 23(4): e249-254. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.10.022
[5] Kim EY, Song KY. Prognostic value of D-dimer levels in patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy[J]. Surg Oncol, 2021, 37: 101570. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2021.101570
[6] Hisada Y, Mackman N. Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis[J]. Blood, 2017, 130(13): 1499-1506. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-03-743211
[7] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺栓塞与肺血管病学组, 中国医师协会呼吸医师分会肺栓塞与肺血管病工作委员会, 全国肺栓塞与肺血管病防治协作组. 肺血栓栓塞症诊治与预防指南[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(14): 1060-1087. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.14.007
[8] 林庆荣, 杨明辉, 侯志勇. 中国创伤骨科患者围手术期静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南(2021)[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2021, 23(3): 185-192. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115530-20201228-00795
[9] Rijneveld AW, Weijer S, Bresser P, et al. Local activation of the tissue factor-factor VⅡa pathway in patients with pneumonia and the effect of inhibition of this pathway in murine pneumococcal pneumonia[J]. Crit Care Med, 2006, 34(6): 1725-1730. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000218807.20570.C2
[10] Jiang RM, Pourzanjani AA, Cohen MJ, et al. Associations of longitudinal D-Dimer and Factor Ⅱ on early trauma survival risk[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2021, 22(1): 122. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04065-z
[11] Langness S, Ward E, Halbach J, et al. Plasma D-dimer safely reduces unnecessary CT scans obtained in the evaluation of pediatric head trauma[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2018, 53(4): 752-757. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.08.017
[12] Owings JT, Gosselin RC, Anderson JT, et al. Practical utility of the D-dimer assay for excluding thromboembolism in severely injured trauma patients[J]. J Trauma, 2001, 51(3): 425-429;discussion 429-430.
[13] Zhang LD, Liu HB, Li YN, et al. Correlation analysis between plasma D-dimer levels and orthopedic trauma severity[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2012, 125(17): 3133-3136.
[14] Yumoto T, Naito H, Yamakawa Y, et al. Venous thromboembolism in major trauma patients: a single-center retrospective cohort study of the epidemiology and utility of D-dimer for screening[J]. Acute Med Surg, 2017, 4(4): 394-400. doi: 10.1002/ams2.290
[15] An ZP, Huang HB, Wang ZG. Correlation between plasma D-Dimer level and severity and prognosis in patients admitted at emergency department with trauma[J]. Clin Lab, 2020, 66(1): 100. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190520
[16] 杨超, 张旭, 李潭, 等. 创伤严重程度评分对多发创伤患者深静脉血栓形成的预测价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2021, 37(18): 2371-2374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2021.18.013
-




 下载:
下载: