Real-time visualization of esophageal position by intracardiac echocardiography during AI-guided atrial fibrillation ablation
-
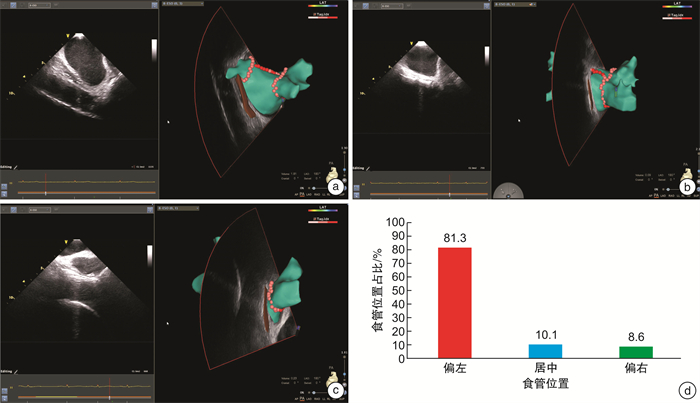
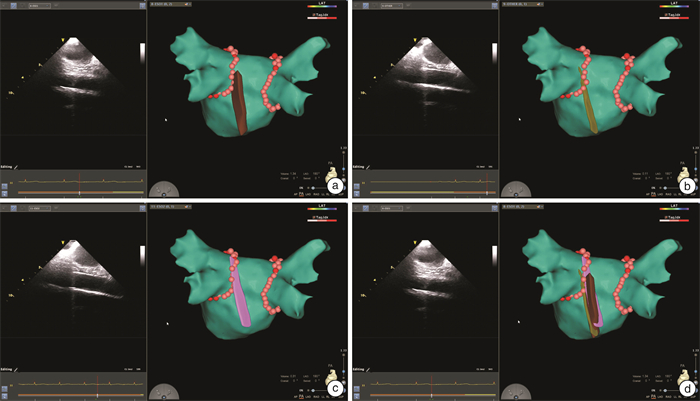
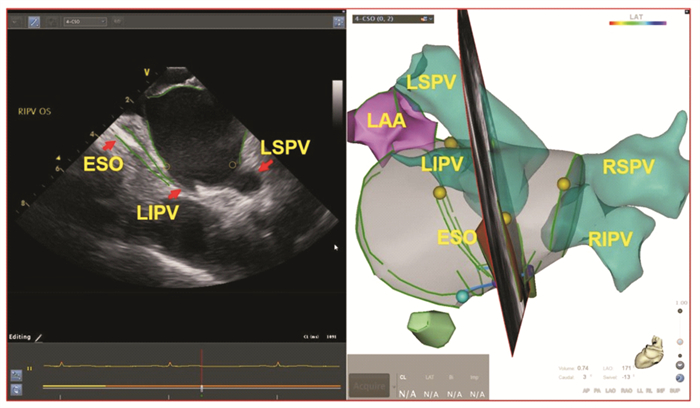
摘要: 目的 回顾性探讨腔内超声(ICE)在消融指数(AI)指导的心房颤动(房颤)消融术中实时监测食管位置的价值。方法 选取2020年6月—2021年8月于苏州大学附属第一医院住院的房颤患者,在术中应用ICE实时观察食管位置,在食管附近消融时目标AI值设置为320~350 U。患者出院后定期进行门诊或电话随访。复发定义为3个月空白期后心电图记录或24 h动态心电图检查中发现持续30 s以上的房颤、心房扑动(房扑)或房性心动过速(房速)。应用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析房颤患者消融术后未复发率。结果 ① 共纳入139例房颤患者,阵发性房颤患者84例(60.4%),男性占59.0%,年龄为64(55,70)岁,病程为15(4,48)个月,CHA2DS2-VASc评分为2(1,4)分,左房内径为(44.0±6.62) mm;术中ICE检测食管位于左肺静脉后壁、左房后壁中部和右肺静脉后壁分别占81.3%、10.1%和8.6%;消融过程中未发现食管位置发生>1 cm的移位;ICE联合AI指导左、右肺静脉单圈隔离率分别为92.6%、89.4%;平均随访时间为(10±6.4)个月,无心房食管瘘发生。在未服抗心律失常药物时,阵发性房颤患者未复发率为85.5%,持续性房颤患者未复发率80.8%。结论 ICE可实时监测食管位置,食管附近目标AI值320~350 U指导肺静脉隔离安全有效。Abstract: Objective To retrospectively investigate the real-time visualization of the esophagus by intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) undergoing ablation index (AI)-guided pulmonary vein (PV) isolation.Methods Patients with atrial fibrillation who underwent ICE to visualize the esophagus during AI-guided PV isolation were included from June 2020 to August 2021 in The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. A target AI value was 320-350 near the esophagus demonstrated by ICE. The patients were followed up regularly at outpatient or by telephone after discharge. Atrial fibrillation recurrence was defined as any atrial tachyarrhythmia (AF, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia) lasting ≥30 s by ECGs or Holters after a post-ablation 3-month blanking period. Kaplan-Meier survival curve was used to analyze the non-recurrence rate of AF patients after ablation.Results (1) A total of 139 patients with atrial fibrillation were included, of which 84 (60.4%) were patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, 59.0% were male, the age was 64 (55, 70) years old, the course of the disease was 15 (4, 48) months, CHA2DS2- The VASc score was 2 (1, 4) points, and the inner diameter of the left atrium was (44.0±6.62) mm. (2) The proportion of esophageal position located in the posterior wall of the left pulmonary vein, the middle of the posterior wall of the left atrium, and the posterior wall of the right pulmonary vein, were 81.3%, 10.1%, and 8.6%, respectively. No displacement of the esophagus >1 cm was found during ablation. (3) The isolation rates of left and right pulmonary veins guided by ICE combined with AI were 92.6% and 89.4%, respectively. The average follow-up time was (10±6.4) months, no atrial esophageal fistula occurred, the non-recurrence rate was 85.5% in patients with paroxysmal AF and 80.8% in persistent AF without antiarrhythmic drugs.Conclusion ICE can provide real-time localization of the esophagus during AF ablation, and the targeted AI at 320-350 near the esophagus confirmed by ICE is safe and effectiveness of pulmonary vein isolation.
-

-
-
[1] 中华医学会心电生理和起搏分会, 中国医师协会心律学专业委员会, 中国房颤中心联盟心房颤动防治专家工作委员会. 心房颤动: 目前的认识和治疗建议(2021)[J]. 中华心律失常学杂志, 2022, 26(1): 15-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHHL201301033.htm
[2] 郑伟, 李小荣, 王学成, 等. 心房颤动射频消融术后的食管损伤[J]. 中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志, 2020, 34(6): 530-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXZ202006005.htm
[3] Han HC, Ha FJ, Sanders P, et al. Atrioesophageal Fistula: Clinical Presentation, Procedural Characteristics, Diagnostic Investigations, and Treatment Outcomes[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2017, 10(11).
[4] Leung L, Akhtar Z, Sheppard MN, et al. Preventing esophageal complications from atrial fibrillation ablation: A review[J]. Heart Rhythm O2, 2021, 2(6Part A): 651-664.
[5] Pollak SJ, Monir G, Chernoby MS, et al. Novel imaging techniques of the esophagus enhancing safety of left atrial ablation[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2005, 16(3): 244-248. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2005.40560.x
[6] Yamane T, Matsuo S, Date T, et al. Visualization of the esophagus throughout left atrial catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2006, 17(1): 105.
[7] Sherzer AI, Feigenblum DY, Kulkarni S, et al. Continuous nonfluoroscopic localization of the esophagus during radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2007, 18(2): 157-160. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2006.00674.x
[8] Romero J, Avendano R, Grushko M, et al. Oesophageal Injury During AF Ablation: Techniques for Prevention[J]. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev, 2018, 7(1): 24-31.
[9] Hayashi K, Okumura K, Okamatsu H, et al. Real-time visualization of the esophagus and left atrial posterior wall by intra-left atrial echocardiography[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2022, 63(3): 629-637. doi: 10.1007/s10840-021-01093-w
[10] Basman C, Parmar YJ, Kronzon I. Intracardiac Echocardiography for Structural Heart and Electrophysiological Interventions[J]. Curr Cardiol Rep, 2017, 19(10): 102. doi: 10.1007/s11886-017-0902-6
[11] 张晶, 郝应禄, 李燕萍, 等. STSF导管结合消融指数在阵发性心房颤动射频消融术中的应用[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2020, 36(5): 468-471. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB202005015.htm
[12] 陈丽竹, 梁拓, 陈小璐, 等. 消融指数在射频消融治疗阵发性心房颤动中的作用研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(3): 259-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB202103015.htm
[13] 张晶, 王玮, 王禹川, 等. 脑微出血与冠心病抗栓治疗患者主要不良心血管事件发生风险的相关性研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(4): 281-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB202204006.htm
[14] 王温立, 邹操, 李勋, 等. 消融指数指导心房颤动导管消融的短期疗效及安全性[J]. 中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志, 2020, 34(4): 337-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXZ202004005.htm
[15] Ariyaratnam JP, Sanders P. Protecting the oesophagus during left atrial ablation: A surplus of options but an absence of evidence[J]. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J, 2020, 20(6): 219-220.
[16] Good E, Oral H, Lemola K, et al. Movement of the esophagus during left atrial catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2005, 46(11): 2107-2110.
[17] Kottkamp H, Piorkowski C, Tanner H, et al. Topographic variability of the esophageal left atrial relation influencing ablation lines in patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2005, 16(2): 146-150.
[18] Piorkowski C, Hindricks G, Schreiber D, et al. Electroanatomic reconstruction of the left atrium, pulmonary veins, and esophagus compared with the "true anatomy" on multislice computed tomography in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2006, 3(3): 317-327.
[19] Starek Z, Lehar F, Jez J, et al. Esophageal positions relative to the left atrium; data from 293 patients before catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. Indian Heart J, 2018, 70(1): 37-44.
[20] Helms A, West JJ, Patel A, et al. Real-time rotational ICE imaging of the relationship of the ablation catheter tip and the esophagus during atrial fibrillation ablation[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2009, 20(2): 130-137.
[21] Müller P, Dietrich JW, Halbfass P, et al. Higher incidence of esophageal lesions after ablation of atrial fibrillation related to the use of esophageal temperature probes[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2015, 12(7): 1464-1469.
[22] Ren J, Callans DJ, Marchlinski FE, et al. 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography/CartoSoundTM Imaging of Esophagus Guided Left Atrial Posterior Wall Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation[J]. J Atr Fibrillation, 2014, 7(4): 1184.
-




 下载:
下载: