Efficacy and safety of high power radiofrequency ablation guided by ablation index in atrial fibrillation ablation: a meta-analysis
-
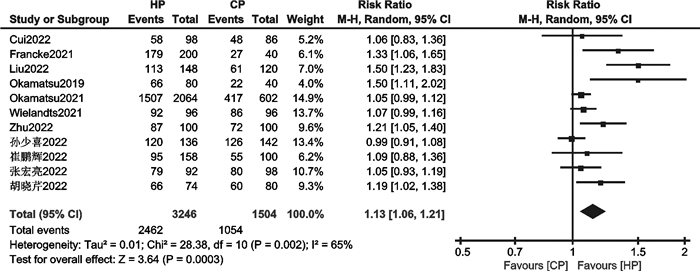
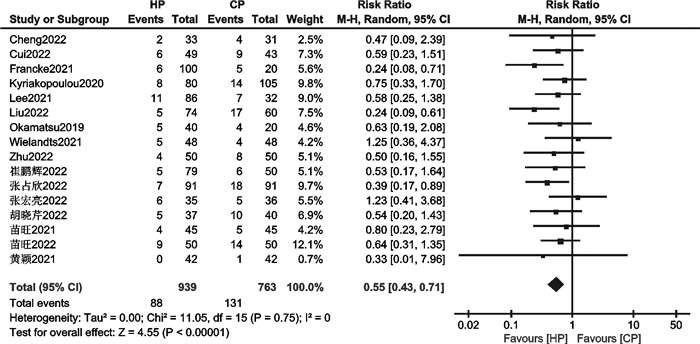
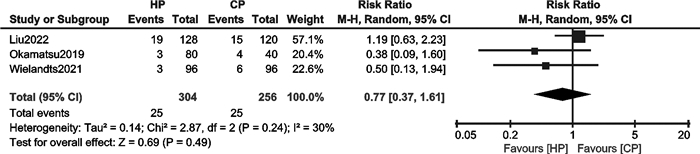
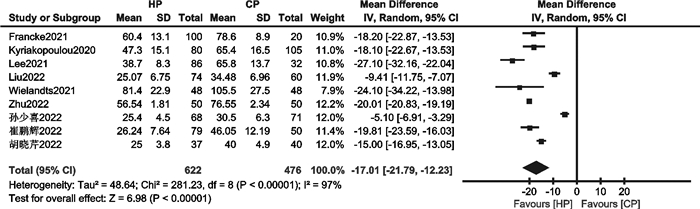
摘要: 目的 评价消融指数(ablation index,AI)指导下心房颤动(房颤)高功率射频消融的有效性和安全性。方法 检索PubMed、EMBASE、Cochrane Library、中国知网、万方数据库中自建库以来至2023年1月19日关于比较AI指导下高功率与常规功率房颤射频消融的文献。使用Revman 5.4、Stata 15.1进行统计学分析。结果 18篇文献,共3 206例患者被纳入本研究。与常规功率组比较,高功率组单圈隔离率高(RR=1.13,95%CI:1.06~1.21,P=0.000 3);房颤复发率低(RR=0.55,95%CI:0.43~0.71,P < 0.000 01);急性肺静脉传导恢复率无显著差异(RR=0.77,95%CI:0.34~1.61,P=0.49);食管并发症发生率无显著差异(RR=1.06,95%CI:0.33~3.40,P=0.92);肺静脉隔离时间明显缩短(MD=-17.01,95%CI:-21.79~-12.23,P < 0.000 01)。结论 AI指导下房颤高功率射频消融是安全、有效的。与常规功率消融相比,其单圈隔离率更高,复发率更低,手术时间更短,急性肺静脉传导恢复率和食管并发症发生率相当。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the efficacy and safety of ablation index(AI) -guided high power radiofrequency ablation in atrial fibrillation(AF).Methods The PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CNKI, and Wanfang databases were searched for studies comparing high power with conventional power atrial fibrillation radiofrequency ablation guided by AI since the established until January 19, 2023. Statistical analysis was performed using Revman 5.4 and Stata15.1.Results Eighteen papers with a total of 3 206 patients were included in this study. The high power group showed higher first-pass PVI of PVs(RR=1.13, 95%CI: 1.06-1.21, P=0.000 3) and lower recurrence of AF(RR=0.55, 95%CI: 0.43-0.71, P < 0.000 01). There were insignificant differences in acute pulmonary vein reconnection(RR=0.77, 95%CI: 0.34-1.61, P=0.49) and esophageal complications(RR=1.06, 95%CI: 0.33-3.40, P=0.92). The PVI time were significantly shorter(MD=-17.01, 95%CI: -21.79—-12.23, P < 0.000 01) in high power group.Conclusion AI-guided high power radiofrequency ablation was safe and efficient for treating AF, it showed higher first-pass PVI of PVs, lower recurrence of AF, and shorter procedure times. The events of acute pulmonary vein reconnection and esophageal complications were similar between the two groups.
-
Key words:
- atrial fibrillation /
- catheter ablation /
- ablation index /
- high power
-

-
表 1 纳入研究手术基本特征
Table 1. Basic procedural characteristics of studies
纳入研究 研究类型 研究样本量(高功率/常规功率) 房颤类型 高功率参数 常规功率参数 随访时间 监测方法 Wielandts 2021 随机对照试验 48/48 阵发性 45 W功率控制模式;AI:前壁≥550、其余区域≥400 35 W功率控制模式;AI:前壁≥550、其余区域≥400 6个月 临床随访、心电图、心律失常症状 苗旺2021 队列研究 45/45 阵发性+持续性 前壁、底部、顶部、后壁功率45 W;AI:前壁480、底部450、顶部400、后壁380 前壁、底部、顶部、后壁功率35 W;AI:前壁480、底部450、顶部400、后壁380 3个月 门诊随访/电话随访、心电图、心律失常症状 Okamatsu 2021 队列研究 1032/301 阵发性+持续性 前壁功率50 W、AI≥400;后壁功率40 W、AI≥360;食管区功率25 W、AI≥260 前壁功率30~40 W、AI≥400;后壁功率20~25 W、AI≥360;食管区功率20 W、AI≥260 12个月 门诊随访、症状、常规心电图、动态心电图 Francke 2021 队列研究 100/20 阵发性+持续性 功率均为50 W,AI:前壁550、后壁400 前壁、顶部功率40 W、AI 550;后壁功率20 W、AI 400 12周 临床随访,消化内镜、症状、心电图 Kyriakopoulou 2020 队列研究 80/105 阵发性 功率40 W;AI:前壁≥550、后壁和顶部≥400;温度超过38.5℃时AI 300 功率35 W;AI:前壁≥550、后壁和顶部≥400;温度超过38.5℃时AI 300 12个月 临床随访、心电图 Lee 2021 队列研究 86/32 阵发性+持续性 前壁、顶部功率40 W,AI≥450;后壁、下壁、嵴部功率30 W,AI≥350;食管区功率25 W,AI 300 前壁、顶部功率30~35 W,AI≥450;后壁、下壁、嵴部功率25~30 W,AI≥350;食管区功率25 W,AI 300 1年 临床随访、心电图 Okamatsu 2019 队列研究 40/20 阵发性+持续性 前壁功率50 W, 后壁40 W,食管区30 W;前壁40 W,后壁30 W;AI:前壁400、后壁360、食管区260 前壁功率30 W、后壁20 W;AI:前壁400、后壁360、食管区260 12个月 门诊随访、心电图、症状 黄颖2021 队列研究 42/42 阵发性+持续性 前壁功率50 W,其他部位40 W;AI:前壁450、其他部位400 前壁功率35 W,其他部位30 W;AI:前壁450、其他部位400 12个月 门诊随访、症状、ECG、动态心电图 苗旺2022 队列研究 50/50 阵发性+持续性 功率45 W,AI: 前壁480、底部450、顶部400、后壁380 功率35 W,AI: 前壁480、底部450、顶部400、后壁380 3个月 临床随访、症状、常规心电图、动态心电图 Cheng 2022 队列研究 36/36 阵发性 前壁、嵴部、顶部、下壁功率50 W,后壁功率45 W;AI:前壁450~480、嵴部480~500、顶部400~450、下壁400~450、后壁380~420 前壁、嵴部、顶部、下壁功率35 W,后壁功率30 W;AI:前壁450~480、嵴部480~500、顶部400~450、下壁400~450、后壁380~420 3个月 常规心电图检查或动态心电图 Cui 2022 队列研究 49/43 阵发性+持续性 前壁、顶部功率50 W,AI 500~550;后壁功率50 W,AI 350~400;下壁功率50 W,AI 400~450;上壁功率50 W,AI 450~500 前壁功率35~40 W,AI 500~550;顶部功率30~40 W,AI 500~550;后壁功率30~35 W,AI 350~400;下壁功率30~35 W,AI 400~450;上壁功率30~35 W,AI 450~500 18个月 心电图、动态心电图、超声心动图 Liu 2022 队列研究 74/60 阵发性+持续性 功率45 W;AI:前壁450~500、后壁350~400 功率35 W;AI:前壁450~500、后壁350~400 12个月 心电图、动态心电图 Zhu 2022 队列研究 50/50 阵发性 功率40 W,AI:后壁400、其他500 功率30 W;AI:后壁400、其他500 12个月 心电图、动态心电图 崔鹏辉2022 队列研究 79/50 阵发性+持续性 前壁50 W、AI 500~550;后壁功率50 W、AI 350~400;下壁功率50 W、AI 400~450;顶部功率50 W、AI 450~500;嵴部功率50 W、AI 500~550 前壁功率35~40 W、AI 500~550;后壁功率30~35 W、AI 350~400;下壁功率30~35 W、AI 400~450;顶部功率30~35 W、AI 450~500;嵴部功率30~40 W、AI 500~550 3个月 常规12导联体表心电图和(或)24 h动态心电图、超声心动图 胡晓芹2022 队列研究 37/40 阵发性+持续性 功率45~50 W;AI:前壁450~500,顶部400~450,后壁和底部350~400 功率30~35 W;AI:前壁450~500,顶部400~450,后壁和底部350~400 6个月 心电图或动态心电图 孙少喜2022 队列研究 68/71 阵发性 功率45 W;AI:前壁500、后壁350~400、顶部450、底部420 功率35 W;AI:前壁500、后壁350~400、顶部450、底部420 NA NA 张宏亮2022 队列研究 46/49 阵发性 前壁、顶部及嵴部功率45~50 W,后壁、底部功率跟前壁保持一致或降为40 W;AI:前壁和嵴部450、顶部和底部400、后壁360~380 前壁、顶部、嵴部、后壁、底部功率35~40 W;AI:前壁和嵴部450、顶部和底部400、后壁360~380 12个月 门诊随访或电话随访、24h动态心电图、超声心动图 张占欣2022 队列研究 91/91 阵发性+持续性 功率45~50 W;AI:前壁430~450、嵴部430~450、左顶部430~450、左后壁350~380、右顶部430~450、右后壁380~420 功率35~40 W;AI:前壁430~450、嵴部430~450、左顶部430~450、左后壁350~380、右顶部430~450、右后壁380~420 10~24个月 电话随访或门诊随访、常规12导联心电图、24h动态心电图及心脏超声 表 2 纳入研究患者基线特征
Table 2. Basic patient characteristics of studies
例(%), X±S, M(P25, P75) 纳入研究 组别 例数 年龄/年 女性 阵发性房颤/
持续性房颤体重指数/
(kg·m-2)CHA2DS2-VASc
评分左房直径
/mm左室射血分数/% Wielandts 2021 高功率 48 64.0±11.0 16(33.3) 48/0 26.4±4.2 1(0,3) 39.0±7.0 NA 常规功率 48 61.0±11.0 15(31.3) 48/0 26.8±4.0 1(0,3) 40.0±7.0 NA 苗旺2021 高功率 45 63.0±10.0 14(31.1) 34/11 25.6±3.0 3.5±1.8 42.3±5.5 63.3±8.2 常规功率 45 62.4±10.0 13(28.9) 25/20 25.6±2.7 3.9±1.8 42.7±7.3 63.0±10.6 Okamatsu 2021 高功率 1032 68(61,74) 316(30.6) 583/449 24(22,26) 2(1,3) 41(37,46) 62(58,66) 常规功率 301 67(61,73) 91(30.2) 172/129 24(22,26) 2(1,3) 41(37,46) 62(58,68) Francke 2021 高功率 100 66.4±10.0 40(40.0) 49/51 NA 2.8±1.5 NA 54.2±13.3 常规功率 20 66.4±10.0 13(65.0) 9/11 NA 3.2±1.5 NA 59.5±5.5 Kyriakopoulou 高功率 80 67(58,73) 33(41.2) 80/0 28.0±5.0 2(1,3) 43.0±8.0 60(60,60) 2020 常规功率 105 64(56,69) 40(38.1) 105/0 27.0±4.0 2(1,2) 44.0±6.0 60(60,60) Lee 2021 高功率 86 59.5±9.0 20(23.3) 62/24 24.9±3.0 1(1,2) 42.6±4.5 59.9±4.8 常规功率 32 59.9±9.1 7(21.9) 24/8 24.8±2.8 1(0,2) 41.2±5.4 59.2±5.1 Okamatsu 2019 高功率 20 65.0±10.0 7(35.0) 13/20 24(22,25) 2(1,3) 40.0±6.0 65(60,71) 中等功率 20 64.0±8.0 9(45.0) 15/20 23(22,26) 2(1,3) 40.0±5.0 64(59,71) 低功率 20 68.0±8.0 5(25.0) 16/20 24(21,28) 2(1,2) 39.0±6.0 64(60,67) 黄颖2021 高功率 42 62.3±8.8 13(31.0) 19/23 NA NA 43.8±4.8 59.45±4.72 常规功率 42 61.0±10.0 15(35.7) 23/19 NA NA 44.0±6.2 57.69±10.91 苗旺2022 高功率 50 67.9±1.1 18(36.0) 38/12 24.6±0.5 4.6±0.9 40.7±0.9 61.7±1.6 常规功率 50 66.6±1.3 25(50.0) 27/23 25.3±0.6 4.5±1.1 43.9±1.8 60.8±11.9 Cheng 2022 高功率 36 58.92±11.92 9(25.0) 36/0 24.11±2.98 1.69±1.49 38.19±6.46 63.04±4.40 常规功率 36 63.11±9.96 16(44.4) 36/0 25.38±3.24 2.31±1.95 38.08±6.40 61.53±4.07 Cui 2022 高功率 49 61.76±9.45 10(20.4) 29/20 25.55±5.67 1(1,2) 37.73±0.87 59.49±10.23 常规功率 43 58.14±9.83 9(20.9) 28/15 25.94±3.34 1(1,2) 38.40±5.28 62.40±6.84 Liu 2022 高功率 74 66.7±11.3 28(37.8) 57/18 23.16±2.63 2.7±1.9 40.8±3.8 NA 常规功率 60 66.4±7.2 23(38.3) 51/9 23.59±2.31 3.1±1.8 38.1±5.0 NA Zhu 2022 高功率 50 64.4±9.45 16(32.0) 50/0 21.27±1.88 3.4±1.14 40.65±5.87 64.74±4.46 常规功率 50 64.9±8.62 18(36.0) 50/0 21.04±2.65 3.15±1.04 42.85±3.10 61.9±5.40 崔鹏辉2022 高功率 79 62.41±9.48 30(38.0) 47/32 25.25±5.67 2(1,3) 38.00±5.43 60.51±9.85 常规功率 50 58.96±10.10 11(22.0) 35/15 26.02±3.23 1(1,2) 38.02±5.15 62.58±6.50 胡晓芹2022 高功率 37 63.8±9.6 14(37.8) 19/18 26.7±3.4 1.8±1.1 39.89±4.0 56.9±8.5 常规功率 40 58.3±12.3 9(22.5) 23/17 26.9±3.8 1.9±1.3 41.8±5.9 57.0±8.5 孙少喜2022 高功率 68 69.3±4.8 29(42.6) 68/0 NA NA 37.1±3.4 55.9±3.6 常规功率 71 68.2±4.3 30(42.3) 71/0 NA NA 36.7±3.6 54.9±3.5 张宏亮2022 高功率 46 59.63±9.53 17(37.0) 46/0 23.95±3.03 1.93±1.64 35.61±5.42 63.46±4.97 常规功率 49 58.73±10.22 14(28.6) 49/0 24.34±2.95 1.57±1.37 37.57±6.64 65.38±6.56 张占欣2022 高功率 91 59.65±9.72 36(40.0) 64/27 26.59±3.29 2.30±1.51 37.23±4.82 64.05±9.50 常规功率 91 59.71±10.61 36(40.0) 64/27 22.77±2.01 2.27±1.63 35.79±5.66 62.10±8.32 表 3 纳入队列研究文献质量评价
Table 3. Evaluation of literature quality of included cohort studies
纳入研究 研究对象选择 可比性 结果 得分 苗旺2021 4 2 2 8 Okamatsu 2021 4 2 1 7 Francke 2021 4 1 2 7 Kyriakopoulou 2020 4 1 2 7 Lee 2021 4 2 1 7 Okamatsu 2019 4 2 2 8 黄颖2021 4 2 2 8 苗旺2022 4 2 1 7 Cheng 2022 4 2 1 7 Cui 2022 4 1 2 7 Liu 2022 4 2 2 8 Zhu 2022 4 2 2 8 崔鹏辉2022 4 1 2 7 胡晓芹2022 4 2 2 8 孙少喜2022 4 1 2 7 张宏亮2022 4 2 1 7 张占欣2022 4 1 2 7 -
[1] 中华医学会心电生理和起搏分会, 中国医师协会心律学专业委员会, 中国房颤中心联盟心房颤动防治专家工作委员会. 心房颤动: 目前的认识和治疗建议(2021)[J]. 中华心律失常学杂志, 2022, 26(1): 15-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHHL201301033.htm
[2] Wittkampf FH, Nakagawa H. RF catheter ablation: Lessons on lesions[J]. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol, 2006, 29(11): 1285-1297. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2006.00533.x
[3] Knotts RJ, Barbhaiya CR. High-power, short-duration ablation for atrial fibrillation: Pros and cons[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2021, 66: 86-91. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2021.06.005
[4] Nilsson B, Chen X, Pehrson S, et al. The effectiveness of a high output/short duration radiofrequency current application technique in segmental pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation[J]. Europace, 2006, 8(11): 962-965. doi: 10.1093/europace/eul100
[5] Shin DG, Ahn J, Han SJ, et al. Efficacy of high-power and short-duration ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation: a prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Europace, 2020, 22(10): 1495-1501. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaa144
[6] Ullah W, Hunter RJ, Finlay MC, et al. Ablation Index and Surround Flow Catheter Irrigation: Impedance-Based Appraisal in Clinical Ablation[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2017, 3(10): 1080-1088. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2017.03.011
[7] Ioannou A, Papageorgiou N, Lim WY, et al. Efficacy and safety of ablation index-guided catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: an updated meta-analysis[J]. Europace, 2020, 22(11): 1659-1671. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaa224
[8] Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials[J]. BMJ, 2011, 343: d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
[9] Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9): 603-605. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
[10] Francke A, Taha NS, Scharfe F, et al. Procedural efficacy and safety of standardized, ablation index guided fixed 50 W high-power short-duration pulmonary vein isolation and substrate modification using the CLOSE protocol[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2021, 32(9): 2408-2417. doi: 10.1111/jce.15158
[11] Kyriakopoulou M, Wielandts JY, Strisciuglio T, et al. Evaluation of higher power delivery during RF pulmonary vein isolation using optimized and contiguous lesions[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2020, 31(5): 1091-1098. doi: 10.1111/jce.14438
[12] Lee SR, Park HS, Choi EK, et al. Acute and long-term efficacy of ablation index-guided higher power shorter duration ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation: A prospective registry[J]. J Arrhythm, 2021, 37(5): 1250-1259. doi: 10.1002/joa3.12605
[13] Okamatsu H, Koyama J, Sakai Y, et al. High-power application is associated with shorter procedure time and higher rate of first-pass pulmonary vein isolation in ablation index-guided atrial fibrillation ablation[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2019, 30(12): 2751-2758. doi: 10.1111/jce.14223
[14] Okamatsu H, Okumura K, Kaneko S, et al. Ablation Index-Guided High-Power Radiofrequency Application Shortens the Procedure Time With Similar Outcomes to Conventional Power Application in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation[J]. Circ Rep, 2021, 3(10): 559-568. doi: 10.1253/circrep.CR-21-0099
[15] Wielandts JY, Kyriakopoulou M, Almorad A, et al. Prospective Randomized Evaluation of High Power During CLOSE-Guided Pulmonary Vein Isolation: The POWER-AF Study[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2021, 14(1): e009112. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.120.009112
[16] 黄颖, 解杨婧. 高功率短时程与常规功率导管射频消融治疗心房颤动有效性和安全性的对比研究[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2021, 29(5): 124-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXL202105025.htm
[17] 苗旺. AI指导下高功率短时程消融在房颤治疗中的应用效果[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2021.
[18] 苗旺, 张楠, 郭敏, 等. 消融指数指导下高功率消融在老年心房颤动患者中的应用效果[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 24(2): 151-154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2022.02.011
[19] Cheng C, Xu B, Sheng J, et al. Procedural Efficiency, Efficacy, and Safety of High-Power, Short-Duration Radiofrequency Ablation Delivered by STSF Catheter for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 6009275.
[20] Cui P, Qu Y, Zhang J, et al. Comparison of effectiveness and safety of high-power vs. conventional-power radiofrequency ablation for treatment of atrial fibrillation[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 988602. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.988602
[21] Liu Z, Liu LF, Liu XQ, et al. Ablation index-guided ablation with milder targets for atrial fibrillation: Comparison between high power and low power ablation[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 949918. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.949918
[22] Zhu X, Wang C, Chu H, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of High-Power Radiofrequency Ablation Guided by Ablation Index for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation[J]. Comput Math MethodsMed, 2022, 2022: 5609764.
[23] 崔鹏辉. 129例高功率和普通功率射频消融策略治疗心房颤动的有效性和安全性比较[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022.
[24] 胡晓芹, 李承宗, 李菲, 等. 消融指数指导下单导管高功率射频消融在肺静脉隔离中的短期疗效及安全性[J]. 徐州医科大学学报, 2022, 42(09): 666-671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZYX202209009.htm
[25] 孙少喜, 谭文亮, 黎镇赐, 等. 应用STSF导管高功率消融模式治疗老年阵发性房颤的临床疗效[J]. 广州医药, 2022, 53(4): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZYY202204003.htm
[26] 张宏亮. 消融指数指导的高功率短时程射频消融在阵发性心房颤动中的安全性及有效性评价[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022.
[27] 张占欣. 应用高功率短时程射频消融治疗心房颤动的疗效及安全性[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2022.
[28] Lozano Granero C, Franco E, Matía Francés R, et al. Impact of power and contact force on index-guided radiofrequency lesions in an ex vivo porcine heart model[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2022, 63(3): 687-697. doi: 10.1007/s10840-021-01110-y
[29] Bhaskaran A, Chik W, Pouliopoulos J, et al. Five seconds of 50-60 W radio frequency atrial ablations were transmural and safe: an in vitro mechanistic assessment and force-controlled in vivo validation[J]. Europace, 2017, 19(5): 874-880.
[30] Ali-Ahmed F, Goyal V, Patel M, et al. High-power, low-flow, short-ablation duration-the key to avoid collateral injury?[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2019, 55(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1007/s10840-018-0473-5
[31] Winkle RA, Mohanty S, Patrawala RA, et al. Low complication rates using high power(45-50 W)for short duration for atrial fibrillation ablations[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2019, 16(2): 165-169. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.11.031
[32] Vassallo F, Cunha C, Serpa E, et al. Comparison of high-power short-duration(HPSD)ablation of atrial fibrillation using a contact force-sensing catheter and conventional technique: Initial results[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2019, 30(10): 1877-1883. doi: 10.1111/jce.14110
[33] Huang ST, Dong JZ, Du X, et al. Relationship Between Ablation Lesion Size Estimated by Ablation Index and Different Ablation Settings-an Ex Vivo Porcine Heart Study[J]. J Cardiovasc Transl Res, 2020, 13(6): 965-969. doi: 10.1007/s12265-020-10037-0
[34] 陈丽竹, 梁拓, 陈小璐, 等. 消融指数在射频消融治疗阵发性心房颤动中的作用研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(3): 259-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB202103015.htm
[35] Hussein A, Das M, Riva S, et al. Use of Ablation Index-Guided Ablation Results in High Rates of Durable Pulmonary Vein Isolation and Freedom From Arrhythmia in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Patients: The PRAISE Study Results[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2018, 11(9): e006576. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.118.006576
[36] 张建军. 心房颤动导管消融中环肺静脉单圈隔离的意义及操作要点[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(11): 847-850. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.11.001
[37] Xu M, Yang Y, Zhang D, et al. Meta-analysis of high power short duration in atrial fibrillation ablation-a superior efficient ablation strategy[J]. Acta Cardiol, 2022, 77(1): 14-32. doi: 10.1080/00015385.2021.1939512
[38] Vcer E, Jungbauer C, Hauck C, et al. The low acute effectiveness of a high-power short duration radiofrequency current application technique in pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation[J]. Cardiol J, 2021, 28(5): 663-670.
[39] Liu X, Gui C, Wen W, et al. Safety and Efficacy of High Power Shorter Duration Ablation Guided by Ablation Index or Lesion Size Index in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. J Interv Cardiol, 2021, 2021: 5591590.
[40] Kaneshiro T, Kamioka M, Hijioka N, et al. Characteristics of Esophageal Injury in Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Using a High-Power Short-Duration Setting[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2020, 13(10): e008602.
[41] Chen S, Schmidt B, Seeger A, et al. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation using ablation index-guided high power(50 W)for pulmonary vein isolation with or without esophageal temperature probe(the AI-HP ESO Ⅱ)[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2020, 17(11): 1833-1840.
[42] Chen S, Schmidt B, Bordignon S, et al. Ablation index-guided 50 W ablation for pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation: Procedural data, lesion analysis, and initial results from the FAFA AI High Power Study[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2019, 30(12): 2724-2731.
[43] Takigawa M, Kitamura T, Martin CA, et al. Temperature-and flow-controlled ablation/very-high-power short-duration ablation vs conventional power-controlled ablation: Comparison of focal and linear lesion characteristics[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2021, 18(4): 553-561.
[44] Reddy VY, Grimaldi M, De Potter T, et al. Pulmonary Vein Isolation With Very High Power, Short Duration, Temperature-Controlled Lesions: The QDOT-FAST Trial[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2019, 5(7): 778-786.
-




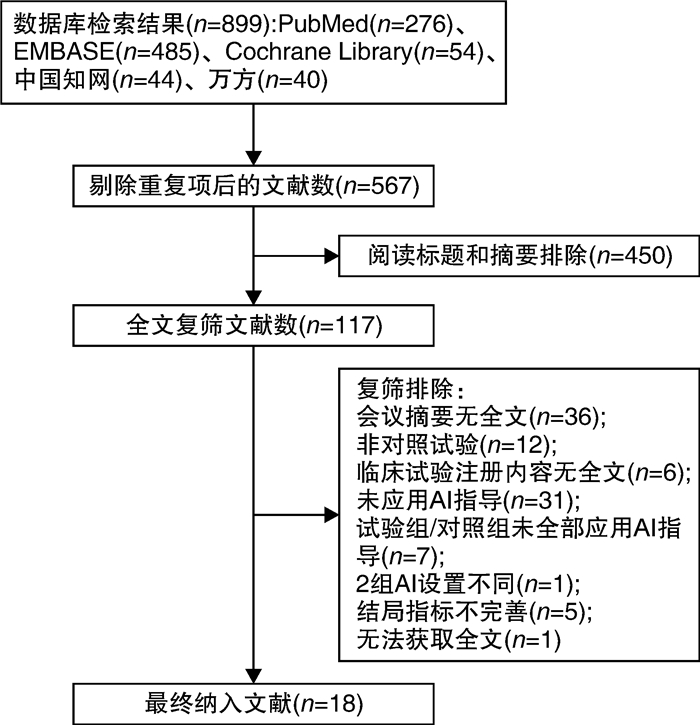
 下载:
下载: