Clinical application and effect of Castor stent combined with fenestration technique in the treatment of aortic arch aneurysm
-
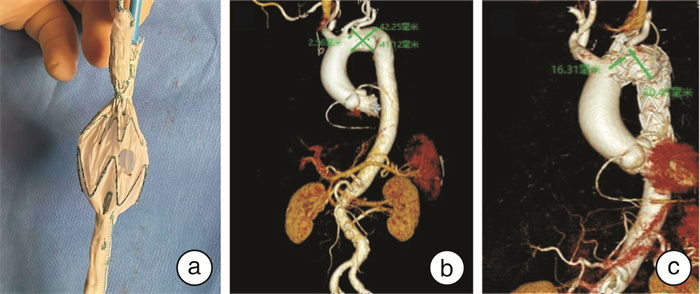
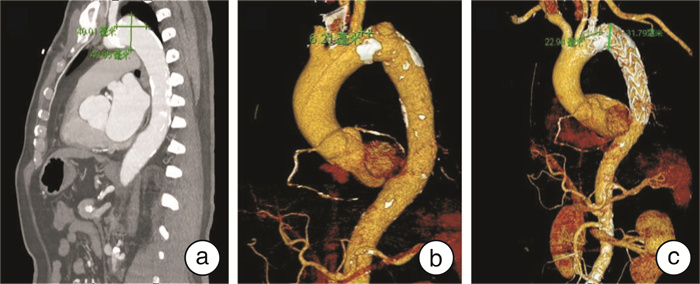
摘要: 目的 探讨Castor支架结合体外预开窗技术治疗累及Z1区、Z2区的主动脉弓部动脉瘤的临床应用及效果。 方法 回顾性分析2021年6月—2023年6月主动脉弓部瘤接受Castor支架手术患者32例。其中主动脉弓部真性动脉瘤14例,主动脉弓部夹层动脉瘤18例。Castor支架分支仅应用于左锁骨下动脉且未合并其他手术作为单纯手术组(23例),Castor支架分支应用于左颈总动脉且左锁骨下动脉开窗重建为开窗手术组(9例)。 结果 32例患者手术成功率为100%。术后并发症1例(1/32,3.12%),发生在开窗手术组(1/9,11.11%),患者术后1 d出现脑梗死,表现为右下肢肌力降低(肌力0/1级)。32例患者随访1~24.4个月,中位随访时间8个月,期间1例(1/32,3.12%)患者死亡,发生在单纯手术组(1/23,4.35%),该患者术前合并食管癌,术后2年因营养不良及多器官功能衰竭死亡。术后复查胸主动脉CTA单纯手术组瘤体内径(35.3±4.6) mm,开窗手术组瘤体内径(33.2±3.9) mm,均较术前明显降低(均P<0.05)。 结论 Castor支架技术结合开窗技术治疗累及Z1区、Z2区的主动脉弓部瘤病变疗效确切,具有一定的安全性。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical application and effects of Castor stent combined with in vitro pre-fenestration technique in treating aortic arch aneurysms involving Z1 and Z2 zones. Methods Thirty-two patients with aortic arch aneurysms who underwent Castor stent surgery from June 2021 to June 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. There were 14 patients with true aortic arch aneurysms and 18 patients with dissected aortic arch aneurysms. The Castor stent branch was applied to the left subclavian artery only and was not combined with other operations as the simple surgery group(n=23). The Castor stent branch was applied to the left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery was reconstructed as the fenestration surgery group(n=9). Results The surgical success rate of 32 patients was 100%. Postoperative complications occurred in 1 case(1/32, 3.12%), which occurred in the fenestrated surgery group(1/9, 11.11%). Cerebral infarction occurred in the patient one day after surgery and was manifested as decreased muscle strength of the right lower limb(grade 0/1 muscle strength). All patients were followed up for 1-24.4 months, with a median time of 8 months. During the follow-up period, 1 patient died(1/32, 3.12%), which occurred in the simple surgery group(1/23, 4.35%). The patient was diagnosed with esophageal cancer before surgery and died 2 years after surgery due to malnutrition and multiple organ failure. The internal diameter of the thoracic aorta was(35.3±4.6) mm in the simple surgery group and(33.2±3.9) mm in the fenestrated surgery group, which were significantly lower than those before surgery(both P < 0.05). Conclusion The castor stent technique combined with the fenestration technique in treating aortic arch tumors involving Z1 and Z2 zones has a definite therapeutic effect and certain safety.
-
Key words:
- Castor stent /
- prefenestration technique /
- aortic arch aneurysm /
- clinical application
-

-
表 1 患者术后临床资料
Table 1. Postoperative clinical data
例(%), X±S 项目 单纯手术组(23例) 开窗手术组(9例) 手术时间/min 110.4±31.7 156.9±22.51) 术后并发症 0 1(11.11) 术后1周胸腹主动脉CTA 瘤体近端锚定区/mm 26.4±2.3 24.1±4.1 术后瘤体部位内径/mm 35.3±4.6 33.2±3.9 支架主体近端内径/mm 33.5±2.0 34.0±2.8 支架主体近端扩大比例/% 16.5±5.8 15.8±5.3 随访死亡 1(4.35) 0 与单纯手术组比较,1)P<0.05。 -
[1] Ho J, Chow S, Kwok M, et al. Total Aortic Arch Replacement and Frozen Elephant Trunk[J]. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2021, 33(3): 656-662. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2020.11.016
[2] 张潇文, 李小平, 刘胜中. 经瘤腔内人工血管置换术治疗巨大主动脉弓部瘤1例[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(9): 764-766. . https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.09.017
[3] Sanphasitvong V, Wongkornrat W, Jantarawan T, et al. Mortality and complications following total aortic arch replacement: 14 years' experience[J]. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann, 2022, 30(6): 679-687. doi: 10.1177/02184923211072488
[4] Preventza O, Le Huu A, Olive J, et al. Endovascular repair of the ascending aorta: the last frontier[J]. Ann Cardiothorac Surg, 2022, 11(1): 26-30. doi: 10.21037/acs-2021-taes-71
[5] Sharaf OM, Kohtz PD, Arnaoutakis GJ. Aortic Arch Repair Using Open and Hybrid Techniques: A Systematic Review[J]. Innovations(Phila), 2022, 17(4): 273-282. doi: 10.1177/15569845221115355
[6] Sharples L, Sastry P, Freeman C, et al. Endovascular stent grafting and open surgical replacement for chronic thoracic aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and prospective cohort study[J]. Health Technol Assess, 2022, 26(6): 1-166. doi: 10.3310/ABUT7744
[7] Fang C, Wang C, Liu K, et al. Early Outcomes of Left Subclavian Artery Revascularization Using Castor Single-Branched Stent-Graft in the Treatment of Type B Aortic Dissection or Intramural Hematoma[J]. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2021, 27(4): 251-259. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.20-00166
[8] Lu Q. Application and evaluation of branch stent technique in the reconstruction of partial arch branch vessels[J]. Chin J Practical Surg, 2018, 38(12): 1369-1373.
[9] Carrel T, Sundt TM 3rd, Kodolitsch Y, et al. Acute aortic dissection[J]. Lancet, 2023, 401(10378): 773-788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01970-5
[10] Tian Y, Wang C, Xie P. Mid-term outcomes of left subclavian artery revascularization with Castor stent graft in treatment of type B aortic dissection in left subclavian artery[J]. J Interv Med, 2023, 6(2): 74-80.
[11] Zhu J, Dai X, Noiniyom P, et al. Fenestrated Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair Using Physician-Modified Stent Grafts(PMSGs)in Zone 0 and Zone 1 for Aortic Arch Diseases[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2019, 42(1): 19-27. doi: 10.1007/s00270-018-2079-9
[12] Huang B, Jia H, Lai H, et al. Outcomes of thoracic endovascular aortic repair for penetrating aortic ulcers involving the left subclavian artery with the Castor single-branched stent graft[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2022, 62(2): ezac102. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezac102
[13] Luo ZR, Zhang JX, Huang ZY, et al. Endovascular repair of aortic pathologies involving the aortic arch using castor stent-graft combined with in-vitro fenestration technology[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2023, 23(1): 107. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03138-6
[14] D'Oria M, Wanhainen A, DeMartino RR, et al. A scoping review of the rationale and evidence for cost-effectiveness analysis of fenestrated-branched endovascular repair for intact complex aortic aneurysms[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2020, 72(5): 1772-1782. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.05.037
[15] Okamura H, Arakawa M, Kitada Y, et al. Bail-Out Pull-Through Pull-Back Technique for Accidental Coverage of the Left Common Carotid Artery During Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair[J]. J Endovasc Ther, 2022, 29(2): 289-293. doi: 10.1177/15266028211036482
[16] Shu C, Fan B, Luo M, et al. Endovascular treatment for aortic arch pathologies: chimney, on-the-table fenestration, and in-situ fenestration techniques[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2020, 12(4): 1437-1448. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.03.10
[17] Shah AS, Akhmerov A, Gupta N, et al. Use of a Dual-Filter Cerebral Embolic Protection Device in Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2020, 65: 54. e1-54. e4. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2020.01.077
[18] Tazaki J, Inoue K, Higami H, et al. Thoracic endovascular aortic repair with branched Inoue Stent Graft for arch aortic aneurysms[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2017, 66(5): 1340-1348. e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.03.432
[19] Wong J, Tenorio ER, Lima G, et al. Early Feasibility of Endovascular Repair of Distal Aortic Arch Aneurysms Using Patient-Specific Single Retrograde Left Subclavian Artery Branch Stent Graft[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2023, 46(2): 249-254. doi: 10.1007/s00270-022-03304-x
-




 下载:
下载: