The correlation between FHF expression in atrial tissue and atrial remodeling in patients with atrial fibrillation
-
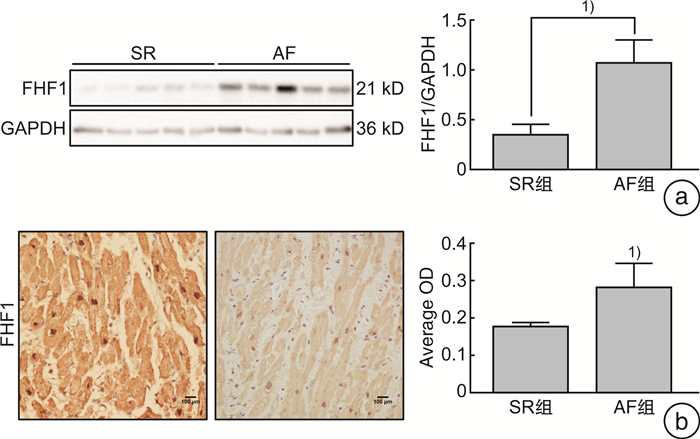
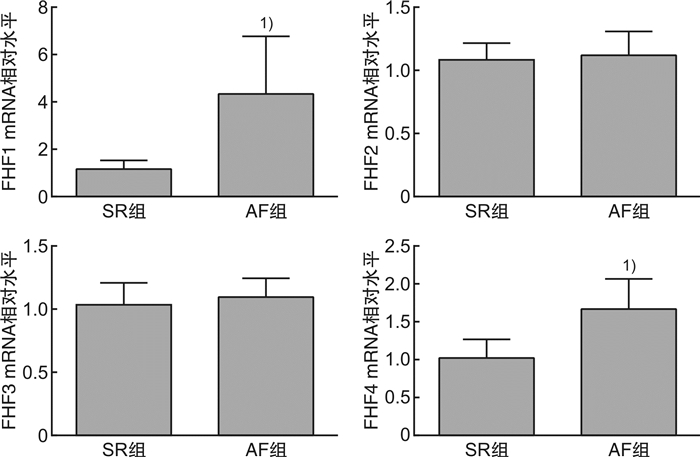
摘要: 目的 观察心房颤动(AF)患者心房组织成纤维细胞生长因子同源因子(FHF)的表达及其与心房重构的关系。方法 选取因风湿性心脏病在南昌大学第二附属医院心脏大血管外科手术的患者,手术时切取小块右心耳组织,收集临床资料,根据是否合并AF分为窦性心律组(SR组)和心房颤动组(AF组),实时定量PCR检测各型FHF(FHF1、FHF2、FHF3、FHF4) mRNA表达水平。评估各型FHF mRNA水平与左房内径(LAD)相关性分析,免疫组织化学、Western blot检测两组患者相关FHF表达。结果 共纳入68例病例,其中AF组50例,SR组18例。与SR组相比,AF组B型脑钠肽(BNP)、LAD升高,左室射血分数(LVEF)降低。AF组心房组织FHF1、FHF4的mRNA水平均高于SR组。两组间FHF2、FHF3的mRNA水平无明显差异。FHF1与LAD呈正相关(r=0.477 8,P < 0.05);FHF2、FHF3、FHF4与LAD无明显相关性。Western Blot和免疫组织化学结果显示AF组心房组织FHF1蛋白表达水平高于SR组。结论 AF患者心房组织中FHF1、FHF4表达升高,FHF1表达与LAD呈正相关,提示FHF1促进心房重构,是AF发生发展的潜在分子靶点。
-
关键词:
- 心房颤动 /
- 成纤维细胞生长因子同源因子 /
- 心房重构 /
- 左房内径
Abstract: Objective To investigate the expression of fibroblast growth factor homologous factors(FHF) and its relation with atrial remodeling.Methods We collected the right atrial appendage tissue of patients with rheumatic heart disease undergoing cardiac surgery in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University. Patients were divided to group SR(with sinus rhythm) and group AF(with AF history). The expression of FHF mRNA were examined by RT-PCR. The correlation between LAD and FHFs mRNA level were evaluated. The expression of related FHF in atrial tissues were detected by immunohistochemical and Western blot.Results A total of 68 cases were enrolled and 50 cases in the AF group and 18 cases in the SR group. Compared with the SR group, the BNP and LAD in AF group were significantly increased, and the LVEF was significantly decreased. The mRNA expression of FHF1 and FHF4 in AF group were significantly higher than those of SR group. There was no significant difference in FHF2 and FHF3 mRNA levels between the two groups. The expression of FHF1 mRNA was positively correlated with LAD(r=0.477 8, P < 0.05). The expression of FHF2, FHF3, and FHF4 had no correlation with LAD. The expression of FHF1 protein in AF group was higher than that in SR group.Conclusion The expression of atrial FHF1 and FHF4 mRNA in patients with AF were higher than that in patients with SR. And the expression of FHF1 is positively correlated with LAD, suggesting that FHF1 may promote atrial remodeling and be a potential target for the occurrence and development of AF. -

-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequence
引物 序列 FHF1 F:5′-GGCGAAATCATCAGATTGGCT-3′ R:5′-ATCCCTGCTGGCTGAATAACC-3′ FHF2 F:5′-GTTACCAAGCTATACAGCCGAC-3′ R:5′-ACAGGGATGAGGTTAAACAGAGT-3′ FHF3 F:5′-CTGTACGCCTCTGCTCTCTAC-3′ R:5′-GCCTTGGTCTTCTTAACTCGGT-3′ FHF4 F:5′-CTTGCCTCCCTCTATCTCCTG-3′ R:5′-CTGAGCTTCCATATGCATCTTTGT-3′ GADPH F:5′-GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT-3′ R:5′-GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG-3′ 表 2 两组患者临床基线资料比较
Table 2. General data
例(%), X±S 项目 SR组(18例) AF组(50例) 男性 6(33.3) 14(28.0) 年龄/岁 55.3±12.6 53.2±11.2 BMI/(kg/m2) 21.5±1.7 21.8±2.9 吸烟史 0 0 酗酒史 0 0 高血压 4(22.2) 6(12.0) 糖尿病 0 1(2.0) 脑卒中 1(5.6) 1(2.0) 甲亢 0 1(2.0) 慢性肾脏病 1(5.6) 1(2.0) 心率/(次/min) 90.3±7.1 89.8±7.2 收缩压/mmHg 116.8±16.2 121.2±13.6 舒张压/mmHg 76.2±12.0 78.6±16.1 BNP/(pg/mL) 100.3±73.5 653.0±752.71) eGFR/(mL/min/1.73 m2) 94.6±40.1 95.2±21.7 血糖/(mmol/L) 4.8±0.7 4.8±0.9 LAD/mm 43.5±6.3 52.0±9.21) LVEF/% 67.7±6.9 50.9±8.11) 与SR组比较,1)P < 0.05。 -
[1] Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, et al. The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms[J]. Circ Res, 2014, 114(9): 1453-1468. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303211
[2] Marsan NA, Maffessanti F, Tamborini G, et al. Left atrial reverse remodeling and functional improvement after mitral valve repair in degenerative mitral regurgitation: a real-time 3-dimensional echocardiography study[J]. Am Heart J, 2011, 161(2): 314-321. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.10.029
[3] Nattel S. New ideas about atrial fibrillation 50 years on[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6868): 219-226. doi: 10.1038/415219a
[4] 邹仕英, 王聪, 严冲, 等. 心房颤动患者血清NLRC4/Caspase-1表达及临床意义[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2022, 38(12): 988-993. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2022.12.011
[5] Bizhanov KA, Capital ACK, Baimbetov AK, et al. Atrial fibrillation: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical complications (literature review)[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2023, 34(1): 153-165. doi: 10.1111/jce.15759
[6] Guillemot F, Zimmer C. From cradle to grave: the multiple roles of fibroblast growth factors in neural development[J]. Neuron, 2011, 71(4): 574-588. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.002
[7] Hennessey JA, Marcou CA, Wang C, et al. FGF12 is a candidate Brugada syndrome locus[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2013, 10(12): 1886-1894. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.09.064
[8] Dover K, Marra C, Solinas S, et al. FHF-independent conduction of action potentials along the leak-resistant cerebellar granule cell axon[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 12895. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12895
[9] Liu CJ, Dib-Hajj SD, Renganathan M, et al. Modulation of the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 by fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 1B[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(2): 1029-1036. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207074200
[10] Yan H, Pablo JL, Pitt GS. FGF14 regulates presynaptic Ca2+ channels and synaptic transmission[J]. Cell Rep, 2013, 4(1): 66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.012
[11] Hennessey JA, Wei EQ, Pitt GS. Fibroblast growth factor homologous factors modulate cardiac calcium channels[J]. Circ Res, 2013, 113(4): 381-388. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301215
[12] Zhang Y, Qi Y, Li JJ, et al. Stretch-induced sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium leak is causatively associated with atrial fibrillation in pressure-overloaded hearts[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2021, 117(4): 1091-1102. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa163
[13] Sanfilippo AJ, Abascal VM, Sheehan M, et al. Atrial enlargement as a consequence of atrial fibrillation. A prospective echocardiographic study[J]. Circulation, 1990, 82(3): 792-797. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.82.3.792
[14] Masuda M, Matsuda Y, Uematsu H, et al. Clinical impact of left atrial remodeling pattern in patients with atrial fibrillation: Comparison of volumetric, electrical, and combined remodeling[J]. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2024, 35(1): 171-181. doi: 10.1111/jce.16129
[15] Li Q, Zhai Z, Li J. Fibroblast growth factor homologous factors are potential ion channel modifiers associated with cardiac arrhythmias[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 871: 172920. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.172920
[16] Wang C, Hennessey JA, Kirkton RD, et al. Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 13 regulates Na+ channels and conduction velocity in murine hearts[J]. Circ Res, 2011, 109(7): 775-782. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.247957
[17] Wang X, Tang H, Wei EQ, et al. Conditional knockout of Fgf13 in murine hearts increases arrhythmia susceptibility and reveals novel ion channel modulatory roles[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2017, 104: 63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.01.009
[18] Li Q, Zhao Y, Wu G, et al. De Novo FGF12(Fibroblast Growth Factor 12) functional variation is potentially associated with idiopathic ventricular tachycardia[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2017, 6(8): 110.
[19] Liu C, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 1B binds to the C terminus of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel rNav1.9a(NaN)[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(22): 18925-18933. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101606200
[20] Tsai FC, Lin YC, Chang SH, et al. Differential left-to-right atria gene expression ratio in human sinus rhythm and atrial fibrillation: Implications for arrhythmogenesis and thrombogenesis[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2016, 222: 104-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.07.103
[21] McCauley MD, Hong L, Sridhar A, et al. Ion channel and structural remodeling in obesity-mediated atrial fibrillation[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2020, 13(8): e8296.
[22] Avula U, Dridi H, Chen BX, et al. Attenuating persistent sodium current-induced atrial myopathy and fibrillation by preventing mitochondrial oxidative stress[J]. JCI Insight, 2021, 6(23): 110.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 284
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: