Research progress on gene polymorphisms in the dopaminesystem pathway and smoking behavior
-
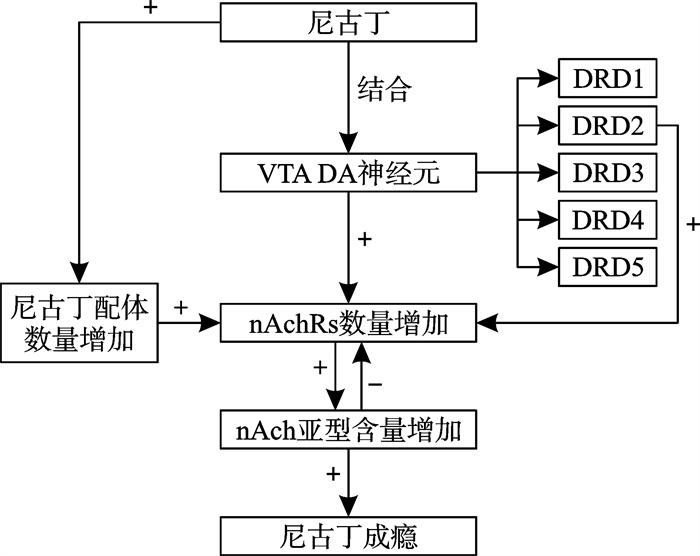
摘要: 烟草内的尼古丁增加大脑中多巴胺(dopamine,DA)等兴奋类神经递质的释放,同时,DA系统通路中的部分基因作为重要的吸烟相关基因,可能对尼古丁成瘾有影响。研究显示,尼古丁可能通过促进乙酰胆碱与其受体结合以及改变DA合成及转运途经的受体与酶的基因多态性达到依赖成瘾结果。DA系统与吸烟行为存在一定的正相关关系,这一结论或许能为更好地聚焦重点人群以降低吸烟率及分析烟草依赖特点提供理论基础。Abstract: Nicotine in tobacco enhances the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as dopamine(DA) in the brain. Concurrently, some genes in the DA system pathway as important smoking-related genes, may have an impact on nicotine addiction. Researches have shown that nicotine may facilitate addiction by promoting acetylcholine binding to its receptor, while also altering gene polymorphisms associated with receptors and enzymes involved in DA synthesis and transport pathways. It can be concluded that there exists a certain positive correlation between the DA system and smoking behavior, this conclusion may provide a theoretical foundation for targeting critical populations to reduce smoking rates and to analyze the attributes of tobacco dependence.
-
Key words:
- dopamine system pathway /
- gene polymorphisms /
- nicotine /
- smoking behavior
-

-
[1] Laffond A, Rivera-Picón C, Rodríguez-Muñoz PM, et al. Mediterranean Diet for Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality: An Updated Systematic Review[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15(15): 3356. doi: 10.3390/nu15153356
[2] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2021概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2022, 37(6): 553-578.
[3] 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2021》编写组. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2021》概述[J]. 中国心血管病研究, 2022, 20(7): 577-596.
[4] 杨娉婷, 袁洪, 王雅琴, 等. 中国人群血管内皮功能与心血管危险因素的相关性[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2015, 31(4): 415-420. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2015.04.019
[5] 莫睿, 吴强, 周瑜, 等. 冠心病患者外周血HOXA4基因表达及心血管病危险因素与冠心病病变特点的分析[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2024, 40(4): 291-295. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2024.04.008
[6] Wise RA, Robble MA. Dopamine and addiction[J]. Annu Rev Psychol, 2020, 71: 79-106. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010418-103337
[7] Volkow ND, Michaelides M, Baler R. The neuroscience of drug reward and addiction[J]. Physiol Rev, 2019, 99(4): 2115-2140. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00014.2018
[8] Wittenberg RE, Wolfman SL, De Biasi M, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotine addiction: A brief introduction[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2020, 177: 108256. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108256
[9] Li H, Liu Y, Xing L, et al. Association of Cigarette Smoking with Sleep Disturbance and Neurotransmitters in Cerebrospinal Fluid[J]. Nat Sci Sleep, 2020, 12: 801-808. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S272883
[10] White O, Roeder N, Blum K, et al. Prenatal Effects of Nicotine on Obesity Risks: A Narrative Review[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(15): 9477. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159477
[11] Laviolette SR. Molecular and neuronal mechanisms underlying the effects of adolescent nicotine exposure on anxiety and mood disorders[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2021, 184: 108411. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108411
[12] Hou G, Hao M, Duan J, et al. The Formation and Function of the VTA Dopamine System[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(7): 3875. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073875
[13] Wills L, Kenny PJ. Addiction-related neuroadaptations following chronic nicotine exposure[J]. J Neurochem, 2021, 157(5): 1652-1673. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15356
[14] Wani A, Prabhakar B, Shende P. Competitive inhibition of nicotine acetylcholine receptors using microneedles of nicotine and varenicline for smoking withdrawal therapy[J]. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2024, 195: 114171. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.114171
[15] Chaisai C, Patikorn C, Thavorn K, et al. Incremental net monetary benefit of using varenicline for smoking cessation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of economic evaluation studies[J]. Addiction, 2024, 119(7): 1188-1202. doi: 10.1111/add.16464
[16] Hou G, Hao M, Duan J, et al. The Formation and Function of the VTA Dopamine System[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(7): 3875. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073875
[17] Jiang Z, Chen Z, Chen X. Candidate gene-environment interactions in substance abuse: A systematic review[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(10): e0287446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287446
[18] Guerri L, Dobbs LK, da Silva E Silva DA, et al. Low Dopamine D2 Receptor Expression Drives Gene Networks Related to GABA, cAMP, Growth and Neuroinflammation in Striatal Indirect Pathway Neurons[J]. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci, 2022, 3(4): 1104-1115.
[19] Noble EP, St Jeor ST, Ritchie T, et al. D2 dopamine receptor gene and cigarette smoking: a reward gene?[J]. Med Hypotheses, 1994, 42(4): 257-260. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(94)90127-9
[20] Munafò MR, Timpson NJ, David SP, et al. Association of the DRD2 gene Taq1A polymorphism and smoking behavior: a meta-analysis and new data[J]. Nicotine Tob Res, 2009, 11(1): 64-76. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntn012
[21] Voisey J, Swagell CD, Hughes IP, et al. A DRD2 and ANKK1 haplotype is associated with nicotine dependence[J]. Psychiatry Res, 2012, 196(2-3): 285-289. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2011.09.024
[22] Macare C, Ducci F, Zhang YR, et al. A neurobiological pathway to smoking in adolescence: TTC12-ANKK1-DRD2 variants and reward response[J]. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 2018, 28(10): 1103-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.07.101
[23] Singleton AB, Thomson JH, Morris CM, et al. Lack of association between the dopamine D2 receptor gene allele DRD2*A1 and cigarette smoking in a United Kingdom population[J]. Pharmacogenetics, 1998, 8(2): 125-128. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199804000-00005
[24] Miller DR, Guenther DT, Maurer AP, et al. Dopamine Transporter Is a Master Regulator of Dopaminergic Neural Network Connectivity[J]. J Neurosci, 2021, 41(25): 5453-5470. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0223-21.2021
[25] Reith MEA, Kortagere S, Wiers CE, et al. The dopamine transporter gene SLC6A3: multidisease risks[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2022, 27(2): 1031-1046. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01341-5
[26] Sieminska A, Buczkowski K, Jassem E, et al. Influences of polymorphic variants of DRD2 and SLC6A3 genes, and their combinations on smoking in Polish population[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2009, 10: 92. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-92
[27] Faraone SV, Spencer TJ, Madras BK, et al. Functional effects of dopamine transporter gene genotypes on in vivo dopamine transporter functioning: a meta-analysis[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2014, 19(8): 880-889. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.126
[28] Erblich J, Lerman C, Self DW, et al. Effects of dopamine D2 receptor(DRD2) and transporter(SLC6A3) polymorphisms on smoking cue-induced cigarette craving among African-American smokers[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2005, 10(4): 407-414. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001588
[29] Wang C, Zhou C, Guo T, et al. Association between cigarette smoking and Parkinson's disease: a neuroimaging study[J]. Ther Adv Neurol Disord, 2022, 15: 17562864221092566. doi: 10.1177/17562864221092566
[30] Proebstl L, Kamp F, Manz K, et al. Effects of stimulant drug use on the dopaminergic system: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vivo neuroimaging studies[J]. Eur Psychiatry, 2019, 59: 15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2019.03.003
[31] DeVito EE, Sofuoglu M. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Effects on Smoking: A Review and Proof of Concept of Sex-Sensitive Effects[J]. Curr Behav Neurosci Rep, 2022, 9(4): 113-123. doi: 10.1007/s40473-022-00251-2
[32] Guo S, Chen DF, Zhou DF, et al. Association of functional catechol O-methyl transferase(COMT)Val108Met polymorphism with smoking severity and age of smoking initiation in Chinese male smokers[J]. Psychopharmacology(Berl), 2007, 190(4): 449-456. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0628-4
[33] Herman AI, Jatlow PI, Gelernter J, et al. COMT Val158Met modulates subjective responses to intravenous nicotine and cognitive performance in abstinent smokers[J]. Pharmacogenomics J, 2013, 13(6): 490-497. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2013.1
[34] Suriyaprom K, Tungtrongchitr R, Harnroongroj T. Impact of COMT Val 108/158 Met and DRD2 Taq1B gene polymorphisms on vulnerability to cigarette smoking of Thai males[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2013, 49(3): 544-549. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9844-z
[35] Munafò MR, Freathy RM, Ring SM, et al. Association of COMT Val(108/158) Met genotype and cigarette smoking in pregnant women[J]. Nicotine Tob Res, 2011, 13(2): 55-63. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntq209
[36] Guillem K, Vouillac C, Azar MR, et al. Monoamine oxiDAse inhibition dramatically increases the motivation to self-administer nicotine in rats[J]. J Neurosci, 2005, 25(38): 8593-8600. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2139-05.2005
[37] Villegier AS, Lotfipour S, McQuown SC, et al. Tranylcypromine enhancement of nicotine self-administration[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2007, 52(6): 1415-1425. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.02.001
[38] Guillem K, Vouillac C, Azar MR, et al. Monoamine oxidase A rather than monoamine oxiDAse B inhibition increases nicotine reinforcement in rats[J]. Eur J Neurosci, 24(12): 3532-3540. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05217.x
[39] Rose KN, Schwarzschild MA, Gomperts SN. Clearing the Smoke: What Protects Smokers from Parkinson's Disease?[J]. Mov Disord, 2024, 39(2): 267-272. doi: 10.1002/mds.29707
[40] Cheung F, Calakos KC, Gueorguieva R, et al. Lower Dorsal Putamen D2/3 Receptor Availability and Amphetamine-Induced Dopamine Release are Related to Poorer Cognitive Function in Recently Abstinent People Who Smoke and Healthy Controls[J]. Nicotine Tob Res, 2024, 26(8): 1038-1044. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntae031
[41] 杨姗姗, 王义艳, 刘淼, 等. 吸烟行为相关基因的全基因组关联研究进展[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2013, 34(12): 1255-1258.
[42] Brody AL, Mandelkern MA, Olmstead RE, et al. Gene variants of brain dopamine pathways and smoking-induced dopamine release in the ventral caudate/nucleus accumbens[J]. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 2006, 63(7): 808-816. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.7.808
[43] Liu M, Wang H, Fu Y, et al. The Role of Nicotine Metabolic Rate on Nicotine Dependence and Rewarding: Nicotine Metabolism in Chinese Male Smokers and Male Mice[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2024, 61(10): 7692-7706. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04040-8
[44] Reumann D, Krauditsch C, Novatchkova M, et al. In vitro modeling of the human dopaminergic system using spatially arranged ventral midbrain-striatum-cortex assembloids[J]. Nat Methods, 2023, 20(12): 2034-2047. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-02080-x
[45] Li S, Wang Q, Pan L, et al. The association of dopamine pathway gene score, nicotine dependence and smoking cessation in a rural male population of Shandong, China[J]. Am J Addict, 2016, 25(6): 493-498. doi: 10.1111/ajad.12421
[46] Ruzilawati AB, Islam MA, Muhamed SKS, et al. Smoking genes: a case-control study of dopamine transporter gene(SLC6A3) and dopamine receptor genes(DRD1, DRD2 and DRD3) polymorphisms and smoking behaviour in a malay male cohort[J]. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(12): 1633. doi: 10.3390/biom10121633
[47] Dahne J, Wahlquist AE, Kustanowitz J, et al. Behavioral activation-based digital smoking cessation intervention for individuals with depressive symptoms: randomized clinical trial[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2023, 25: e49809. doi: 10.2196/49809
-




 下载:
下载: