Revealing novel insights into the mechanism of diuretic resistance in heart failure
-
摘要: 利尿剂是急性心力衰竭(心衰)的一线治疗药物, 也是临床上缓解充血症状的基石。利尿剂抵抗致使心衰患者的再入院率和病死率增加, 是临床治疗的一大难点, 其机制目前尚不明确。最新研究机制包括腹内高压、盆腔化学感受器等, 针对这些机制已有相应的治疗手段, 所涉及的有机阴离子转运多肽2B1、肾脏钠再摄取转运体基因变异机制也将大大开拓利尿剂抵抗治疗的新思路。本文将对可能产生利尿剂抵抗的机制进行梳理以及对利尿剂抵抗的新治疗手段进行概括, 以期全面了解利尿剂抵抗。
-
关键词:
- 利尿剂抵抗 /
- 有机阴离子转运多肽2B1 /
- 腹内高压 /
- 盆腔化学感受器 /
- 肾脏钠再摄取转运体基因
Abstract: Diuretics are the first-line treatment for acute heart failure and are essential for providing relief from congestion symptoms.However, with advancements in heart failure diagnosis and treatment, diuretic resistance has emerged as a significant issue.This resistance can lead to increased rates of hospital readmission and mortality among heart failure patients.The exact mechanism of diuretic resistance is still unclear, posing a challenge in clinical treatment.Recent research has explored potential mechanisms such as intra-abdominal hypertension and pelvic chemoreceptors, leading to the development of corresponding treatment approaches.Additionally, mutations in genes related to organic anion transport polypeptide 2B1 and renal sodium reuptake may provide new avenues for treating diuretic resistance.This article aims to categorize the various mechanisms of diuretic resistance and briefly summarize new treatments for diuretic resistance, enhancing our overall understanding of diuretic resistance. -

-
[1] 王华, 刘宇佳, 杨杰孚. 心力衰竭流行病学[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2023, 39(4): 243-247. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2023.04.001
[2] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2023, 38(6): 583-612. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIXG202304001.htm
[3] Baman JR, Ahmad FS. Heart failure[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324(10): 1015. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.13310
[4] Ellison DH, Ellison DH. Mechanistic insights into loop diuretic responsiveness in heartfailure[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2019, 14(5): 650-652. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03590319
[5] Wilcox CS, Testani JM, Pitt B. Pathophysiology of diuretic resistance and its implications for the management of chronic heart failure[J]. Hypertension, 2020, 76(4): 1045-1054. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15205
[6] Rao VS, Ivey-Miranda JB, Cox ZL, et al. Natriuretic equation to predict loop diuretic response in patients with heart failure[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2021, 77(6): 695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.12.022
[7] Cox ZL, Testani JM. Loop diuretic resistance complicating acute heart failure[J]. Heart Fail Rev, 2020, 25(1): 133-145. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09851-9
[8] Felker GM, Ellison DH, Mullens W, et al. Diuretic therapy for Patients With Heart Failure: JACC state-of-the-art review[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 75(10): 1178-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.12.059
[9] Lee TH, Kuo G, Chang CH, et al. Diuretic effect of co-administration of furosemide and albumin in comparison to furosemide therapy alone: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(12): e0260312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260312
[10] Charokopos A, Griffin M, Rao VS, et al. Serum and urine albumin and response to loop diuretics in heart failure[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2019, 14(5): 712-718. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11600918
[11] Mahmoodpoor A, Zahedi S, Pourakbar A, et al. Efficacy of furosemide-albumin compared with furosemide in critically ill hypoalbuminemia patients admitted to intensive care unit: a prospective randomized clinical trial[J]. Daru, 2020, 28(1): 263-269. doi: 10.1007/s40199-020-00339-8
[12] van de Wouw J, Joles JA. Albumin is an interface between blood plasma and cell membrane, and not just a sponge[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2022, 15(4): 624-634. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfab194
[13] 张圆玉, 杨飞云, 王立立, 等. 血清白蛋白及球蛋白比值与慢性心力衰竭患者近期预后的相关性研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2023, 39(8): 636-643. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2023.08.013
[14] Mullens W, Damman K, Harjola VP, et al. The use of diuretics in heart failure with congestion-a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2019, 21(2): 137-155. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1369
[15] Novak JE, Ellison DH. Diuretics in states of volume overload: core curriculum 2022[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2022, 80(2): 264-276. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.09.029
[16] Ellison DH. Clinical pharmacology in diuretic use[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2019, 14(8): 1248-1257. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09630818
[17] Tang WHW, Li DY, Hazen SL. Dietary metabolism, the gut microbiome, and heart failure[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2019, 16: 137-154. doi: 10.1038/s41569-018-0108-7
[18] Crespo-Aznarez S, Campos-Sáenz de Santamaría A, Sánchez-Marteles M, et al. The association between intra-abdominal pressure and diuretic response in heart failure[J]. Curr Heart Fail Rep, 2023, 20(5): 390-400. doi: 10.1007/s11897-023-00617-x
[19] Abassi Z, Khoury EE, Karram T, et al. Edema formation in congestive heart failure and the underlying mechanisms[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 933215. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.933215
[20] Chapa R, Li CY, Basit A, et al. Contribution of uptake and efflux transporters to oral pharmacokinetics of furosemide[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(51): 32939-32950. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03930
[21] Adin D, Atkins C, Wallace G, et al. Effect of spironolactone and benazepril on furosemide-induced diuresis and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation in normal dogs[J]. J Vet Intern Med, 2021, 35(3): 1245-1254. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16097
[22] Masella C, Viggiano D, Molfino I, et al. Diuretic resistance in cardio-nephrology: role of pharmacokinetics, hypochloremia, and kidney remodeling[J]. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2019, 44(5): 915-927. doi: 10.1159/000502648
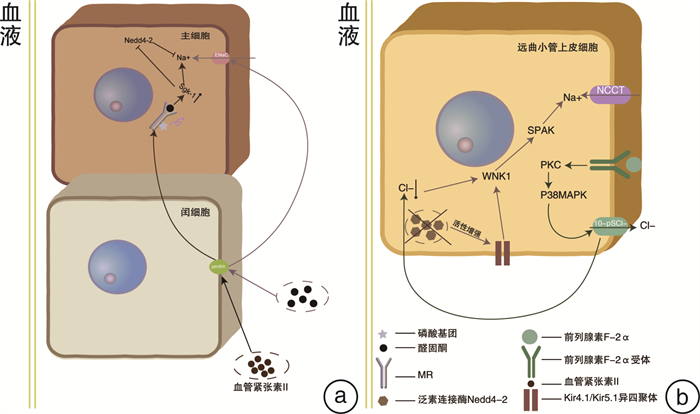
[23] Wall SM, Verlander JW, Romero CA. The renal physiology of pendrin-positive intercalated cells[J]. Physiol Rev, 2020, 100(3): 1119-1147. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2019
[24] Ayuzawa N, Nishimoto M, Ueda K, et al. Two mineralocorticoid receptor-mediated mechanisms of pendrin activation in distal nephrons[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020, 31(4): 748-764. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019080804
[25] Pham TD, Verlander JW, Wang YH, et al. Aldosterone regulates pendrin and epithelial sodium channel activity through intercalated cell mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent and-independent mechanisms over a wide range in serum potassium[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020, 31(3): 483-499. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019050551
[26] Yamazaki O, Ishizawa K, Hirohama D, et al. Electrolyte transport in the renal collecting duct and its regulation by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system[J]. Clin Sci, 2019, 133(1): 75-82. doi: 10.1042/CS20180194
[27] Loungani RS, Felker GM. Is resistance futile?: addressing diuretic resistance during hospitalization for Heart Failure[J]. JACC Heart Fail, 2020, 8(3): 169-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2019.10.008
[28] Bohnert BN, Daiminger S, Wörn M, et al. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator(uPA)is not essential for epithelial sodium channel(ENaC)-mediated sodium retention in experimental nephrotic syndrome[J]. Acta Physiol, 2019, 227(4): e13286. doi: 10.1111/apha.13286
[29] Hoorn EJ, Ellison DH. Diuretic resistance[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2017, 69(1): 136-142. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.08.027
[30] 廖玉华, 廖梦阳, 袁璟. 心力衰竭防治的新机制与新途径[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2024, 40(1): 1-4. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2024.01.001
[31] Ellison DH, Felker GM. Diuretic treatment in heart failure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(20): 1964-1975. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1703100
[32] 林飞宁, 黄丽华, 林超, 等. 持续性低氯血症评估射血分数保留型心力衰竭远期预后的价值[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2024, 40(5): 372-376. https://lcxxg.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2024.05.005
[33] Zandijk AJL, van Norel MR, Julius FEC, et al. Chloride in heart failure the neglected electrolyte[J]. JACC Heart Fail, 2021, 9(12): 904-915. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2021.07.006
[34] Wu P, Su XT, Gao ZX, et al. Renal tubule Nedd4-2 deficiency stimulates Kir4.1/Kir5.1 and thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter in distal convoluted tubule[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020, 31(6): 1226-1242. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019090923
[35] Wang LJ, Xiao Y, Fang J, et al. PGF2αstimulates the 10-pS Cl-channel and thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl- cotransporter in the distal convoluted tubule[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2020, 319(3): F414-F422. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00287.2020
[36] de Denus S, Rouleau JL, Mann DL, et al. A pharmacogenetic investigation of intravenous furosemide in decompensated heart failure: a meta-analysis of three clinical trials[J]. Pharmacogenomics J, 2017, 17(2): 192-200. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2016.4
[37] Osborn JW, Tyshynsky R, Vulchanova L. Function of renal nerves in kidney physiology and pathophysiology[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2021, 83: 429-450. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-091656
[38] Katsurada K, Nandi SS, Sharma NM, et al. Does glucagon-like peptide-1 induce diuresis and natriuresis by modulating afferent renal nerve activity?[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2019, 317(4): F1010-F1021. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00028.2019
[39] Katsurada K, Nandi SS, Zheng H, et al. GLP-1 mediated diuresis and natriuresis are blunted in heart failure and restored by selective afferent renal denervation[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2020, 19(1): 57. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01029-0
[40] Zheng H, Liu XF, Katsurada K, et al. Renal denervation improves sodium excretion in rats with chronic heart failure: effects on expression of renal ENaC and AQP2[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2019, 317(5): H958-H968. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00299.2019
[41] Gupta R, Testani J, Collins S. Diuretic resistance in heart failure[J]. Curr Heart FailRep, 2019, 16(2): 57-66. doi: 10.1007/s11897-019-0424-1
[42] Shams E, Bonnice S, Mayrovitz HN. Diuretic resistance associated with heart failure[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(1): e21369.
[43] Dierckx R, Vanderheyden M, Heggermont W, et al. Treatment of diuretic resistance with a novel percutaneous blood flow regulator: concept and initial experience[J]. J Card Fail, 2019, 25(11): 932-934. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.08.017
[44] Zymliński R, Biegus J, Vanderheyden M, et al. Safety, feasibility of controllable decrease of vena Cava pressure by doraya catheter in heart failure[J]. JACC Basic Transl Sci, 2023, 8(4): 394-402. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.02.010
[45] Gogikar A, Nanda A, Janga LSN, et al. Combination diuretic therapy with thiazides: a systematic review on the beneficial approach to overcome refractory fluid overload in heart failure[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15(9): e44624.
[46] Côté JM, Bouchard J, Murray PT, et al. Diuretic strategies in patients with resistance to loop-diuretics in the intensive care unit: a retrospective study from the MIMIC-Ⅲ database[J]. J Crit Care, 2021, 65: 282-291. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.06.009
[47] Griffin M, Soufer A, Goljo E, et al. Real world use of hypertonic saline in refractory acute decompensated heart failure A U.S. center's experience[J]. JACC Heart Fail, 2020, 8(3): 199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2019.10.012
[48] Covic A, Copur S, Tapoi L, et al. Efficiency of hypertonic saline in the management of decompensated heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies[J]. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs, 2021, 21(3): 331-347. doi: 10.1007/s40256-020-00453-7
[49] Chen Y, Harty GJ, Zheng Y, et al. CRRL269[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(10): 1462-1472. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314164
[50] Bourgeois S, Wagner CA. Regulation of renal pendrin activity by aldosterone[J]. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, 2021, 30(1): 131-137. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000669
[51] Sharp TE, Lefer DJ. Renal denervation to treat heart failure[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2021, 83: 39-58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-093431
[52] Titko T, Perekhoda L, Drapak I, et al. Modern trends in diuretics development[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2020, 208: 112855. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112855
[53] Zhang S, Zhao Y, Wang SY, et al. Discovery of novel diarylamides as orally active diuretics targeting urea transporters[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11(1): 181-202. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.06.001
-




 下载:
下载: